Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Creature Feature: Sharks with Unusual Names

 This month we’re talking about some sharks with unusual names. With names that range from the descriptive to the downright strange. Let’s look at three species with weird and wonderful names!
This month we’re talking about some sharks with unusual names. With names that range from the descriptive to the downright strange. Let’s look at three species with weird and wonderful names!
Tasseled Wobbegong
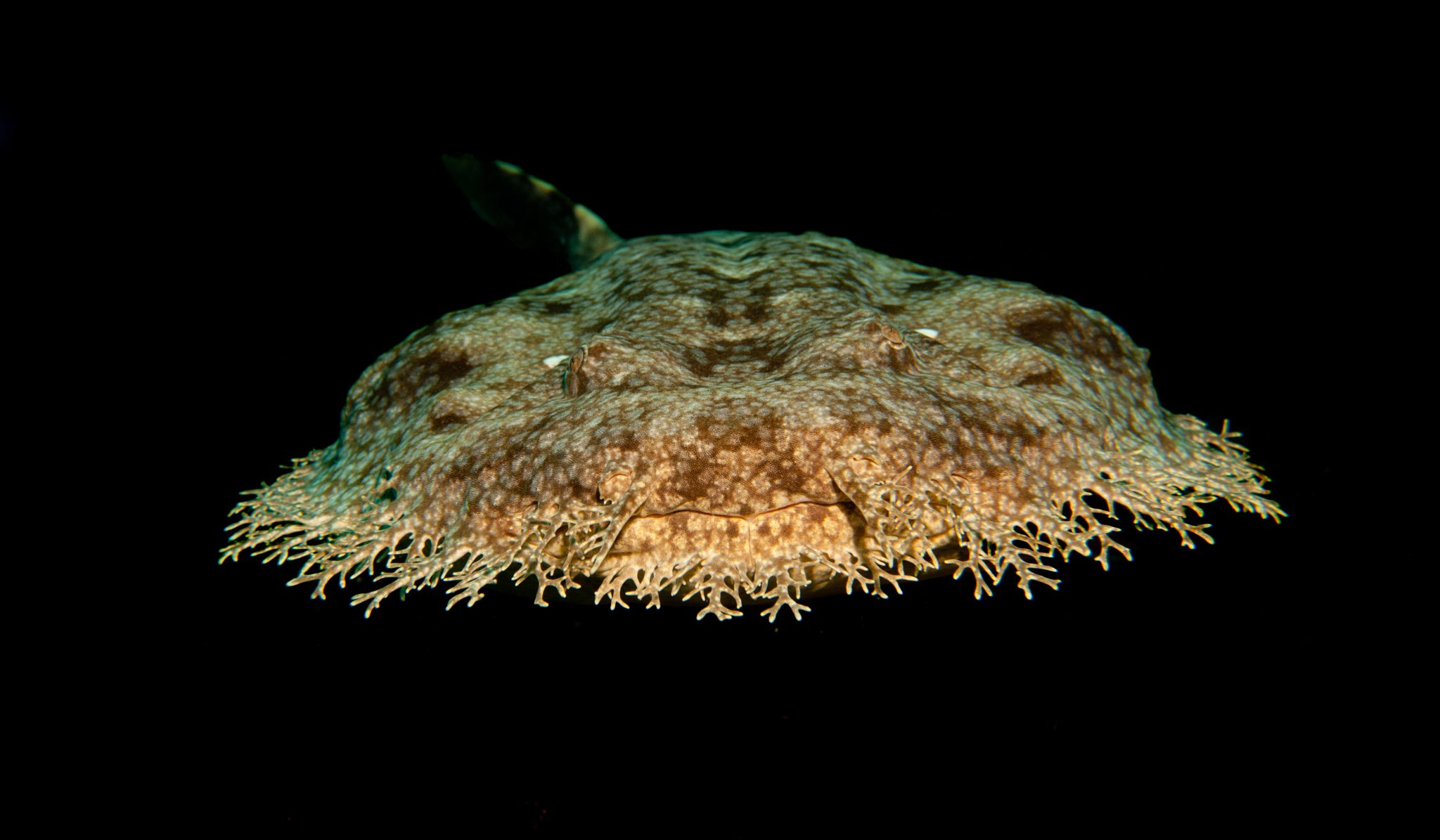
The Tasseled Wobbegong (Eucrossorhinus dasypogon) is a species of carpet shark found in the shallow coral reefs of the Indo-Pacific. This unique shark gets its name from the tassels that hang from its chin and the sides of its head, making it look like it’s wearing a fancy carpet. The scientific name of the Tasseled Wobbegong, Eucrossorhinus dasypogon, comes from the Greek words “eu” meaning good, “krossoi” meaning fringe, “rhinos” meaning nose, and “dasys” meaning hairy, and “pogon” meaning beard, referring to the shark’s characteristic tassels.
