Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Creature Feature: The Houndsharks

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
This month we’re taking a look at a few of the species from the houndshark family. The houndsharks, a.k.a. Triakidae, are a family of around 45 species. In this Creature Feature we’ll be looking at the Leopard Shark and Common Smoothhound.
Houndsharks are known for having two large, spineless dorsal fins, an anal fin and oval-shaped eyes with nictating eyelids. Animals with nictating eyelids have a third, clear, eyelid. This protects the eye whilst still allowing the houndsharks to be able to see. Houndsharks are small to medium in size, with adults ranging from around 37cm to 220cm. They’re one of the largest families of sharks. They are distributed throughout the world in warm and temperate waters. They predominantly feed on fish and invertebrates on the seafloor and in midwater.
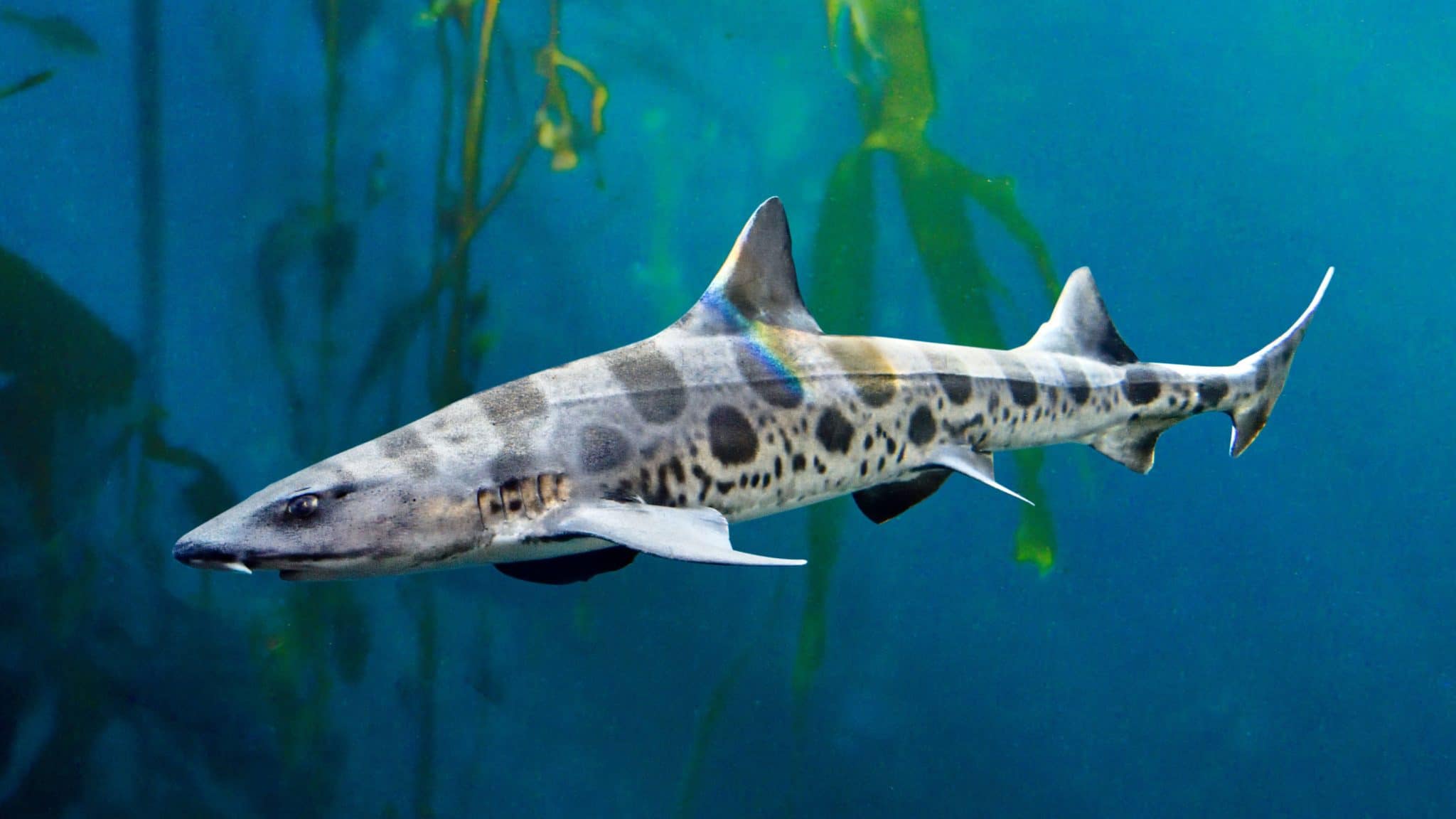
Leopard Shark
Confusingly named after a feline species, the Leopard Shark does indeed belong to the houndshark family. Its name comes from the unique saddle marks and spots that cover the species, resembling those of a leopard (as seen in the banner image).
