Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Sea Shepherd Ship Status Report on Neptune’s Navy

Keep up to date with the Sea Shepherd fleet in this report from Captain Paul Watson…
Read the latest International Union for the Conservation of Nature Report on the Vaquita, which can be found by clicking here. Read on to find out more about what the ships and crew have been up to around the world, protecting our seas, oceans and marine life.
The crews on the Farley Mowat, John Paul DeJoria and the Sharpie have done an incredible job this year with Operation Milagro locating and confiscating more illegal nets than last year with a month left to go.
They have dispatched the John Paul DeJoria to Peru via the Galapagos to meet with the Peruvian Navy to discuss anti-poaching operations in Peruvian waters. The Farley Mowat will complete the Milagro campaign. The Sharpie will move to do anti-poaching patrols in the new Pacific marine sanctuary established by Mexico in the Revillagigedo Islands.
The Martin Sheen recently completed Operation Clean Waves in the Kiribati Islands. This involved coral propagation, plastic debris removal and the providing of water purification equipment to the islanders. The vessel will undergo 4 weeks of maintenance in Oaho, Hawaii before departure for British Columbia for the continuation of Operation Virus Hunter.
The Brigitte Bardot will be shipped next week from Genoa, Italy to Florida for a major overhaul in preparation for conservation projects in the Caribbean.
Sea Shepherd Global Deployment:
The Ocean Warrior currently doing anti-poaching operations in Tanzania in Partnership with the Tanzanian government – Operation Jodari