The Tasseled Wobbegong has a broad, flattened head and a body that is covered in small, thorn-like projections. These projections, called dermal denticles, are a common feature of shark skin and help to protect the shark from predators and parasites. The Tasseled Wobbegong’s skin is also covered in a unique pattern of dark spots and stripes that allows it to camouflage itself on the reef floor. With their striking appearance and docile nature, they are a favorite of divers and underwater photographers.
Despite their wild appearance, Tasseled Wobbegongs are relatively docile and are known to be tolerant of human divers. They are primarily nocturnal, spending most of their days hiding in crevices and under overhangs on the reef. At night, they venture out to hunt small fish and crustaceans, using their powerful jaws to crush their prey.
Although the Tasseled Wobbegong is not considered to be a threatened species, it is facing increasing pressure from habitat degradation and overfishing. In 2018, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) listed the Tasseled Wobbegong as a species of “Least Concern” on their Red List, which is a positive sign that the population is currently stable.
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Eucrossorhinus dasypogon
FAMILY: Orectolobidae
MAXIMUM SIZE: 122cm
DIET: Bony fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods
DISTRIBUTION: Found in the waters around southern Australia, including Tasmania and the Bass Strait.
HABITAT: Shallow, coastal waters with rocky or coral reefs, as well as seagrass beds and sandy areas.
CONSERVATION STATUS:
Crocodile Shark
This unique species (Pseudocarcharias kamoharai) is a small and slender-bodied shark. Which was only disovered in 1985! The genus name, Pseudocarcharias, means “false shark,”. While the species name, kamoharai, honors the Japanese ichthyologist, Kamohara. The English common name “crocodile shark” is derived from its Japanese name mizuwani (水鰐, literally “water crocodile”), which refers to its sharp teeth and habit of snapping vigorously when taken out of the water.
The Crocodile Shark is named for its distinct crocodile-like appearance, with a long snout and sharp teeth. With a maximum length of 1.2 meters. This species is found in deep ocean waters around the globe, from the Atlantic to the Indian Ocean, typically at depths of 200 to 500 meters. However, it has been known to venture as deep as 1,000 meters.
What makes the Crocodile Shark particularly unusual is its opportunistic feeding behavior. This means that it will eat just about anything it comes across. Including small fish, squid, and even other sharks. The Crocodile Shark uses a unique hunting technique to catch its prey. Its slender body and elongated snout allow it to navigate through tight spaces and ambush unsuspecting prey, making it a formidable predator despite its small size.
Since being discovered, we’ve not uncovered much about this elusive species. Not much is known about the biology and behavior of Crocodile Sharks. They are rarely encountered. And in 2019, the Crocodile Shark was listed as “data deficient” on the IUCN Red List. This means that not enough is known about the species to determine its conservation status. This elusive species’ DNA has been analysed and they are determined to be closely related to the Megamouth Shark or sand sharks (Odontaspididae). Alternative research, analysis based on teeth structure, suggests that the closest relatives of the crocodile shark are the thresher sharks.
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Pseudocarcharias kamoharai
FAMILY: Pseudocarchariidae
MAXIMUM SIZE: 1.2m
DIET: Bony fish and cephalopods
DISTRIBUTION: They are found in tropical and warm temperate waters around the world, including off the coasts of Japan, Australia, South Africa, and Brazil.
HABITAT: Deep offshore waters, typically at depths of 200 to 500 meters, but have been known to come up to shallower depths at night to feed.
CONSERVATION STATUS:
Viper Dogfish
The Viper Dogfish (Trigonognathus kabeyai) is a species of deep-sea shark found in the North Pacific Ocean. This unique shark gets its name from its distinctive appearance, which resembles that of a viper snake, due to the long, fang-like teeth protruding from its jaws. The scientific name comes from the Greek words “trigonos” meaning triangular, “gnathos” meaning jaw, and “kabeya” in honor of the late Japanese ichthyologist, Toshiji Kabeya, who made significant contributions to the study of deep-sea sharks.
The Viper Dogfish is a relatively small species of shark, growing up to just 40 centimeters in length. Its body is slim and elongated, with a dark brown or black coloration that allows it to blend in seamlessly with its deep-sea environment. They’re typically found at depths of between 365 and 1,200 meters, where they feed on a variety of prey including small fish, squid, and crustaceans. Their long, fang-like teeth allow them to easily catch and hold onto their prey, despite their small size.
Despite being a relatively unknown species, the Viper Dogfish has been listed as a species of “Least Concern” on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List.
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Trigonognathus kabeyai
FAMILY: Etmopteridae
MAXIMUM SIZE: 40cm
DIET: Small fishes and invertebrates
DISTRIBUTION: Northwest and central Pacific: Japan, Taiwan and Hawaiian Islands.
HABITAT: Deep waters, between 250 – 1000m. Possibly oceanic as some have been caught at 150m over water as deep as 1500m.
