Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
World Wildlife Day: incredible UK sea life in pictures
 Today is World Wildlife Day. The Marine Conservation Society have compiled incredible underwater photography from UK seas, showcasing how special our wildlife is.
Today is World Wildlife Day. The Marine Conservation Society have compiled incredible underwater photography from UK seas, showcasing how special our wildlife is.
Seasoned underwater photographers share how they captured amazing scenes of UK wildlife; get inspired to dive in yourself. While the images below show the colourful and curious world under the surface of the UK’s seas, these fragile ecosystems are in urgent need of protection and restoration. Without a healthy ocean, we cannot have a healthy planet.
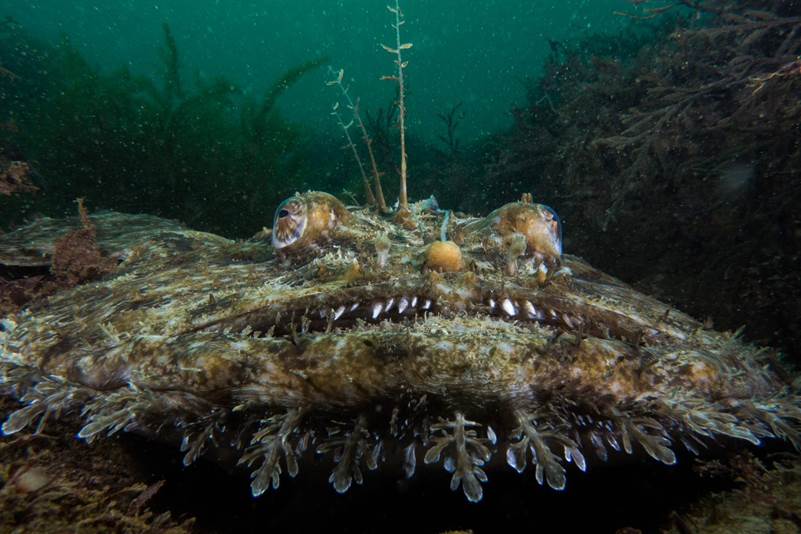
- Anglerfish, Lophius Piscatorius, Chesil Cove, Dorset by Jon Bunker – “Among the most beautiful of our ground-dwelling fishes, the angler fish’s mottled brown tones and leafy protrusions of skin make it almost undistinguishable from the rocky, weed strewn ground that divers often encounter them in. Broad circular pectoral fins seem to grip the seabed like clasping hands on either side of the massive, dustbin-lid head. Ahead of a decreasing series of weed-like dorsal spines, the anglerfish wafts its distinctive lure or ‘illicium’ to entice unwary prey into its cavernous mouth.”
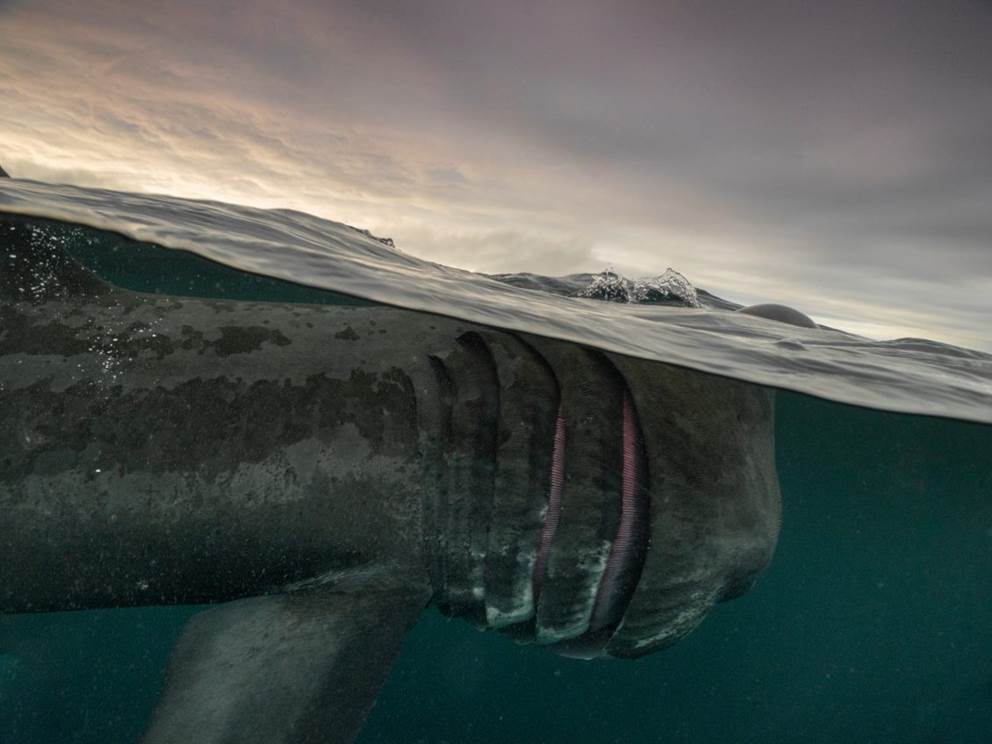
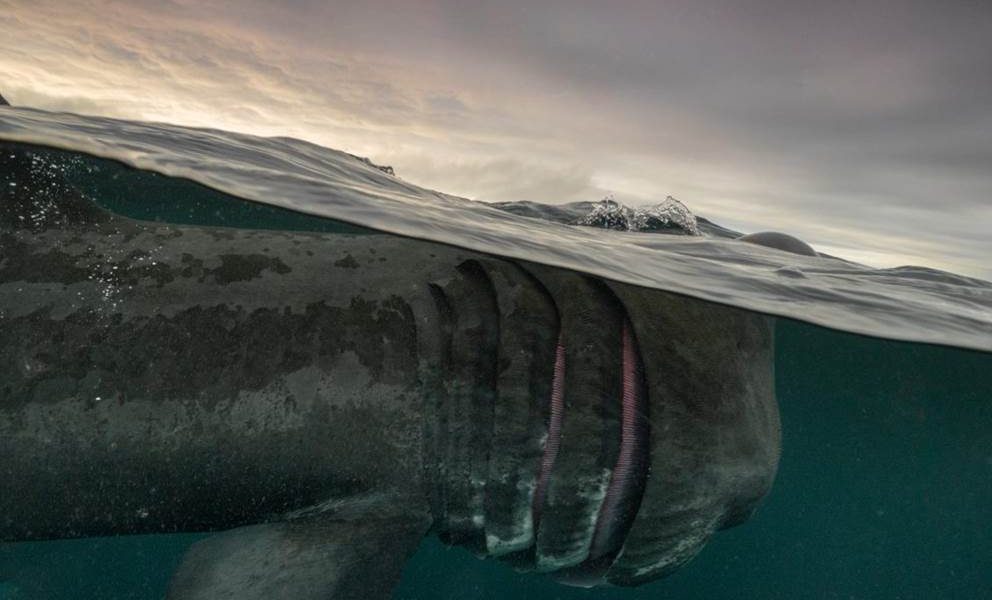
- Basking Shark, Isle of Coll by Mark Kirkland – “Through late summer the basking shark passes though the Isles of Coll and Tiree in huge numbers on its migratory journey north. Despite being the second largest fish in the sea (up to nine meters long) and a close relative to the great white shark, it’s completely harmless, with a preference for microscopic plankton as it’s food. This split shot was taken on a glorious evening’s snorkel with three large individuals.”