It is one of the most common sharks found along the Pacific coast of North America. They are active, strong-swimming sharks. Sometimes spotted resting on sand among rocks. Leopard Sharks form large, nomadic schools with different species (such as the North Pacific Spiny Dogfish and Bat Rays.
The species is classified as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Leopard Sharks are primarily caught by recreational anglers. But they are also taken as incidental catch in commercial fisheries. They are generally well managed by commercial fisheries. They are also popular in aquariums due to their distinctive markings and hardiness. The poaching of pups for the aquarium trade has been a significant problem.
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Triakis semifasciata
FAMILY: Triakidae (Houndsharks)
MAXIMUM SIZE: 180cm
DIET: Small sharks eat crabs, the siphons off clams and worms from the seafloor. Large sharks may eat fishes and even other smaller sharks.
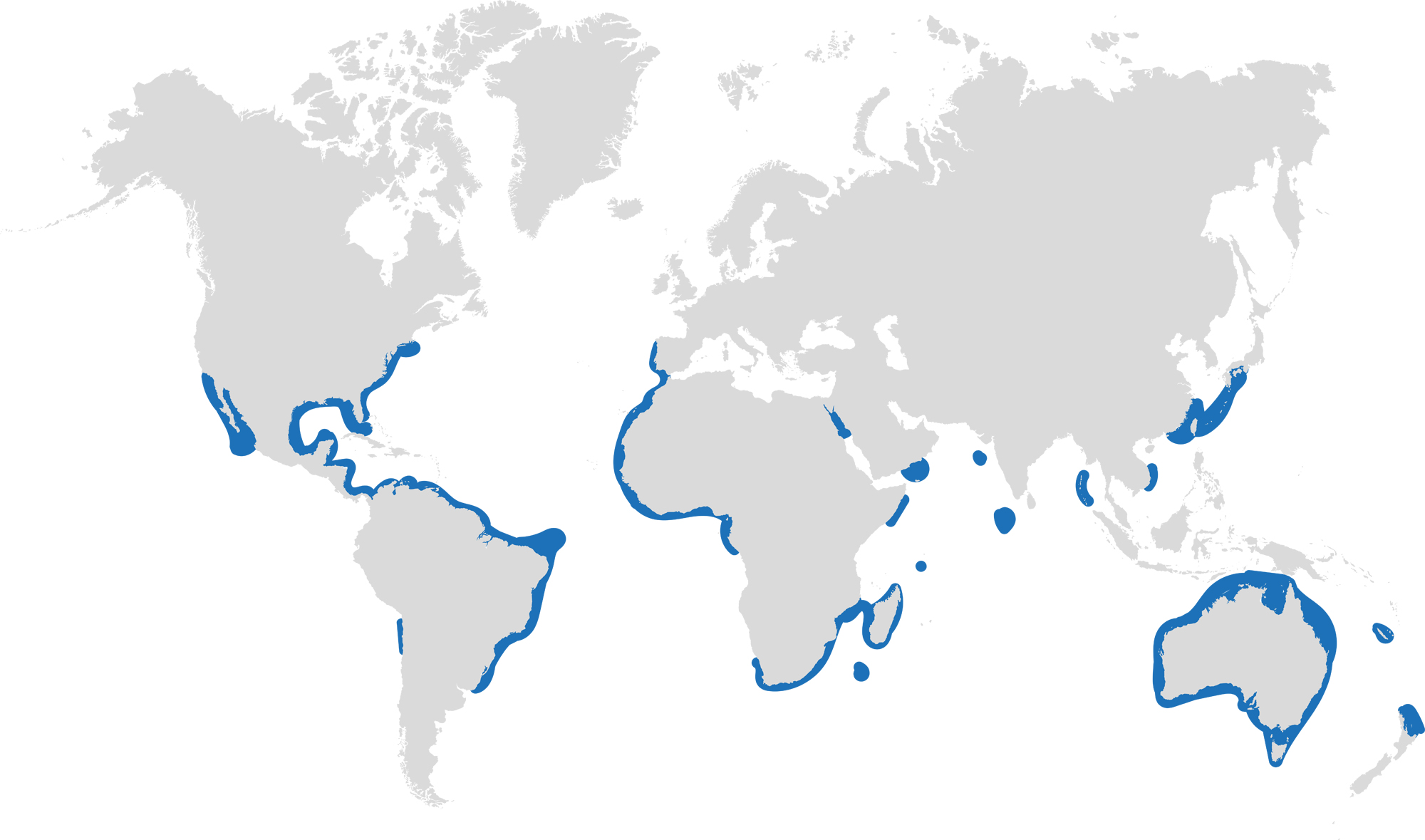
DISTRIBUTION: Northeast Pacific – west coast of the United States from southern Washington to the Gulf of California (Mexico).