CONSERVATION STATUS:
Banner Image – © Frogfish Photography
Wobbegong – © Andy Murch
Crocodile Shark – © Dianne J. Bray, 2011, Crocodile Shark, Pseudocarcharias kamoharai, in Fishes of Australia, accessed 11 May 2014, http://www.fishesofaustralia.net.au/home/species/3001 | Wikimedia Commons
Viper Dogfish – © Stephen M Kajiura | Wikimedia Commons
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Creature Feature: Butterfly Rays

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
As we’re currently in butterfly season, this month we decided to concentrate on the Butterfly Rays!
Within the family Gymnuridae, there are two genera and 12 species of Butterfly Ray. These species are morphologically different to lots of other rays because of the width of the disc and pectoral fins – in contrast to many other species of Butterfly Ray, their bodies are much wider than they are long, especially considering their very short tail. This gives them the appearance of gliding or flying across the sand.
Gymnura altavela – Spiny Butterfly Ray
Gymnura australis – Australian Butterfly Ray
Gymnura crebripunctata – Longsnout Butterfly Ray
Gymnura japonica – Japanese Butterfly Ray
Gymnura lessae – Lessa’s Butterfly Ray
Gymnura marmorata – California Butterfly Ray
Gymnura micrura – Smooth Butterfly Ray
Gymnura natalensis – Backwater Butterfly Ray
Gymnura peocilura – Longtail Butterfly Ray