The Bob Barker is currently undertaking anti-poaching operations in the waters off West Africa in partnership with the governments of Gabon and Liberia. Operation Albacore and Operation Solis Stella.
The Steve Irwin is currently doing Operation Jeedara to block plans by the Norwegian oil company Statoil to drill in the pristine waters of the Great Australian Bight.
The Emmanuel Bronner is currently doing patrols in the Baltic Sea to protect porpoises.
The Jairo Mora Sandoval is currently doing conservation work with the NGO Biosphera in the waters of Cape Verde.
For more information about the work of Sea Shepherd, please click here.
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
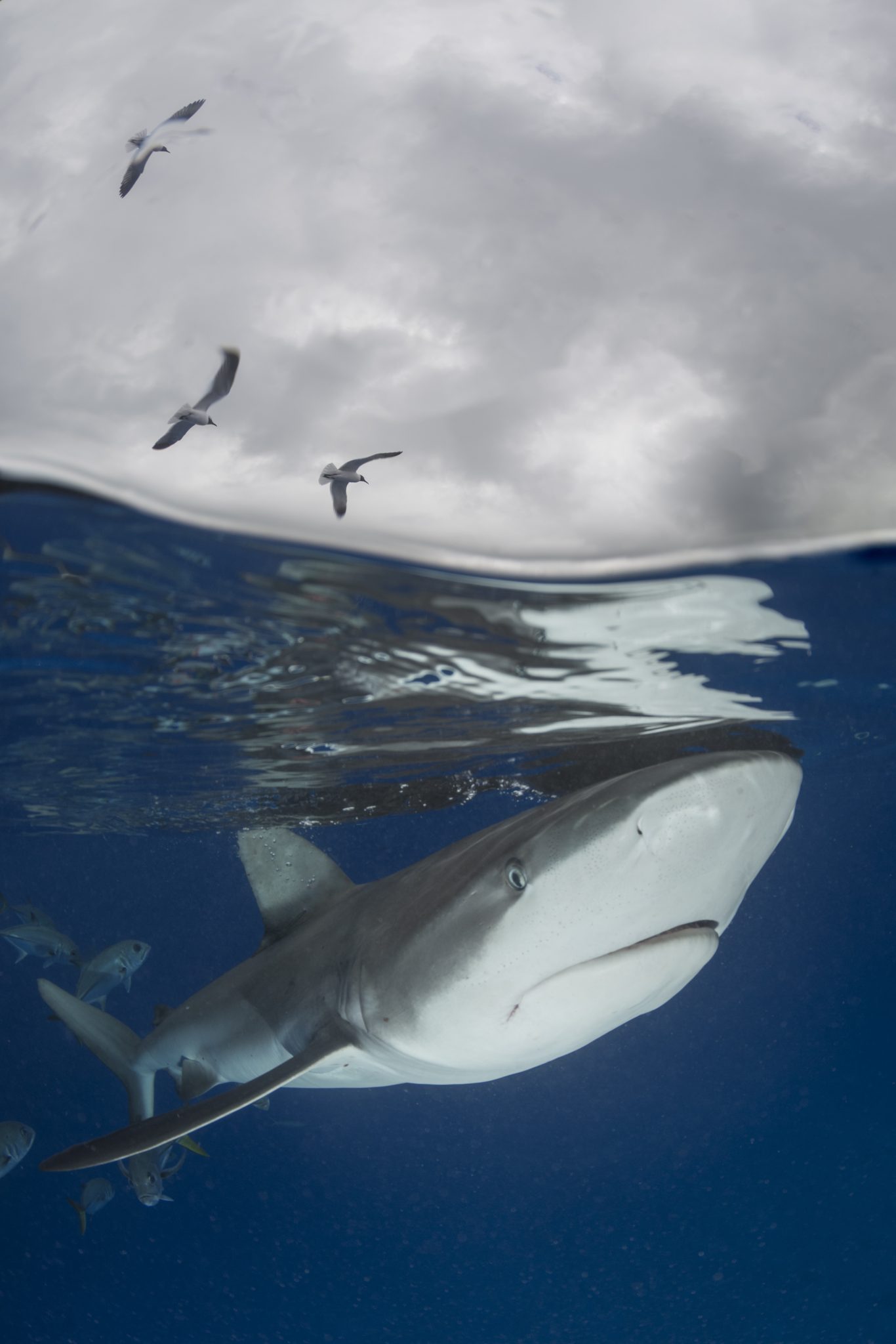
Creature Feature: Dusky Shark

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
This month we’re taking a look at the Dusky Shark, a highly migratory species with a particularly slow growth rate and late age at maturity.
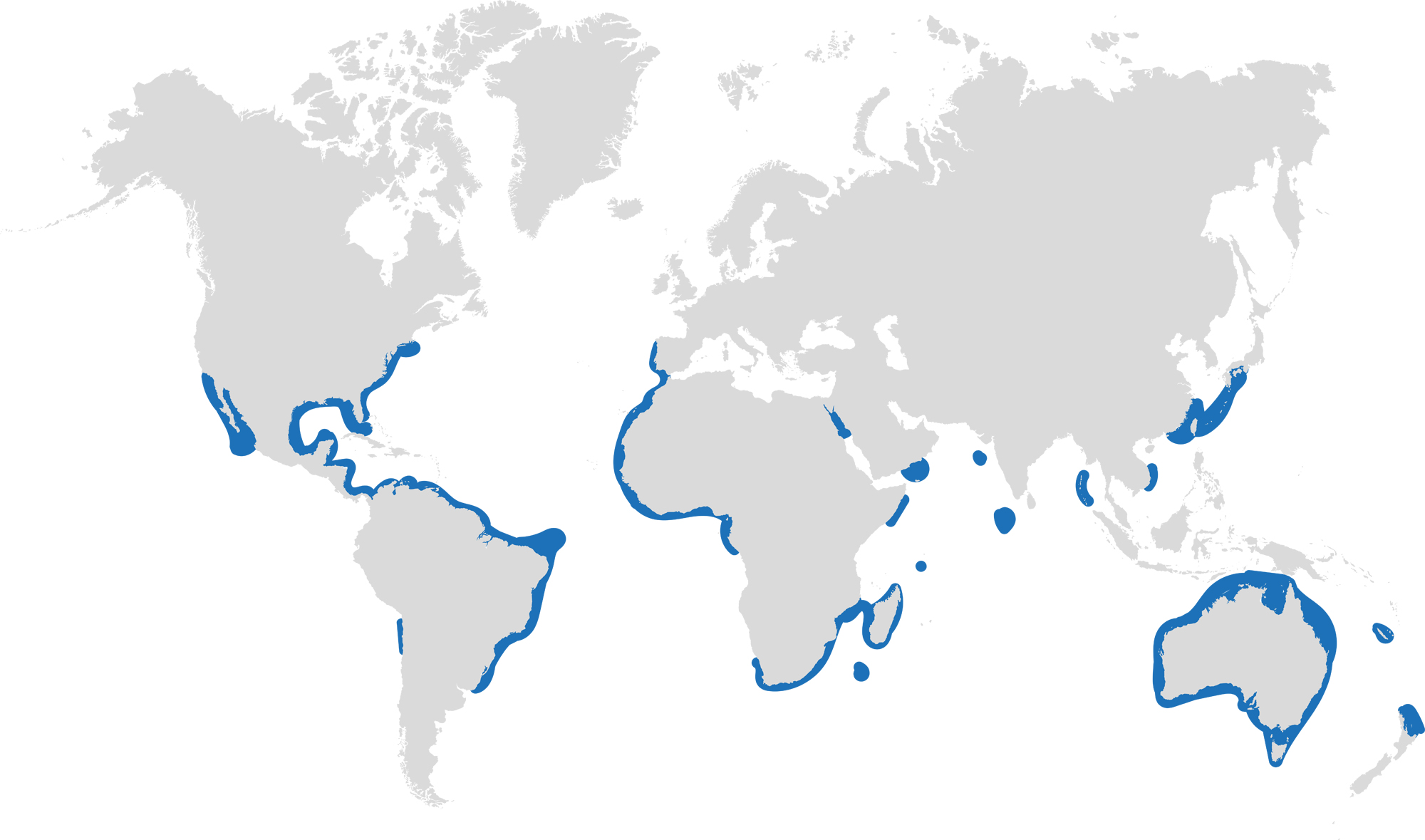
Dusky sharks are one of the largest species within the Carcharhinus genus, generally measuring 3 metres total length but able to reach up to 4.2 metres. They are grey to grey-brown on their dorsal side and their fins usually have dusky margins, with the darkest tips on the caudal fin.
Dusky Sharks can often be confused with other species of the Carcharhinus genus, particularly the Galapagos Shark (Carcharhinus galapagensis). They have very similar external morphology, so it can be easier to ID to species level by taking location into account as the two species occupy very different ecological niches – Galapagos Sharks prefer offshore seamounts and islets, whilst duskies prefer continental margins.
Hybridisation:
A 2019 study found that Dusky Sharks are hybridising with Galapagos Sharks on the Eastern Tropical Pacific (Pazmiño et al., 2019). Hybridisation is when an animal breeds with an individual of another species to produce offspring (a hybrid). Hybrids are often infertile, but this study found that the hybrids were able to produce second generation hybrids!
Long distance swimmers:
Dusky sharks are highly mobile species, undertaking long migrations to stay in warm waters throughout the winter. In the Northern Hemisphere, they head towards the poles in the summer and return southwards towards the equator in winter. The longest distance recorded was 2000 nautical miles!
Very slow to mature and reproduce:
The Dusky Shark are both targeted and caught as bycatch globally. We already know that elasmobranchs are inherently slow reproducers which means that they are heavily impacted by overfishing; it takes them so long to recover that they cannot keep up with the rate at which they are being fished. Dusky Sharks are particularly slow to reproduce – females are only ready to start breeding at roughly 20 years old, their gestation periods can last up to 22 months, and they only give birth every two to three years. This makes duskies one of the most vulnerable of all shark species.
The Dusky Shark is now listed on Appendix II of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS), but further action is required to protect this important species.
Scientific Name: Carcharhinus obscurus
Family: Carcharhinidae
Maximum Size: 420cm (Total Length)
Diet: Bony fishes, cephalopods, can also eat crustaceans, and small sharks, skates and rays
Distribution: Patchy distribution in tropical and warm temperate seas; Atlantic, Indo-Pacific and Mediterranean.
Habitat: Ranges from inshore waters out to the edge of the continental shelf.
Conservation status: Endangered.