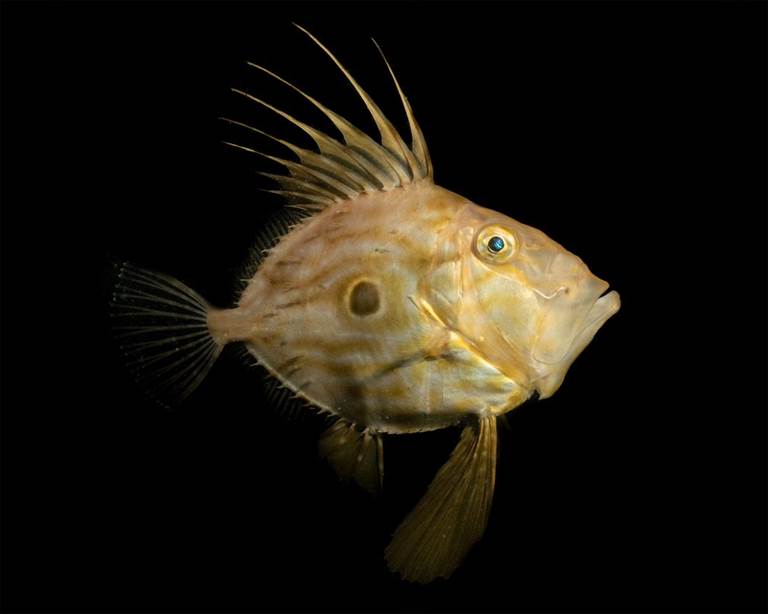
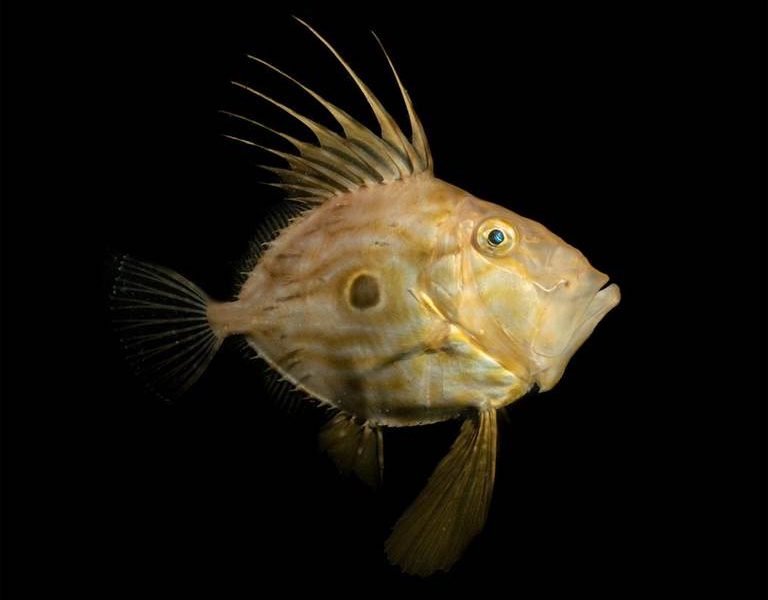
- John Dory, Dorset by Georgie Bull – “I have always had a soft spot for John Dory. When I first started diving in Dorset, we were gifted with many summer nights full of John Dory. I hadn’t seen one for years, but this summer they returned in good number, and I spent a good 10 minutes with this individual who was very keen to check themselves out in the reflection of my dome lens.”
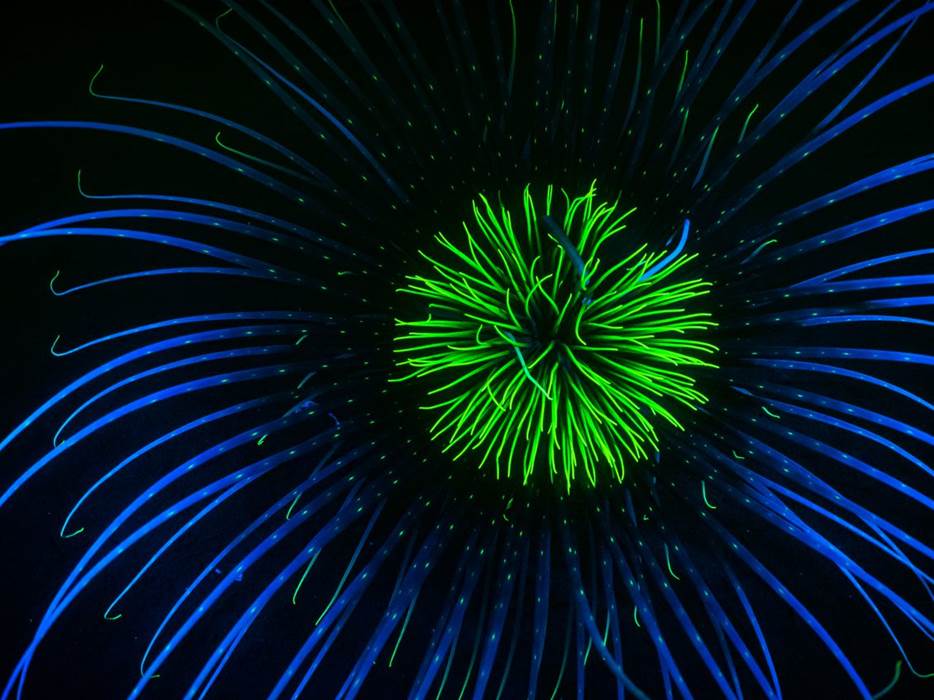
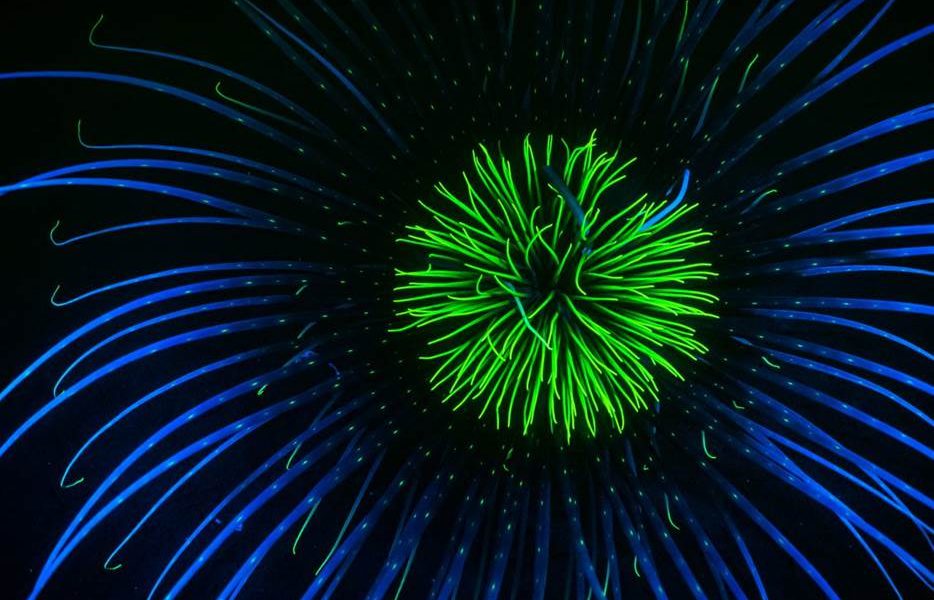
- Firework anemone (Pachycerianthus multiplicatus), Inverary, Loch Fyne by Dan Bolt – “As the UK’s biggest anemone, the Firework anemone can have a stalk and tentacles of up to 30cm long. Usually restricted to deeper waters, in many western Sea Lochs in Scotland they are accessible to sport divers. These beautiful creatures also have a party trick: under UV light they fluoresce and emit blue and green light and display patterns not seen under daylight.”