Gymnura sereti – Seret’s Butterfly Ray
Gymnura tentaculata – Tentacled Butterfly Ray
Gymnura zonura – Zonetail Butterfly Ray
Today we’re taking a look at Gymnura altavela, the Spiny Butterfly Ray. Like all Butterfly Rays, the Spiny Butterfly Ray is a demersal species, meaning it spends the majority of its time on the bottom of the seabed. Butterfly Rays are known for their burying behaviour in the sand, a technique they use to camouflage themselves when they are resting during the day. This protects them from predators, in some areas larger sharks. It also aids them in their ambush hunting technique – by hiding themselves under the sand they are able to easily snatch up their dinner – usually crustaceans, molluscs or other small fish – as they swim by unawares. This behaviour can leave tell-tale butterfly-ray shaped imprints in the bottom of the seabed.
Spiny Butterfly Rays can grow up to 260 cm (disc width (wingspan)), although average is around 200 cm. They give birth to live young, and each litter consists of 1-8 pups. This species has also been found to aggregate, likely for mating. One study found that aggregations of primarily females in the coastal regions off Gran Canaria may correlate with the shifting water temperature.
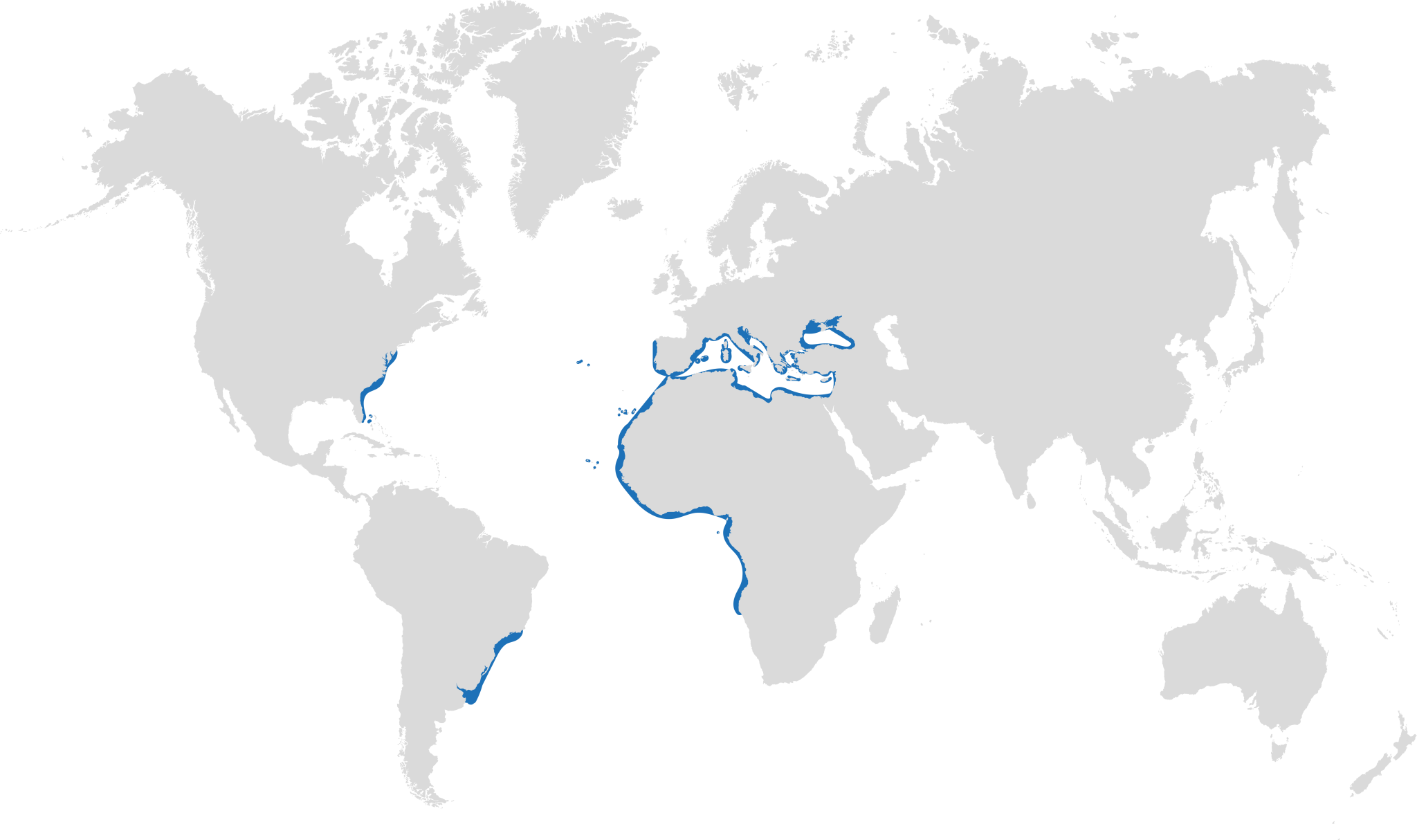