HABITAT: Cool to warm waters. Most common on or near the seabed in bays and estuaries. Females give birth in water less than 1m deep.
CONSERVATION STATUS:
Common Smoothhound
A medium-sized, unspotted houndshark. The Common Smoothhound is often confused with the Starry Smoothhound which usually has white spots along its back. It’s also often confused with the Tope Shark. Smoothounds are so called because they will gather in large numbers, like a pack of dogs.
The Common Smoothhound is classified as globally Endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The species is classed as Vulnerable in Europe. It is targeted by fisheries across its range, both for sport and in commercial fisheries. The species is caught for food across the Mediterranean, European and West African fisheries. There is often confusion between the Common Smoothhound and Starry Smoothhound. Starry Smoothounds often doesn’t have any stars/spots. So they are very similar in appearance. Genetic analysis is the most reliable way to distinguish smoothhounds.
SCIENTIFIC NAME: Mustelus mustelus
FAMILY: Triakidae (Houndsharks)
MAXIMUM SIZE: 175cm
DIET: Mainly crustaceans. Also cephalopods and bony fishes.
DISTRIBUTION: Temperate east Atlantic. UK to the Mediterranean, Morocco down to South Africa and the Indian Ocean coast.
HABITAT: Continental shelves and upper slopes. Usually 5-50m, but occasionally down to at least 800m.
CONSERVATION STATUS:
For more amazing facts about sharks and what you can do to help the Shark Trust protect them visit the Shark Trust website by clicking here.
Banner Image – ©Barbar Ash via Shutterstock
Image of Leopard Shark – ©ScubaZoo
Maps – ©Chris_huh, via Wikimedia Commons
Smoothound Illustration – ©Marc Dando
Blogs
The Ocean Cleanup Breaks 10,000,000 KG Barrier
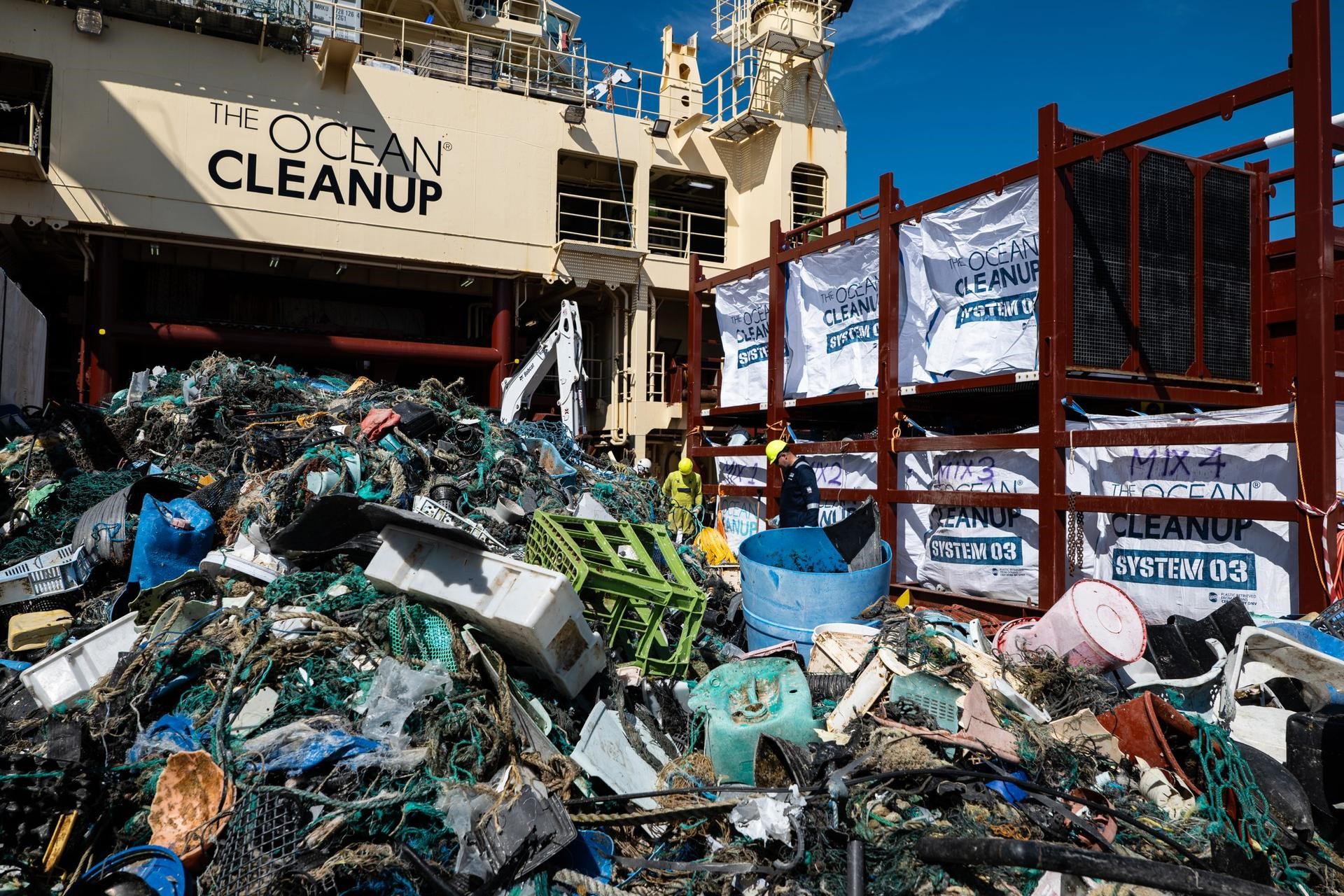

The Ocean Cleanup, the global non-profit project, has removed a verified all-time total of ten million kilograms (22 million lbs.) of trash from oceans and rivers around the world – approximately the same weight as the Eiffel Tower.
To complete its mission of ridding the oceans of plastic, The Ocean Cleanup uses a dual strategy: cleaning up the Great Pacific Garbage Patch (GPGP) to remove the plastic already afloat in the oceans, while stopping the flow of plastic from the world’s most polluting rivers.