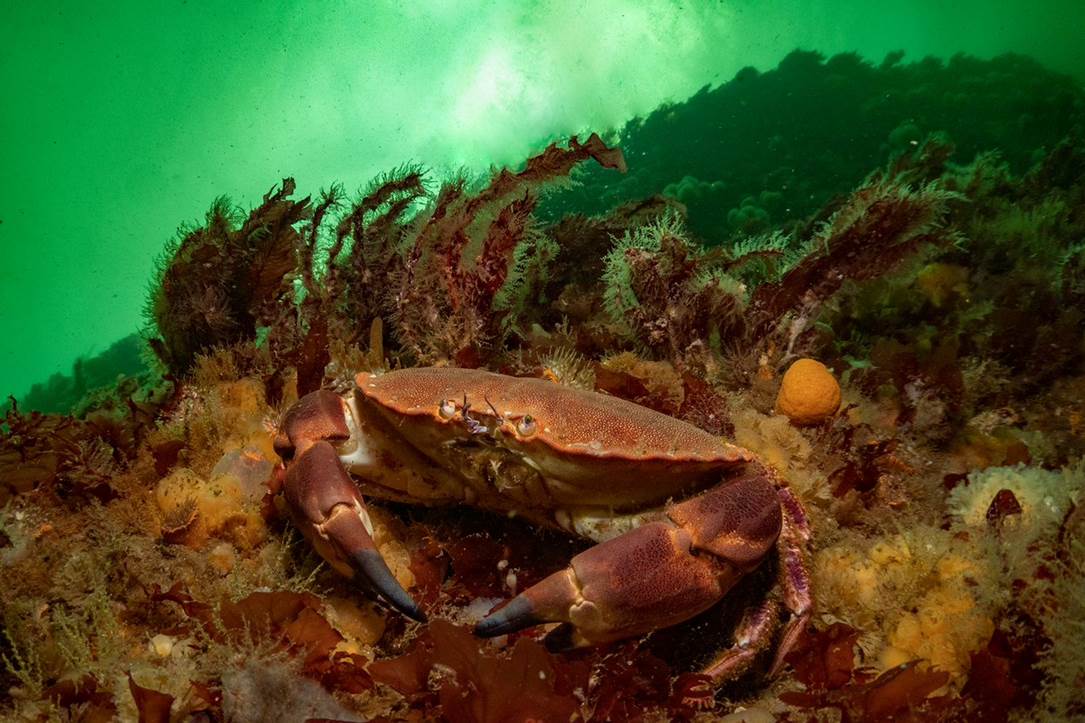
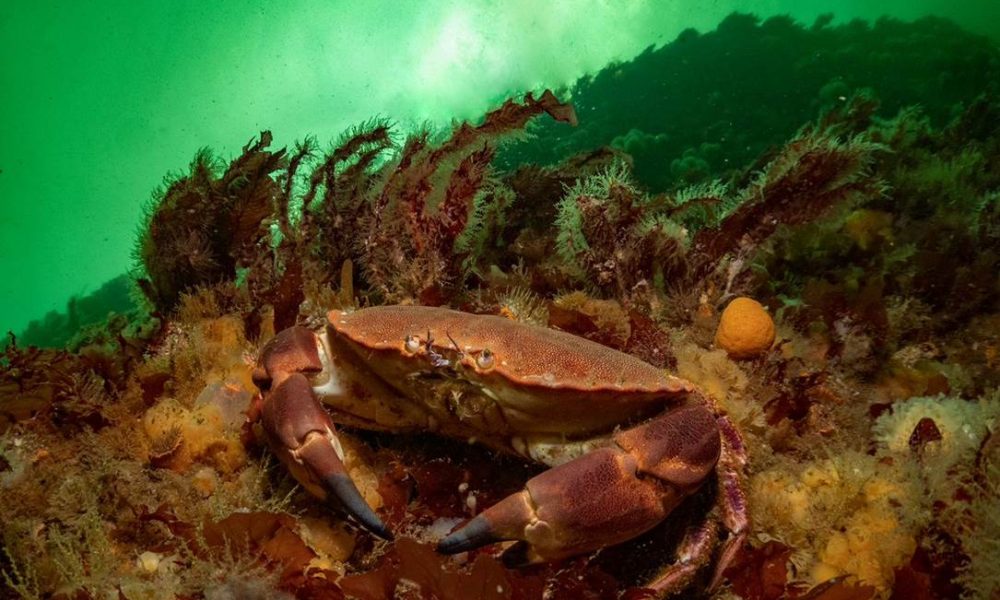
- Edible crab, Ar. Abbs, Berwickshire marine reserve by Georgie Bull – “Over the summer I visited St. Abbs and was blown away by how many crabs and lobsters there were. The Berwickshire Marine Reserve is a very special place to dive because it is a voluntary no-take zone. Many of the marine animals here have no need to fear divers and exist in higher numbers than outside of the reserve.”
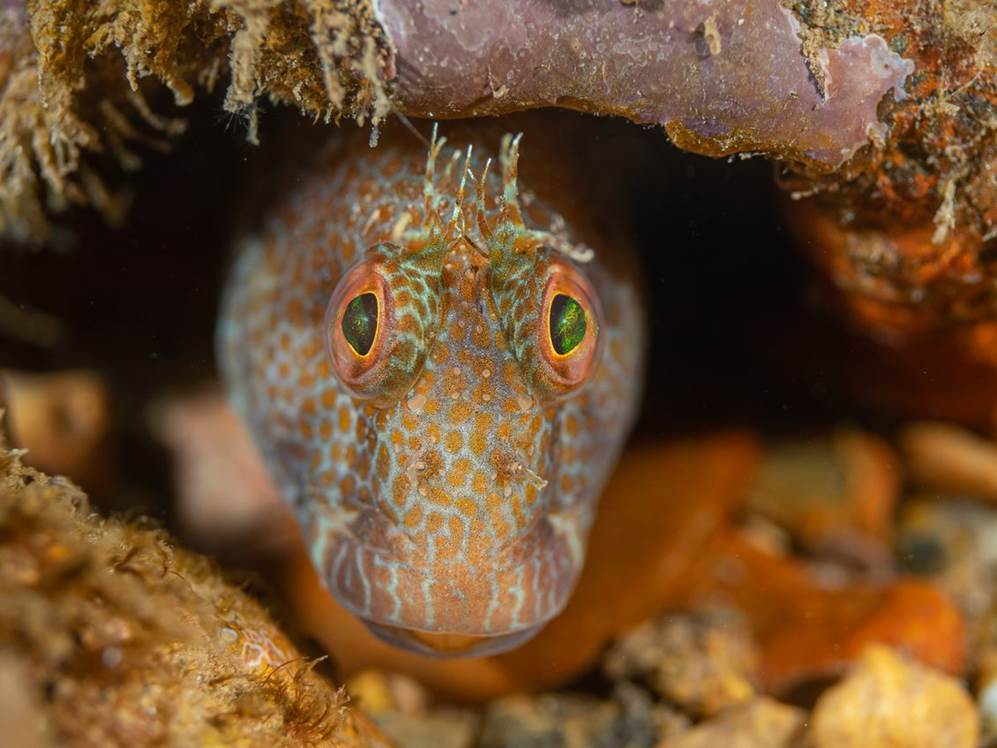
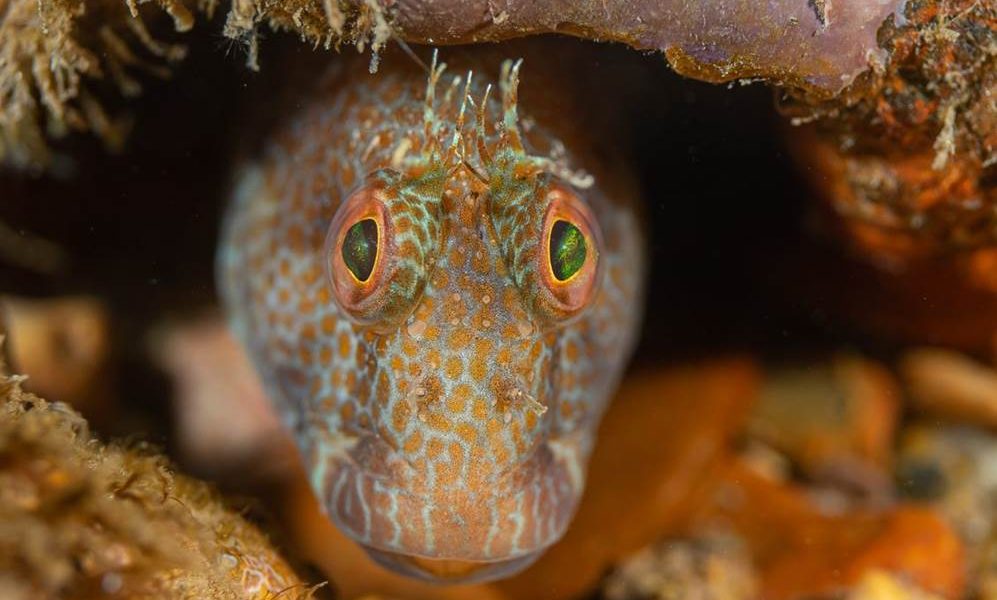
- Variable blenny, Babbacombe, south Devon by Dan Bolt – “The variable blenny is a relative newcomer to UK waters, arriving from the Mediterranean as a summer visitor some years ago, but is now firmly established in Babbacombe all year round. As their name suggests they are variable in colour, not only between male and female, but also when either mating or looking after a clutch of delicate eggs for weeks at a time.”