It is estimated that the species has undergone a population reduction of 50-79% over the last 33 years. This is primarily due to fishing pressure – the Spiny Butterfly Ray is targeted and bycaught in both industrial and artisanal fisheries types using a variety of gear types. The species is now Critically Endangered in the Mediterranean and Southwest Atlantic.
Scientific Name: Gymnura altavela
Family: Gymnuridae
Maximum Size: 260 cm (disc width)
Diet: crabs, shrimps, various invertebrates, fishes, small crustaceans, and molluscs.
Distribution: throughout the Atlantic and Mediterranean and Black Seas.
Habitat: muddy and sandy substrates down to 150m.
Conservation status: Critically Endangered in the Mediterranean and Europe, Endangered Globally.
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Banner Image: ©Tomas Willems. Main image: ©Andy Murch
Blogs
Seal Encounter Dives at Lundy Island
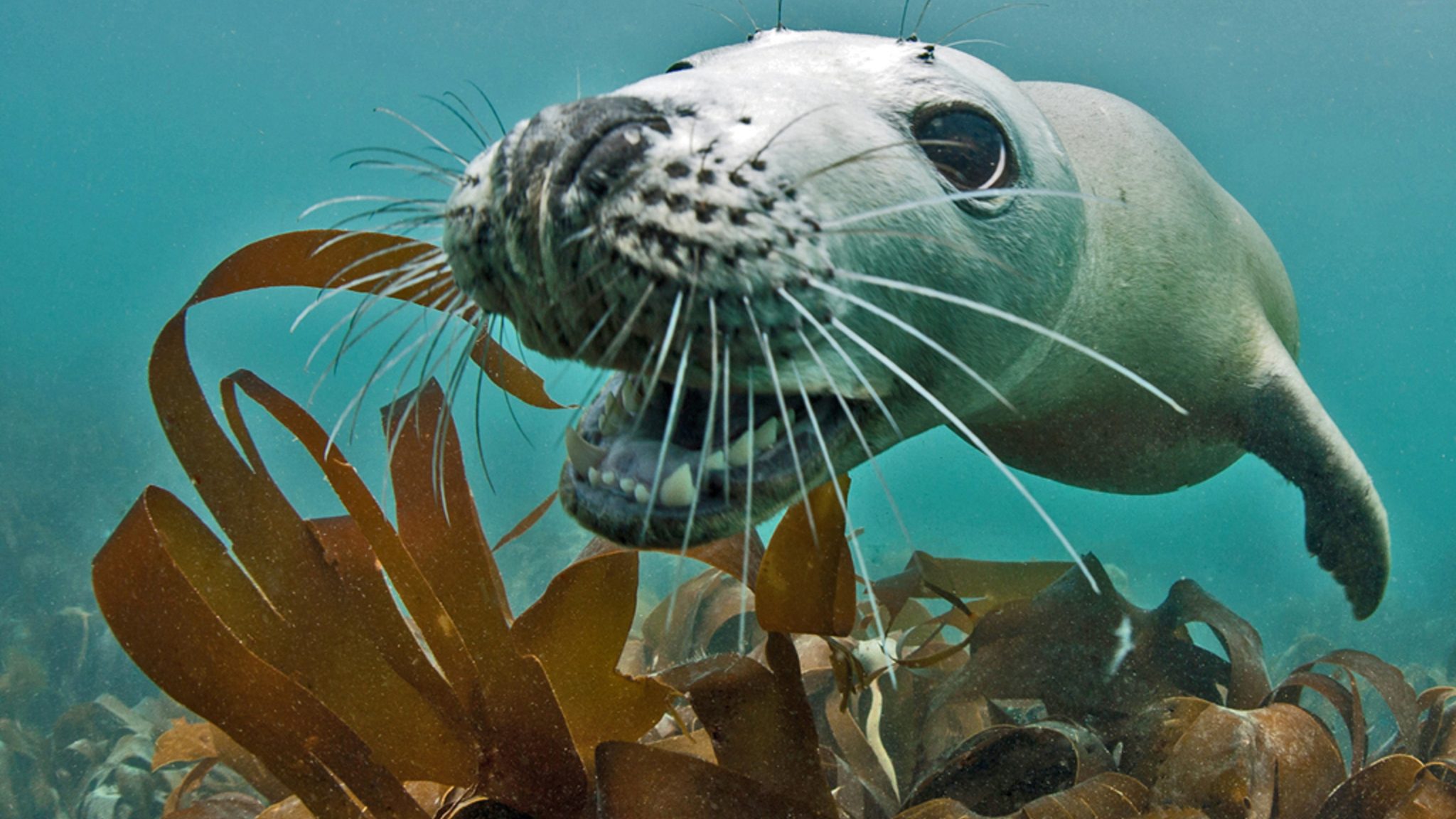

Voted No. 3 on the Top 10 Ultimate British Isles Bucket List by The Independent, these dives offer the closest marine mammal encounter available to divers in the UK. Friendly and playful, respectful divers are often rewarded by incredible interaction with the Lundy Seals.
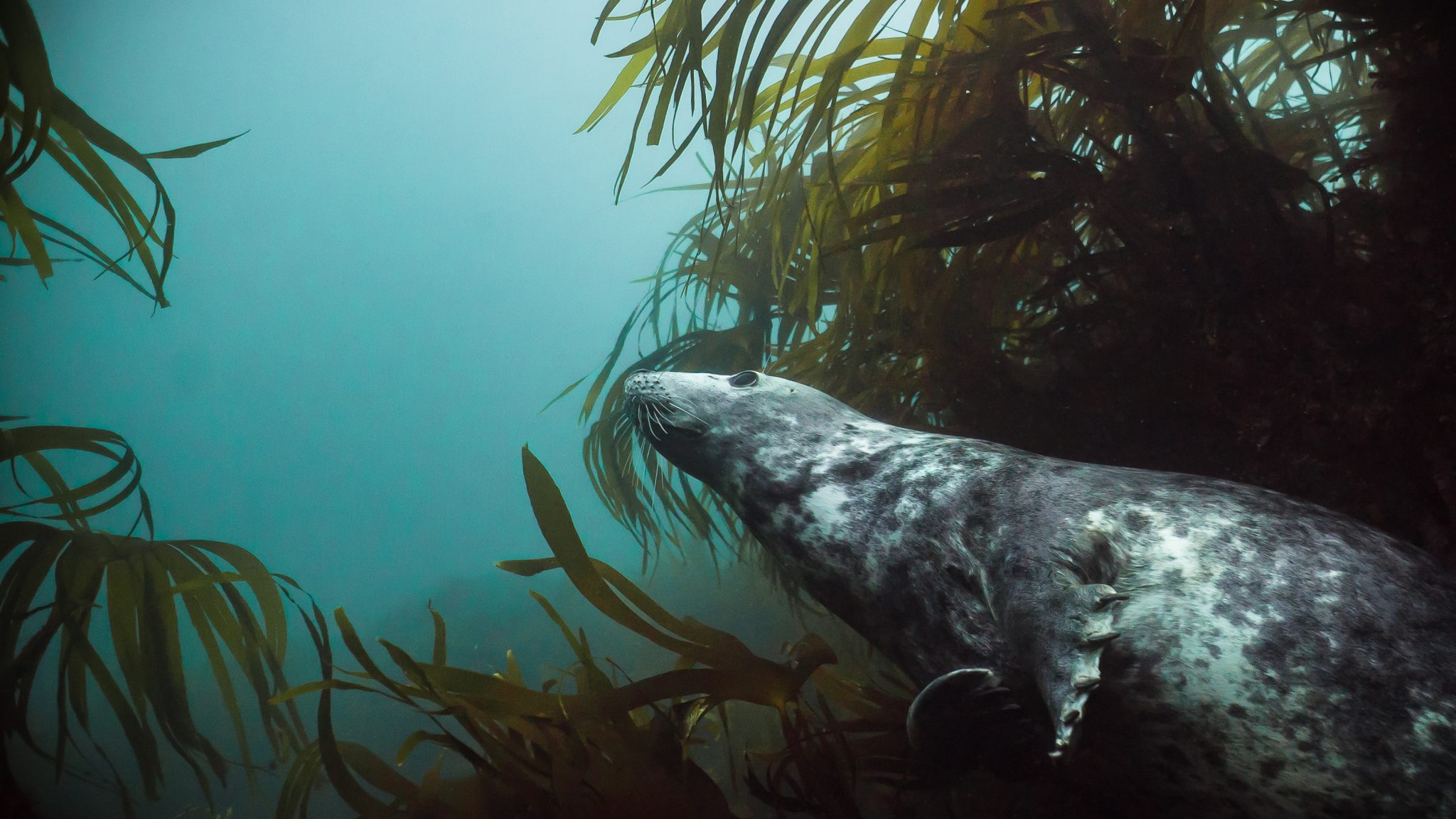

Easy Divers has been running guided dive trips to Lundy for nearly 10 years and offers dive equipment hire if required. Trips depart from the stunning harbour town of Ilfracombe in North Devon and Dolphins are often seen during the boat passage.