Through cleaning operations in the GPGP and in rivers in eight countries, the cumulative total of trash removed has now surpassed ten million kilograms. This milestone demonstrates the acceleration of The Ocean Cleanup’s impact, while underlining the astonishing scale of the plastic pollution problem and the need for continued support and action.
While encouraging for the mission, this milestone is only a staging point: millions more tons of plastic still pollute our oceans and The Ocean Cleanup intends to continue learning, improving and innovating to solve this global catastrophe.
This announcement comes as governments from around the world meet to continue negotiations to develop a new legally binding instrument to end plastic pollution at INC4 in Ottawa, Canada. Representatives of The Ocean Cleanup will be in attendance and the organization will be urging decision-makers to collaborate towards a comprehensive and ambitious global treaty which addresses plastic at all stages of its life cycle and in all marine environments worldwide, including in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
It is encouraging to see that the need for remediation is reflected in the various options for potential treaty provisions. It is essential that the final treaty contains clear targets for the remediation of legacy plastic pollution, and reduction of riverine plastic emissions.
Tackling plastic pollution requires innovative and impactful solutions. The treaty should therefore incentivize the innovation ecosystem by fostering innovations that make maximal use of data, technology and scientific knowledge – such as those designed and deployed by The Ocean Cleanup.
‘After many tough years of trial and error, it’s amazing to see our work is starting to pay off – and I am proud of the team who has brought us to this point.’ said Boyan Slat, Founder and CEO of The Ocean Cleanup. ‘While we still have a long way to go, our recent successes fill us with renewed confidence that the oceans can be cleaned.’
The Ocean Cleanup was founded in 2013 and captured its first plastic in 2019, with the first confirmed catch in the GPGP coming soon after the deployment of Interceptor 001 in Jakarta, Indonesia. After surpassing one million kilograms of trash removed in early 2022, the non-profit project has since progressed to the third iteration of its GPGP cleaning solution, known as System 03, and a network of Interceptors currently covering rivers in eight countries, with more deployments set for 2024.