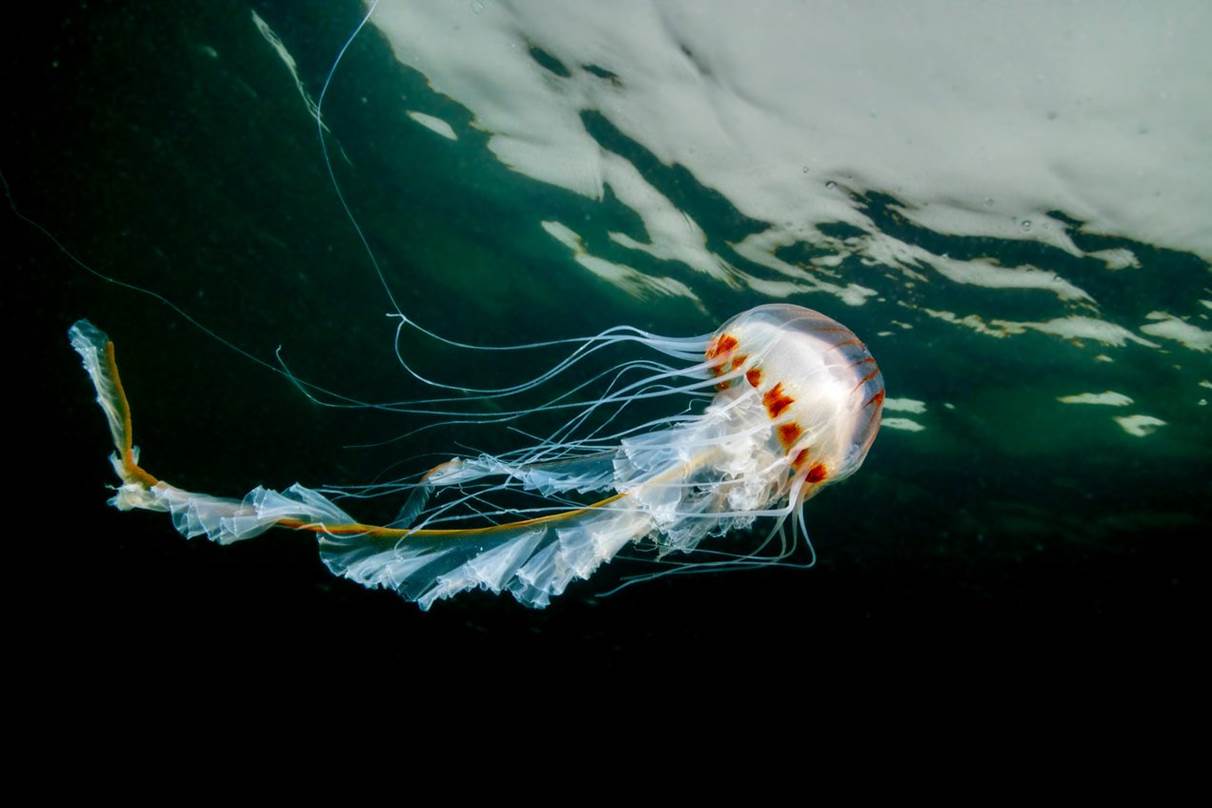
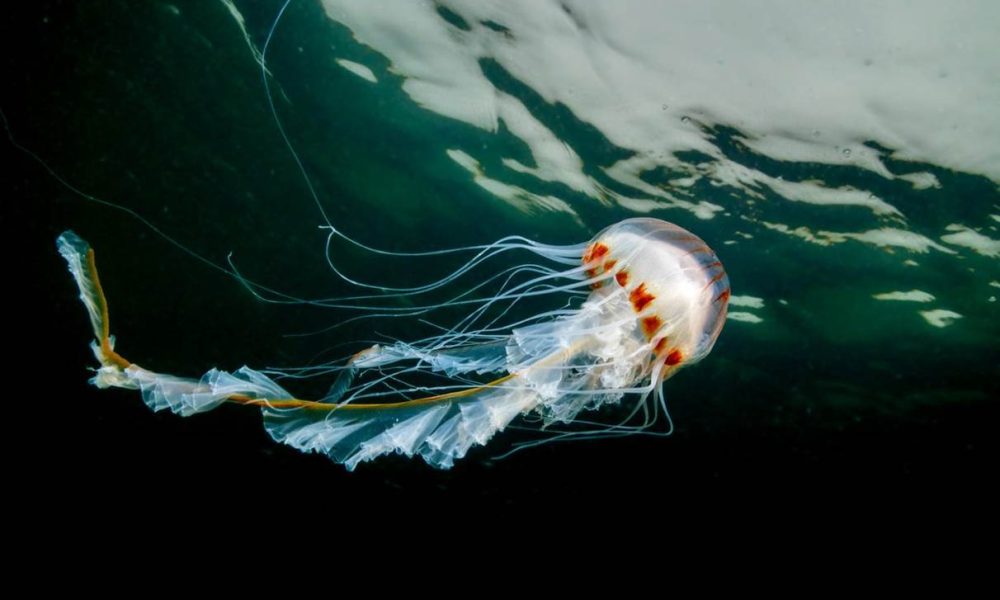
- Compass jellyfish, Falmouth, Cornwall by Martin Stevens – “The jellyfish is a compass jellyfish, smaller individual from Falmouth, Cornwall in springtime. A nice encounter with a great species, locally. Taken under overcast skies, moody weather, one of the first compass jellyfish of the year.”