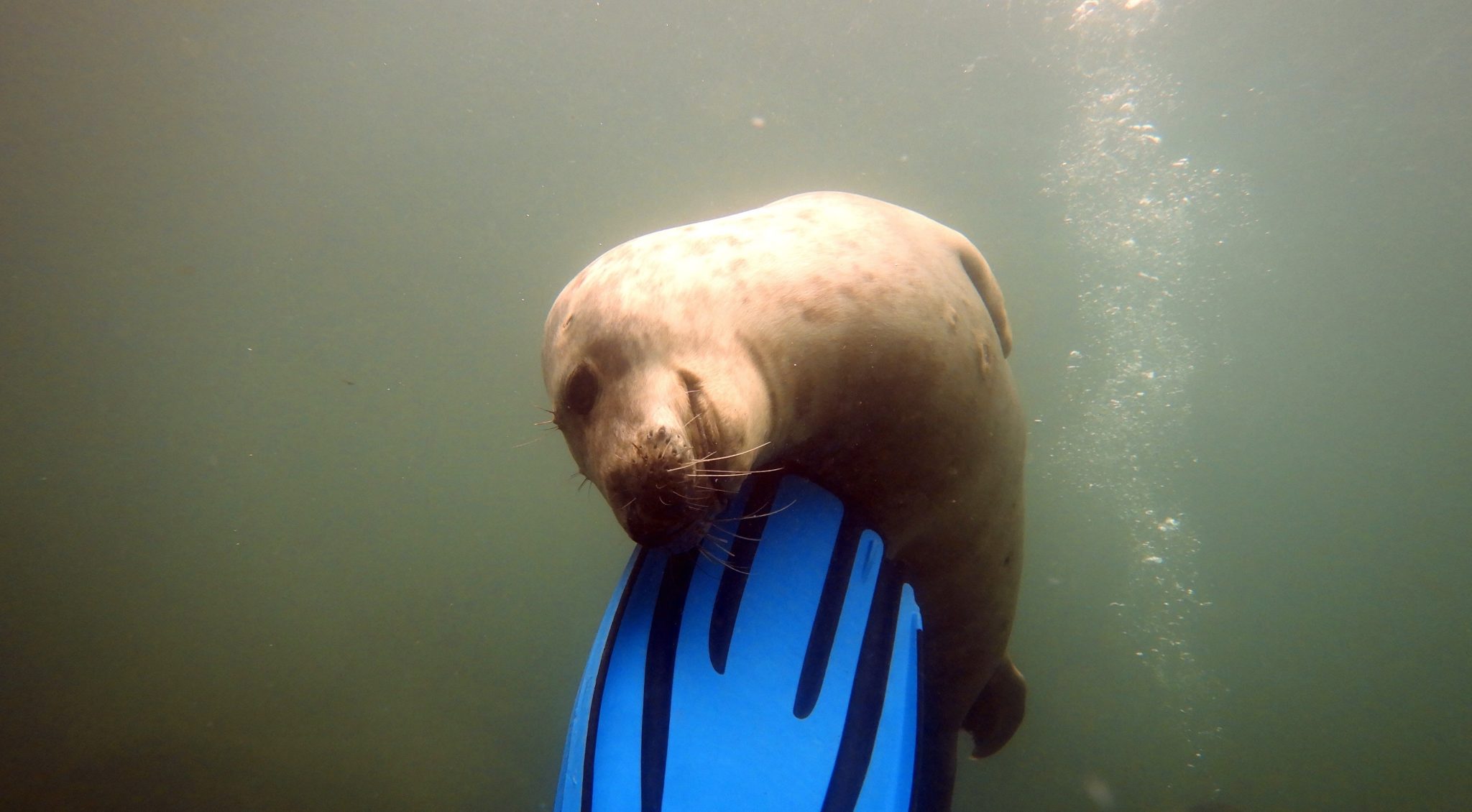

In addition to diving, Ilfracombe is a great base from which to hike the South West Coast Path, dip into surfing at the UK’s first World Surf reserve, enjoy other water sports or head to Exmoor National Park.