About The Ocean Cleanup
The Ocean Cleanup is an international non-profit organization that develops and scales technologies to rid the world’s oceans of plastic. They aim to achieve this goal through a dual strategy: stemming the inflow via rivers and cleaning up the legacy plastic that has already accumulated in the ocean. For the latter, The Ocean Cleanup develops large-scale systems to efficiently concentrate the plastic for periodic removal. This plastic is tracked and traced through DNV’s chain of custody model to certify claims of origin when recycling it into new products. To curb the tide via rivers, The Ocean Cleanup has developed Interceptor™ solutions to halt and extract riverine plastic before it reaches the ocean. Founded in 2013 by Boyan Slat, The Ocean Cleanup now employs a broadly multi-disciplined team of approximately 140. The foundation is headquartered in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit: theoceancleanup.com and follow @theoceancleanup on social media.
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Creature Feature: Dusky Shark

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
This month we’re taking a look at the Dusky Shark, a highly migratory species with a particularly slow growth rate and late age at maturity.
Dusky sharks are one of the largest species within the Carcharhinus genus, generally measuring 3 metres total length but able to reach up to 4.2 metres. They are grey to grey-brown on their dorsal side and their fins usually have dusky margins, with the darkest tips on the caudal fin.
Dusky Sharks can often be confused with other species of the Carcharhinus genus, particularly the Galapagos Shark (Carcharhinus galapagensis). They have very similar external morphology, so it can be easier to ID to species level by taking location into account as the two species occupy very different ecological niches – Galapagos Sharks prefer offshore seamounts and islets, whilst duskies prefer continental margins.
Hybridisation:
A 2019 study found that Dusky Sharks are hybridising with Galapagos Sharks on the Eastern Tropical Pacific (Pazmiño et al., 2019). Hybridisation is when an animal breeds with an individual of another species to produce offspring (a hybrid). Hybrids are often infertile, but this study found that the hybrids were able to produce second generation hybrids!
Long distance swimmers:
Dusky sharks are highly mobile species, undertaking long migrations to stay in warm waters throughout the winter. In the Northern Hemisphere, they head towards the poles in the summer and return southwards towards the equator in winter. The longest distance recorded was 2000 nautical miles!
Very slow to mature and reproduce:
The Dusky Shark are both targeted and caught as bycatch globally. We already know that elasmobranchs are inherently slow reproducers which means that they are heavily impacted by overfishing; it takes them so long to recover that they cannot keep up with the rate at which they are being fished. Dusky Sharks are particularly slow to reproduce – females are only ready to start breeding at roughly 20 years old, their gestation periods can last up to 22 months, and they only give birth every two to three years. This makes duskies one of the most vulnerable of all shark species.
The Dusky Shark is now listed on Appendix II of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS), but further action is required to protect this important species.
Scientific Name: Carcharhinus obscurus
Family: Carcharhinidae
Maximum Size: 420cm (Total Length)
Diet: Bony fishes, cephalopods, can also eat crustaceans, and small sharks, skates and rays
Distribution: Patchy distribution in tropical and warm temperate seas; Atlantic, Indo-Pacific and Mediterranean.
Habitat: Ranges from inshore waters out to the edge of the continental shelf.
Conservation status: Endangered.
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Images: Andy Murch
Diana A. Pazmiño, Lynne van Herderden, Colin A. Simpfendorfer, Claudia Junge, Stephen C. Donnellan, E. Mauricio Hoyos-Padilla, Clinton A.J. Duffy, Charlie Huveneers, Bronwyn M. Gillanders, Paul A. Butcher, Gregory E. Maes. (2019). Introgressive hybridisation between two widespread sharks in the east Pacific region, Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 136(119-127), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.04.013.
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Gear Reviews3 weeks ago
Gear Reviews3 weeks agoGEAR REVIEW – Revolutionising Diving Comfort: The Sharkskin T2 Chillproof Suit
-

 Blogs3 months ago
Blogs3 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoPADI Teams Up with Wellness Brand Neuro to Drive Ocean Change and Create a Blue State of Mind
-

 Gear Reviews3 months ago
Gear Reviews3 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoWorld’s Best Underwater Photographers Unveil Breathtaking Images at World Shootout 2023