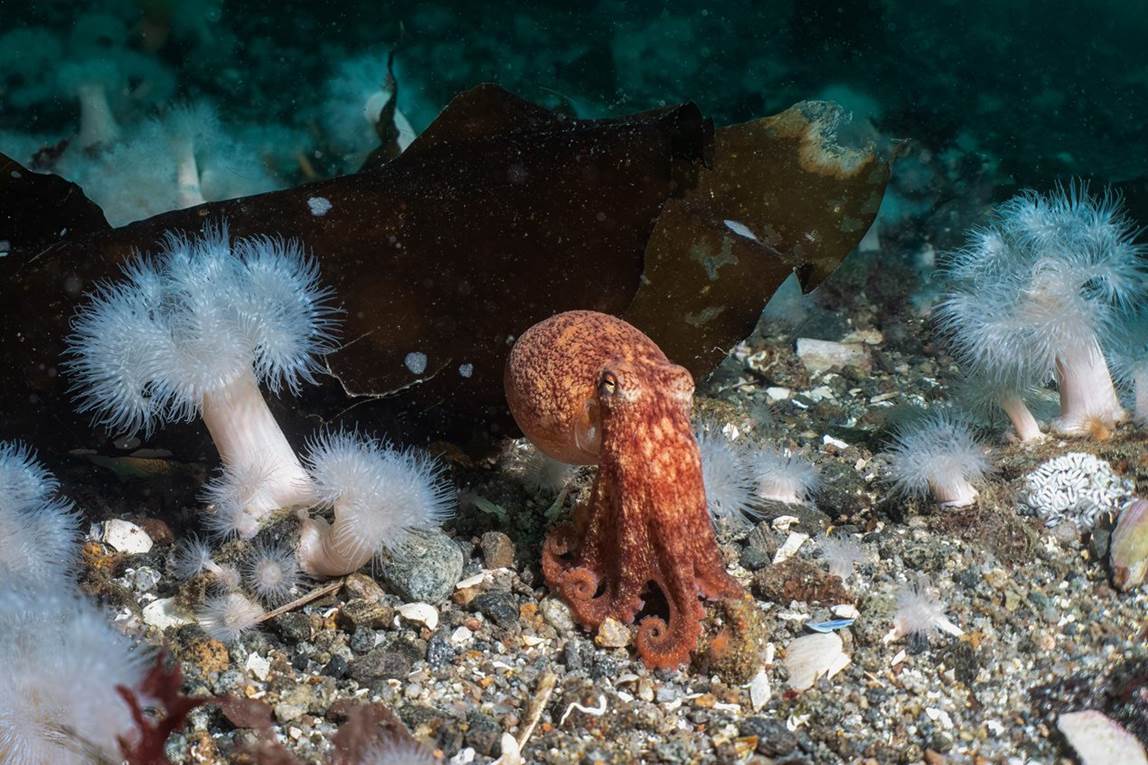
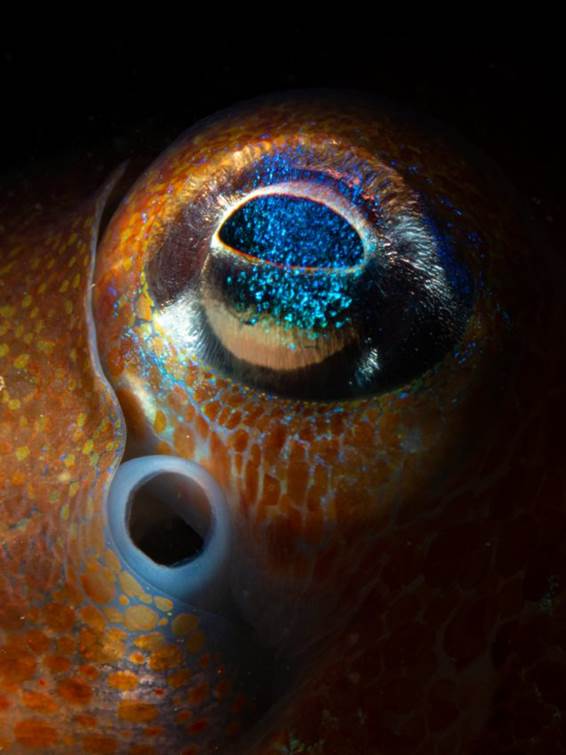
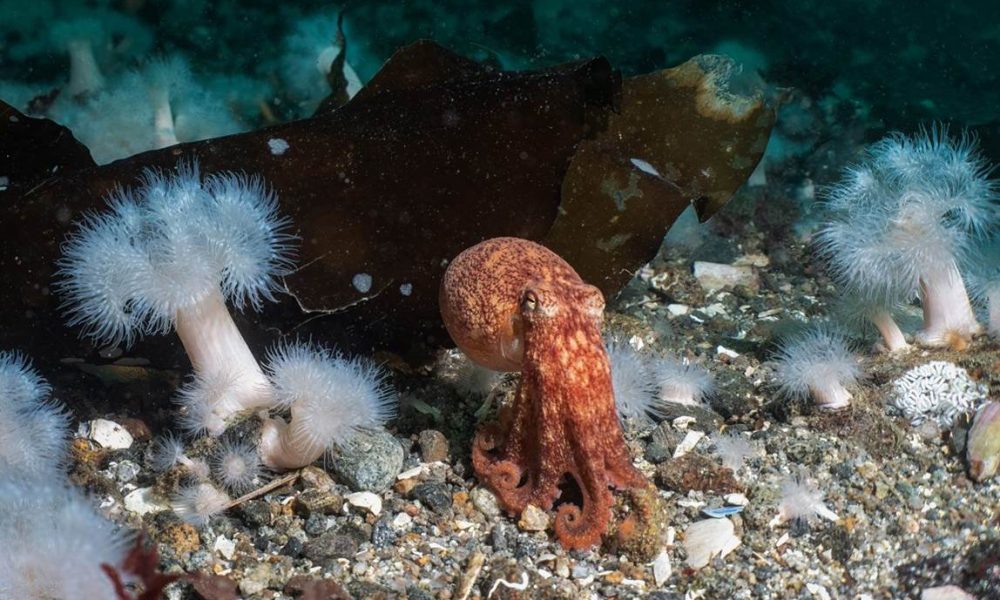
- Curled octopus, Toft pier, Shetland Islands by Billy Arthur – “Instantly a great dive when an octopus encounter is involved! Being quite sheltered and having lots of prey available for them, this site is a hotspot for curled octopus. It was already watching me when I finally noticed its presence, which is nearly always the case with these masters of camouflage. The plumose anemones which carpet the seabed in patches make it a very special place.”
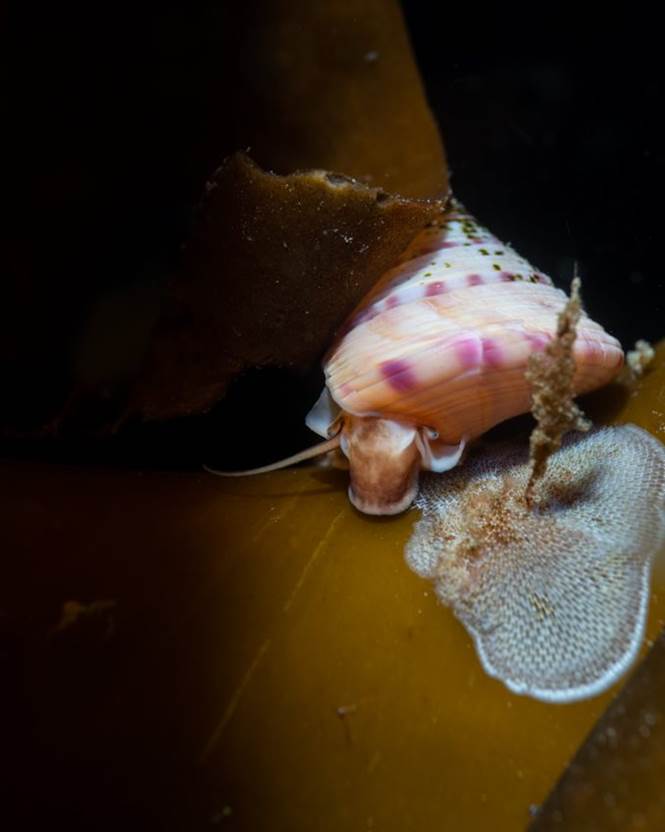
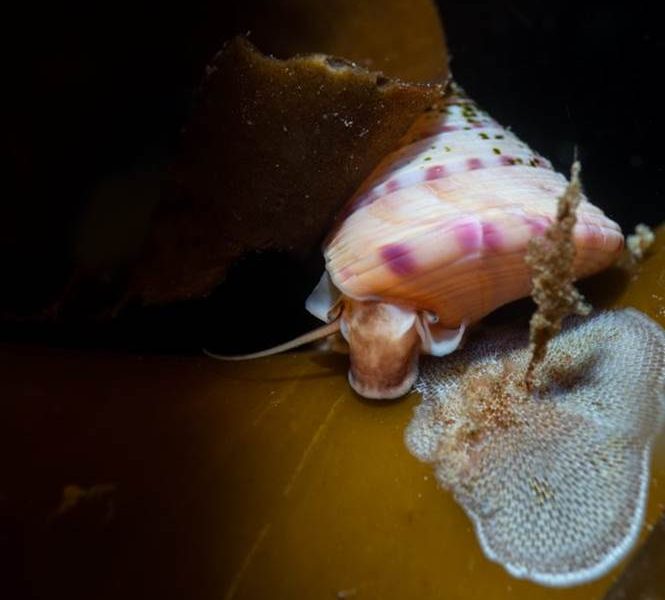
- Painted top-shell, Boddam, Shetland Islands by Billy Arthur – “One of the prettiest molluscs we find up here on the Shetland islands. This one looks to be feeding on a sea-mat which is a type of bryozoan which encrusts kelp fronds. Their stunning shells, which swash up on our beaches, are a prized find for beach combers, but they are much more stunning when alive. If you look closely, you can see its eye poking out from under the shell.”