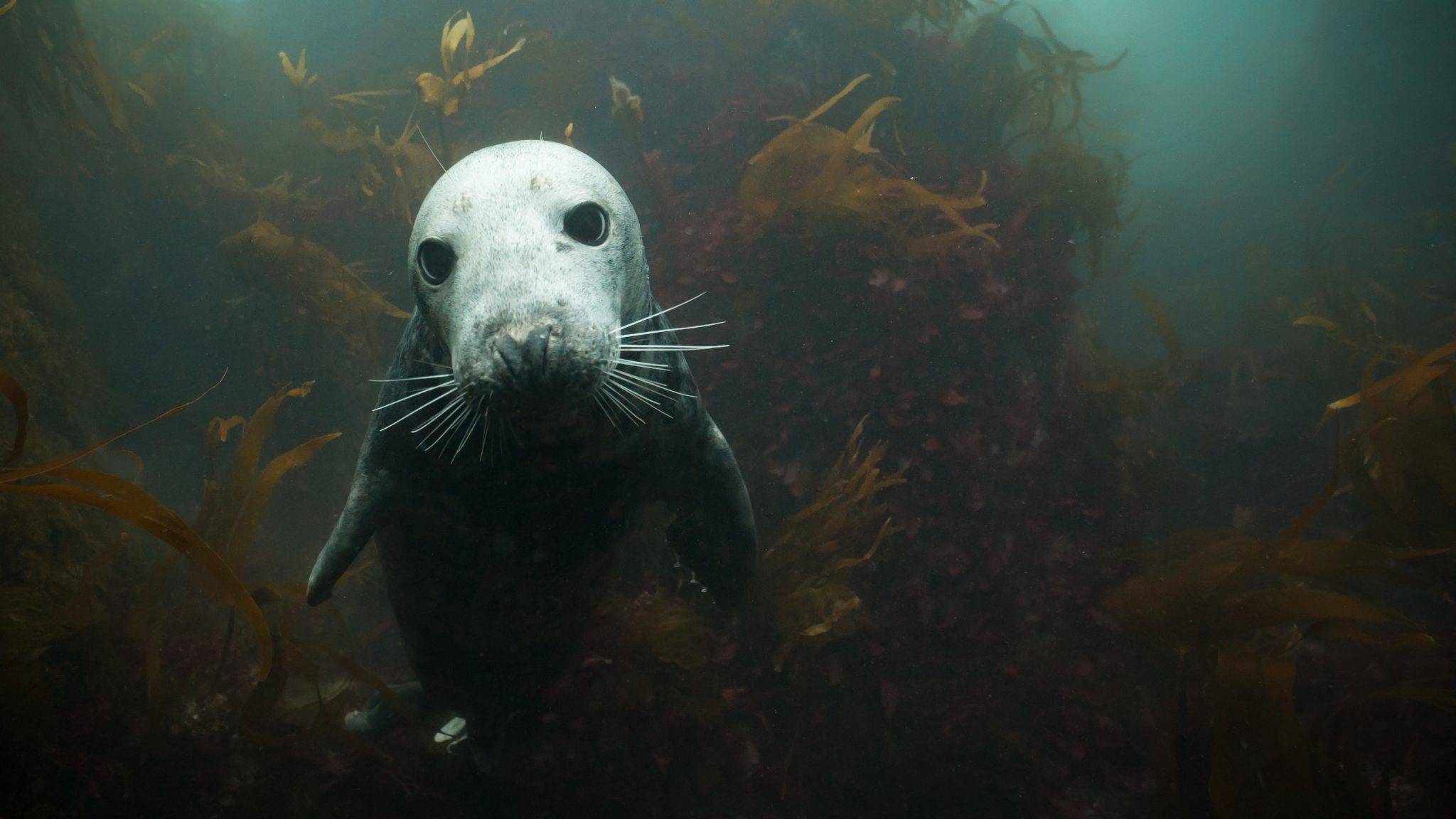
Easy Divers also runs a diver-friendly guest house, with a discount for diving customers and kit rinsing and drying facilities.