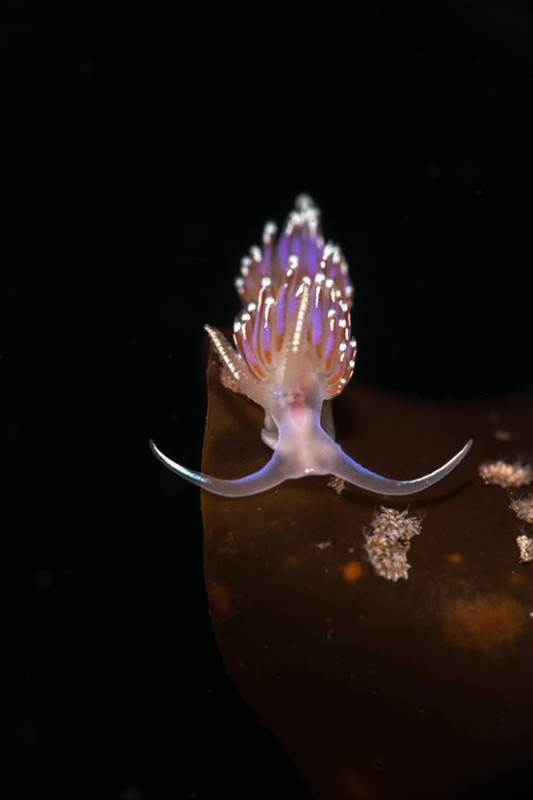
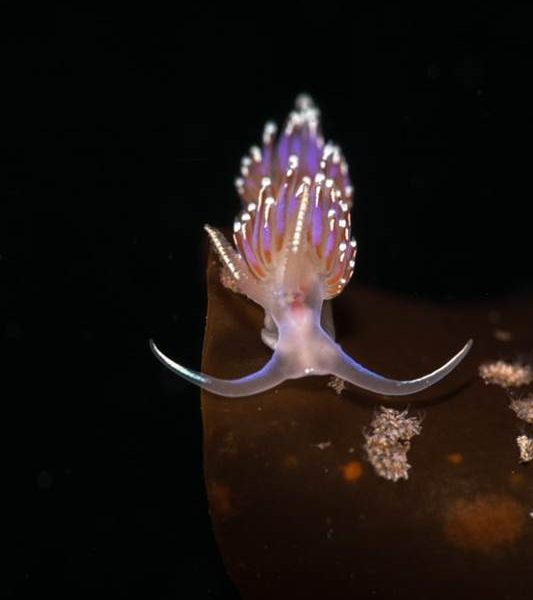
- Facelina auriculata, Lunna, Shetland Islands by Billy Arthur – “An absolute stunner of a nudibranch (sea slug)! Not as common as some of the other species we find here in Shetland, which makes them even more special. Caught by the sun’s rays they almost seem to sparkle. It’s amazing that such tiny, delicate creatures can survive in the wild seas around Shetlands coastline. Our kelp forests around Scotland are rich with life, the biodiversity in these forests is breath-taking and we need to protect them!”
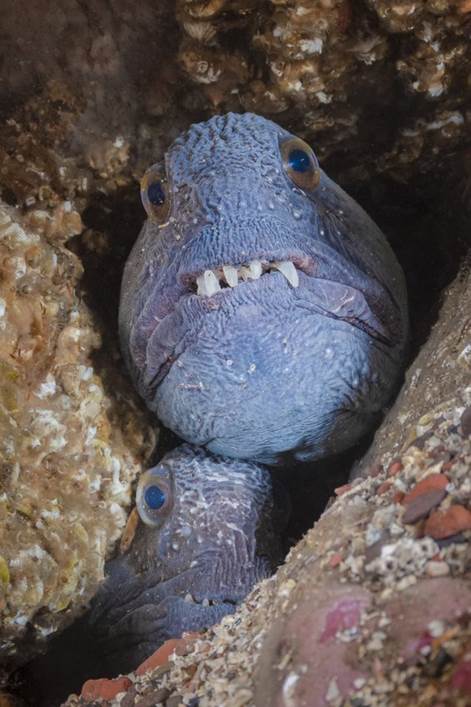
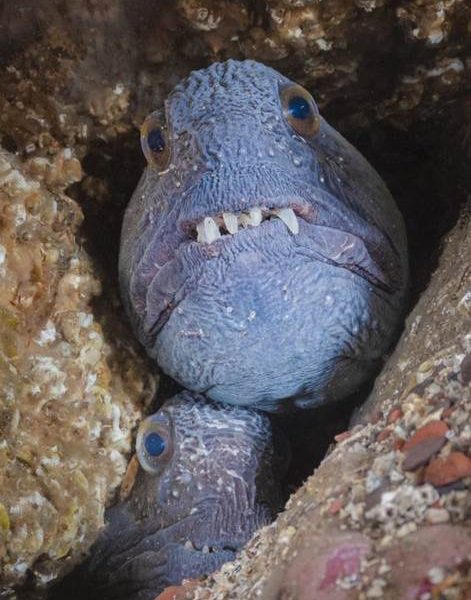
- Pair of wolf fish, Berwickshire marine reserve by Kirsty Andrews – “The Berwickshire marine reserve on the Scottish borders is the most reliable spot for UK divers to see charismatic wolf fish in their rocky lairs. They usually live singly but on one September trip, I spotted five separate pairs huddled together in different rocky hollows. Clearly, love is in the air for wolffish in the Autumn.”
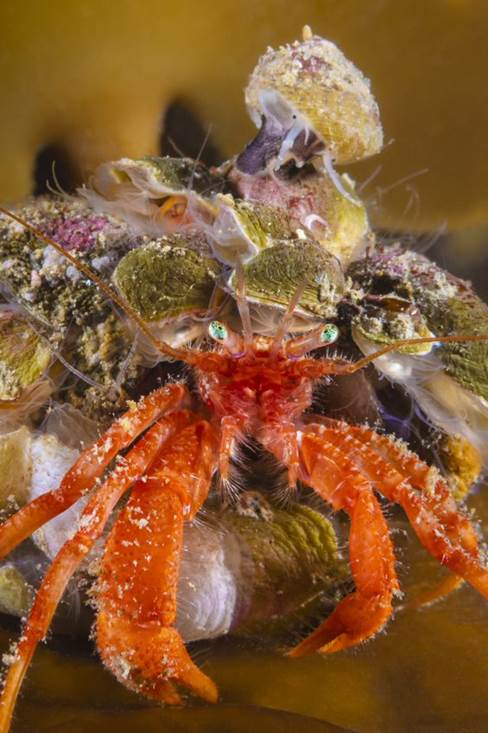
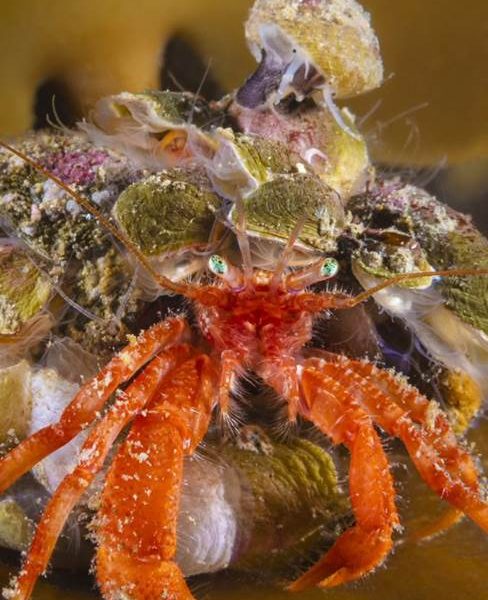
- Hermit crab and other molluscs on kelp, Shetland by Kirsty Andrews – “The closer you look, the more you see. I was drawn to this tiny but colourful hermit crab on a piece of kelp in the shallows in Shetland, but I didn’t appreciate until I looked closer that its shell was in turn covered in life, such as lampshells, pink encrusting algae and at the very top, a topshell. Quite the vibrant community.”
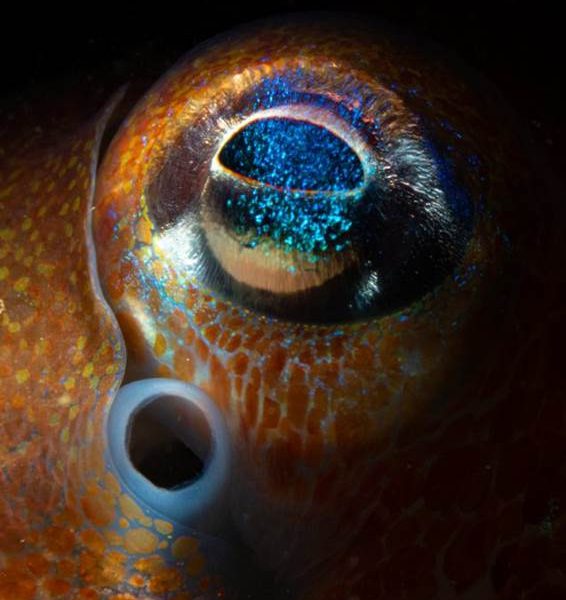
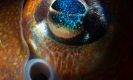
- Bobtail Squid, Loch Long by Mark Kirkland – “As winter creeps in, the tiny Bobtail Squid rises from the depths of the sealochs to breed. Through September and October, they can be found in depths as shallow as ten metres. Often no larger than a golf ball, a macro lens is preferable to get the glorious and colourful details. This shot shows an eye and siphon.”
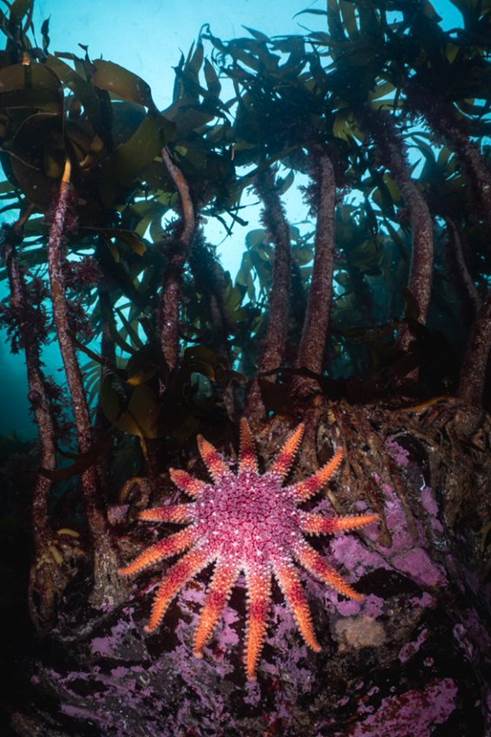
- Common Sunstar, Levenwick, Shetland Islands by Billy Arthur – “Typical rocky Shetland reef capped with a beautiful forest of kelp. This large common sunstar seemed to be making its way up into the kelp forest, likely in search of food. A beautiful starfish but also a voracious predator and scavenger. Once their prey has been caught by one of its many arms, they extrude their stomach out of their mouth and partially digest the meal, a gruesome end.”
To learn more about the Marine Conservation Society’s work, and how to get involved with the Seasearch project, please visit the charity’s website: Marine Conservation Society | Home (mcsuk.org)
Blogs
Invitation from The Ocean Cleanup for San Francisco port call

6 years ago, The Ocean Cleanup set sail for the Great Pacific Garbage Patch with one goal: to develop the technology to be able to relegate the patch to the history books. On 6 September 2024, The Ocean Cleanup fleet returns to San Francisco bringing with it System 03 to announce the next phase of the cleanup of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch and to offer you a chance to view our cleanup system up-close and personal.
We look forward to seeing you there.
To confirm your presence, please RSVP to press@theoceancleanup.com
PROGRAM
Join The Ocean Cleanup as our two iconic ships and the extraction System 03 return to San Francisco, 6 years and over 100 extractions after we set sail, to create and validate the technology needed to rid the oceans of plastic.
Our founder and CEO, Boyan Slat, will announce the next steps for the cleanup of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. Giving you a chance to view our cleanup system and the plastic extracted.
Hear important news on what’s next in the mission of The Ocean Cleanup as it seeks to make its mission of ridding the world’s oceans of plastic an achievable and realistic goal.
Interviews and vessel tours are available on request.
PRACTICALITIES
Date: September 6, 2024
Press conference: 12 pm (noon)
Location: The Exploratorium (Google Maps)
Pier 15 (Embarcadero at Green Street), San Francisco, CA
Parking: Visit The Exploratorium’s website for details.
RSVP: press@theoceancleanup.com
Video & photo material from several viewing spots around the bay
We look forward to seeing you there!
ABOUT THE OCEAN CLEANUP
The Ocean Cleanup is an international non-profit that develops and scales technologies to rid the world’s oceans of plastic. They aim to achieve this goal through a dual strategy: intercepting in rivers to stop the flow and cleaning up what has already accumulated in the ocean. For the latter, The Ocean Cleanup develops and deploys large-scale systems to efficiently concentrate the plastic for periodic removal. This plastic is tracked and traced to certify claims of origin when recycling it into new products. To curb the tide via rivers, The Ocean Cleanup has developed Interceptor™ Solutions to halt and extract riverine plastic before it reaches the ocean. As of June 2024, the non-profit has collected over 12 million kilograms (26.4 million pounds) of plastic from aquatic ecosystems around the world. Founded in 2013 by Boyan Slat, The Ocean Cleanup now employs a broadly multi-disciplined team of approximately 140. The foundation is headquartered in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and opened its first regional office in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, in 2023.
Find out more about The Ocean Cleanup at www.theoceancleanup.com.
Blogs
Smart Shark Diving: The Importance of Awareness Below the Surface

By: Wael Bakr
Introduction to Shark Diving Awareness
In the realm of marine life, few creatures captivate our interest, and sometimes our fear, like the shark. This fascination often finds a home in the hearts of those who venture beneath the waves, particularly scuba divers who love shark diving. It’s here that shark awareness takes the spotlight. Shark awareness is not just about understanding these magnificent creatures; it’s about fostering respect, dispelling fear, and promoting conservation. As Jacques Cousteau once said, “People protect what they love.” And to love something, one must first understand it.
Shark awareness is not a mere fascination; it’s a responsibility that we owe to our oceans and their inhabitants. From the smallest reef shark to the colossal great white, each species plays a crucial role in the underwater ecosystem. Our understanding and appreciation of these creatures can help ensure their survival.