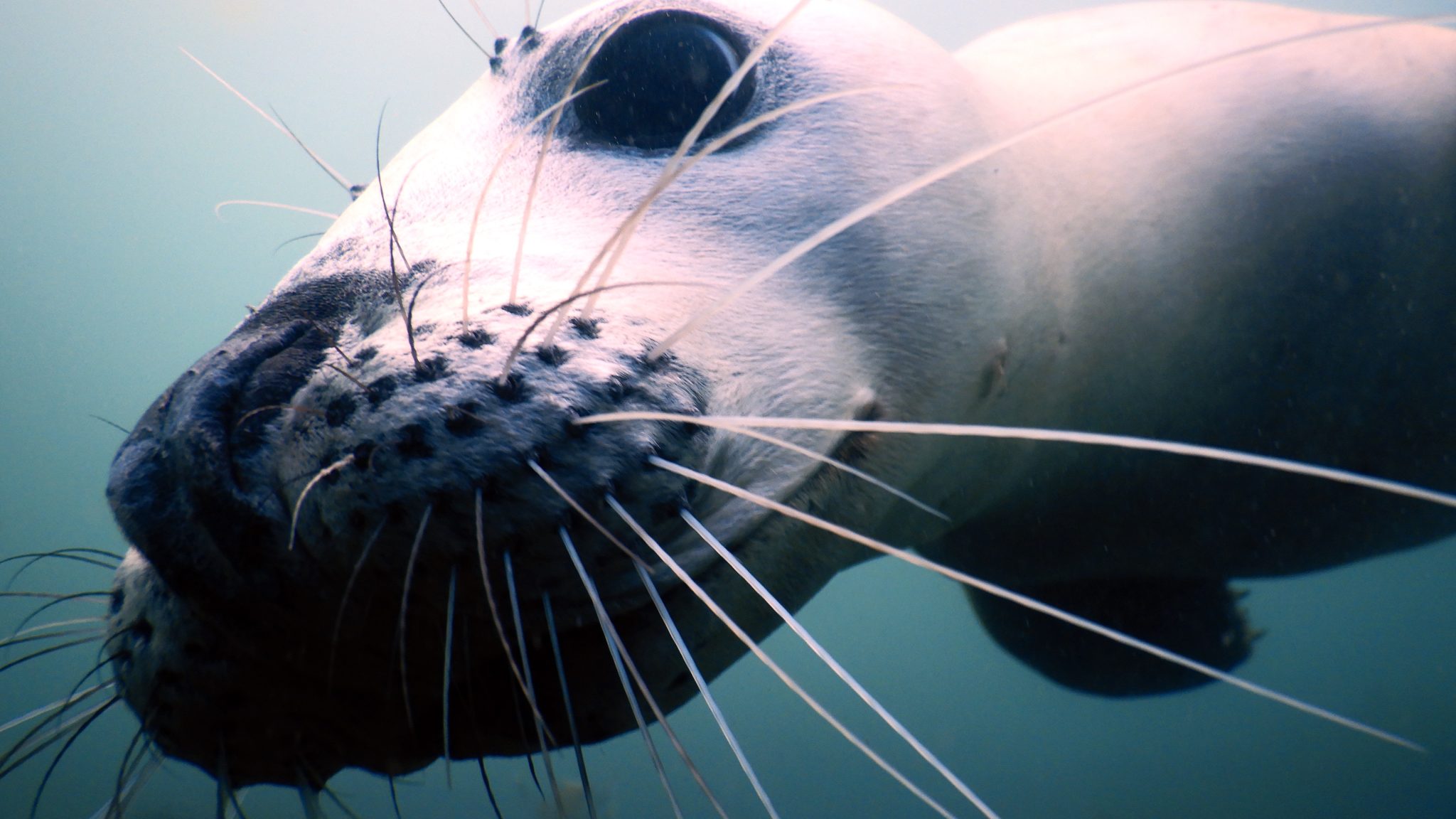

The Seal encounter dive sites are shallow and sheltered and are suitable for divers of all levels, making them a great introduction to British diving.
Exclusive Offer for Scubaverse Subscribers
Use your exclusive Scubaverse discount code scubaverse10% before the end of June and join us for a Seal encounter dive trip to Lundy Island, on any trip date with availability this Summer. Visit https://www.easydiversnorthdevon.co.uk/lundy-dive-trips/seal-encounter-dive-trips/ and enter code scubaverse10% at the on-line check out.
Trips book out well ahead, so book now to avoid disappointment. To save 10% on any 1 night stay at our guest house, please call 07833 020424. We offer free cancellation for divers who book a 1 night stay, if we have to re-schedule due to unsafe weather.
Join us for Britain’s best marine mammal diving experience!
Trips run from end of May to mid-October and are bookable via email at info@easydiversnorthdevon.co.uk, on-line via the Easy Divers website, www.easydiversnorthdevon.co.uk, or call 07833 020424 for more info
-

 Blogs4 weeks ago
Blogs4 weeks agoDive Indonesia Part 3: Dive into Lembeh Trip Report
-

 Gear Reviews1 month ago
Gear Reviews1 month agoGEAR REVIEW – Revolutionising Diving Comfort: The Sharkskin T2 Chillproof Suit
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoPADI Teams Up with Wellness Brand Neuro to Drive Ocean Change and Create a Blue State of Mind
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Blogs3 months ago
Blogs3 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoSeagrass Awareness Month brings critical food source for Manatees to centre stage
-

 Marine Life & Conservation3 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation3 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoSOMABAY: Scubaverse interviews Wolfgang Clausen, General Manager, ORCA Dive Clubs