However, shark awareness isn’t just about protecting the sharks; it’s also about protecting ourselves. As scuba divers, we share the underwater world with these magnificent creatures. Understanding them allows us to dive safely and responsibly, enhancing our experiences beneath the waves.
Importance of Shark Awareness in Scuba Diving
The relevance of shark awareness in scuba diving cannot be overstated. Sharks, like all marine life, are an integral part of the underwater ecosystem. Their presence and behavior directly influence our experiences as divers. By understanding sharks, we can better appreciate their role in the ocean, anticipate their actions, and reduce potential risks.
Awareness is crucial for safety when shark diving. Despite their often-misunderstood reputation, sharks are generally not a threat to humans. However, like any wild animal, they can pose risks if provoked or threatened. By understanding shark behavior, we can identify signs of stress or aggression and adjust our actions accordingly. This not only protects us but also respects the sharks and their natural behaviors.
Moreover, shark awareness enriches our diving experiences. Observing sharks in their natural habitat is a thrilling experience. Understanding them allows us to appreciate this spectacle fully. It’s not just about seeing a shark; it’s about understanding its role in the ecosystem, its behavior, and its interaction with other marine life. This depth of knowledge adds a new dimension to our diving experiences.
Understanding Shark Behavior: The Basics
The first step in shark awareness is understanding shark behavior. Sharks are not the mindless predators they are often portrayed to be. They are complex creatures with unique behaviors and communication methods. Understanding these basics can significantly enhance our interactions with them.
Sharks communicate primarily through body language. By observing their movements, we can gain insights into their mood and intentions. For example, a relaxed shark swims with slow, fluid movements. In contrast, a stressed or agitated shark may exhibit rapid, jerky movements or other signs of discomfort such as gill flaring.
Sharks also use their bodies to express dominance or assertiveness. A dominant shark may swim with its pectoral fins pointed downwards, while a submissive shark may swim with its fins flattened against its body. Understanding these signals can help us interpret shark behavior accurately and respond appropriately.
How Shark Awareness Enhances Scuba Diving Experiences
Shark awareness significantly enhances our scuba diving experiences. It transforms encounters with sharks from mere sightings into meaningful interactions. Knowledge is power, and in this case, it’s the power to appreciate, respect, and safely interact with one of the ocean’s most fascinating inhabitants.
A thorough understanding of behavior when shark diving allows us to interpret their actions and responses accurately. It enables us to recognize signs of stress or aggression and adjust our behavior accordingly. This not only ensures our safety but also promotes responsible interactions that respect the sharks and their natural behaviors.
Furthermore, shark awareness adds a new layer of depth to our diving experiences. It’s one thing to see a shark; it’s another to understand its behavior, its role in the ecosystem, and its interactions with other marine life. This depth of understanding enriches our experiences and fosters a deeper appreciation for our underwater world.
Misconceptions About Sharks: Busting the Myths
Unfortunately, sharks are often misunderstood, feared, and even demonized. These misconceptions can be detrimental, not only to our experiences as divers but also to shark conservation efforts. As part of shark awareness, it’s important to debunk these myths and present sharks in their true light.
First and foremost, sharks are not mindless killing machines. They are complex creatures with unique behaviors and communication methods. They are not interested in humans as prey and, in most cases, prefer to avoid us.
Secondly, not all sharks are dangerous. Out of over 500 species of sharks, only a handful are considered potentially harmful to humans. Most sharks are harmless, and even those that can pose a threat are unlikely to attack unless provoked.
Lastly, sharks are not invincible. They are vulnerable to a host of threats, most notably human activities such as overfishing and habitat destruction. They need our understanding and protection, not our fear and persecution.
Shark Behavior: What to Expect When Scuba Diving
When scuba diving, it’s important to know what to expect from sharks. Most encounters with sharks are peaceful and awe-inspiring. However, as with any wild animal, it’s essential to be prepared and understand their behavior.
Most sharks are shy and cautious creatures. They are likely to observe you from a distance, often circling around to get a better look. This is normal behavior and not a sign of aggression.
However, if a shark becomes agitated or feels threatened, it may exhibit signs of stress such as rapid, jerky movements or gill flaring. In such cases, it’s essential to remain calm, avoid sudden movements, and slowly retreat if possible.
Remember, every encounter with a shark is an opportunity to observe and learn. With understanding and respect, these encounters can be safe, enriching, and truly unforgettable experiences.
Practical Tips for Shark Awareness During Scuba Diving
Being aware of sharks during scuba diving is about more than just understanding their behavior. It’s about applying this knowledge in practical ways to ensure safe and respectful interactions. Here are a few tips for shark awareness during scuba diving.
Firstly, always observe sharks from a safe distance. Avoid approaching them directly or making sudden movements, as this can startle or threaten them.
Secondly, never attempt to touch or feed sharks. This can disrupt their natural behavior and potentially put you at risk.
Lastly, always respect the sharks and their environment. Avoid disturbing their habitat or interfering with their natural behaviors. Remember, we are visitors in their world.
Promoting Shark Conservation through Scuba Diving
Scuba diving offers a unique platform for promoting shark conservation. As divers, we have the privilege of witnessing the beauty and complexity of sharks firsthand. We can share these experiences with others, fostering understanding and appreciation for these magnificent creatures.
Moreover, we can actively contribute to shark conservation. Many diving operators offer opportunities to participate in shark research and conservation initiatives. By participating in these programs, we can help ensure the survival of sharks for future generations.
Lastly, we can advocate for sharks. By sharing our knowledge and experiences, we can help dispel misconceptions about sharks and promote their protection. Every voice counts in the fight for shark conservation.
Courses and Resources for Shark Awareness and Behavior
There are many resources available for those interested in shark awareness and behavior. Scuba Diving International as well as numerous conservation-based organizations offer courses and workshops on shark biology, behavior, and conservation. These courses provide in-depth knowledge and practical skills for interacting with sharks responsibly and safely. From courses like our Marine Ecosystems Awareness Specialty and our Advanced Adventure Certification provide you with the information you need to tackle this new challenge!
Additionally, there are many online resources available, including websites, blogs, and forums dedicated to shark awareness and conservation. These platforms offer a wealth of information and a community of like-minded individuals passionate about sharks.
I encourage anyone interested in sharks to explore these resources, to sign up for one of SDI’s courses call your local dive center or instructor or reach out to your regional representative/ World HQ to find where the class is being taught near you. Knowledge is the first step towards understanding, appreciation, and conservation.
Conclusion: The Role of Shark Awareness in Future Scuba Diving Experiences
As we look to the future, the role of shark awareness in scuba diving will only continue to grow. As our understanding of these magnificent creatures deepens, so too will our appreciation and respect for them. This knowledge will shape our interactions with sharks, enhancing our experiences and promoting responsible and respectful behavior.
Shark awareness is more than just an interest; it’s a responsibility. It’s a commitment to understanding, respecting, and protecting one of the ocean’s most fascinating inhabitants. And it’s a journey that I invite all divers to embark on.
As we dive into the blue, let’s dive with awareness. Let’s dive with respect. And let’s dive with a commitment to understand and protect our underwater world. For in the end, the ocean’s health is our health, and every creature within it, including the sharks, plays a crucial role in maintaining this delicate balance.
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDiving With… Nico, Ocean Earth Travels, Indonesia
-

 News1 month ago
News1 month agoMurex Bangka Announce New Oceanfront Cottages & Beachfront Dining
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoA new idea in freediving from RAID
-

 Marine Life & Conservation1 month ago
Marine Life & Conservation1 month agoIceland issue millionaire whale hunter a licence to murder 128 vulnerable fin whales
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoThe Shark Trust Great Shark Snapshot is back
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCharting New Waters; NovoScuba Goes Global with the Launch of their Revolutionary Dive Training Agency!
-

 Gear News1 month ago
Gear News1 month agoNew Suunto Ocean – a dive computer and GPS sports watch in one for adventures below and above the surface
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs2 months agoBook Review: Plankton