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Images: Andy Murch
Diana A. Pazmiño, Lynne van Herderden, Colin A. Simpfendorfer, Claudia Junge, Stephen C. Donnellan, E. Mauricio Hoyos-Padilla, Clinton A.J. Duffy, Charlie Huveneers, Bronwyn M. Gillanders, Paul A. Butcher, Gregory E. Maes. (2019). Introgressive hybridisation between two widespread sharks in the east Pacific region, Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 136(119-127), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.04.013.
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
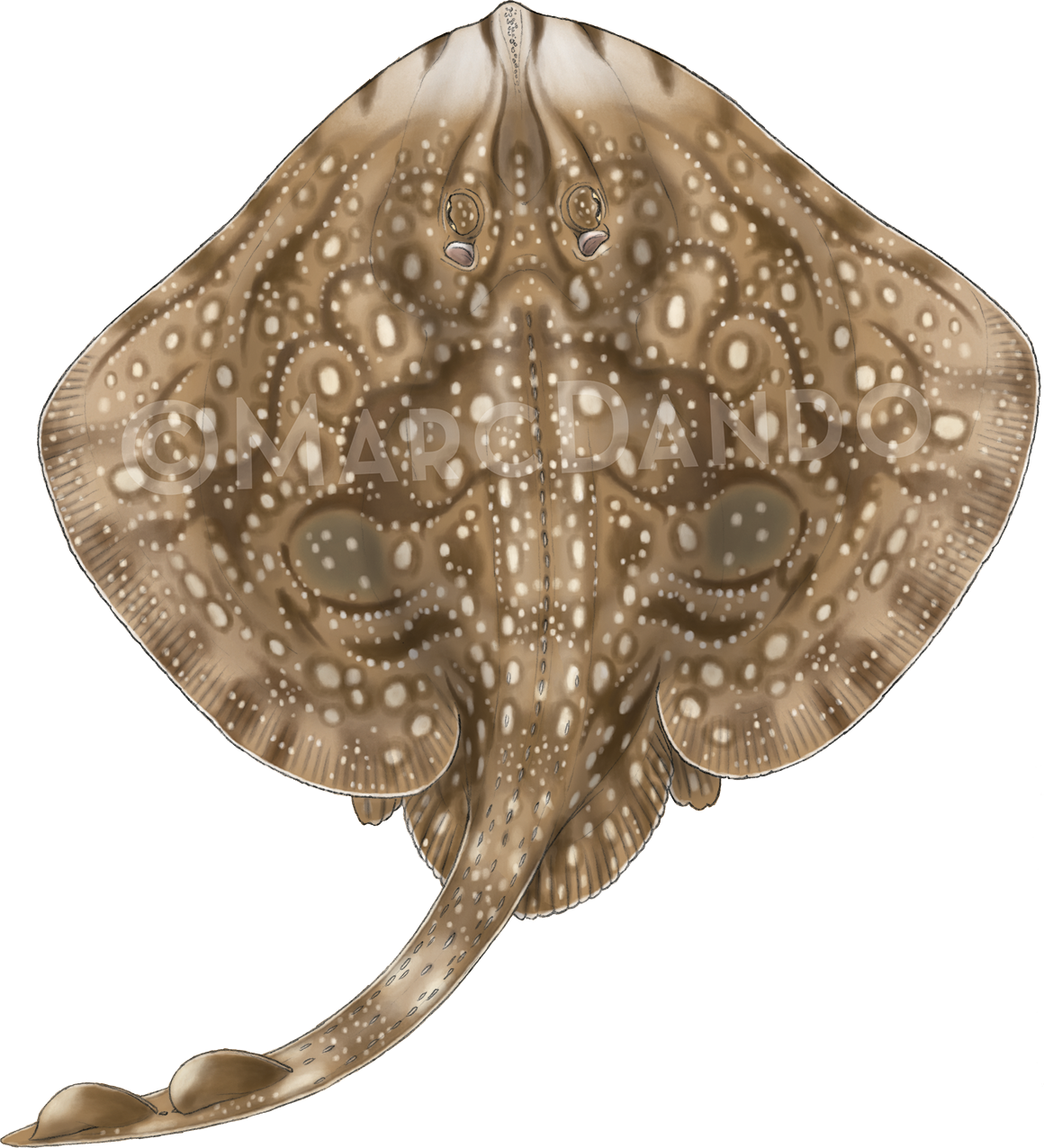
Creature Feature: Undulate Ray

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
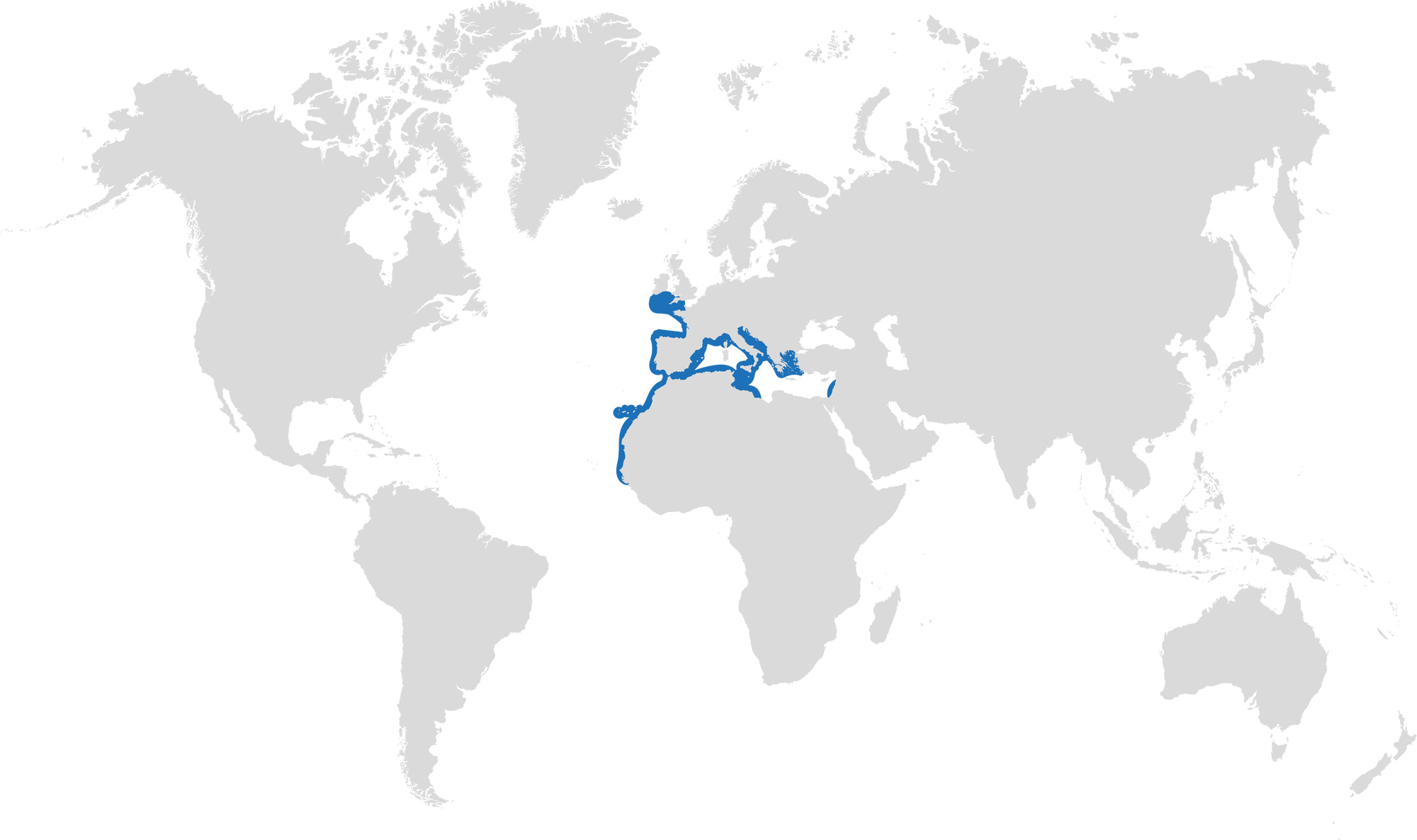
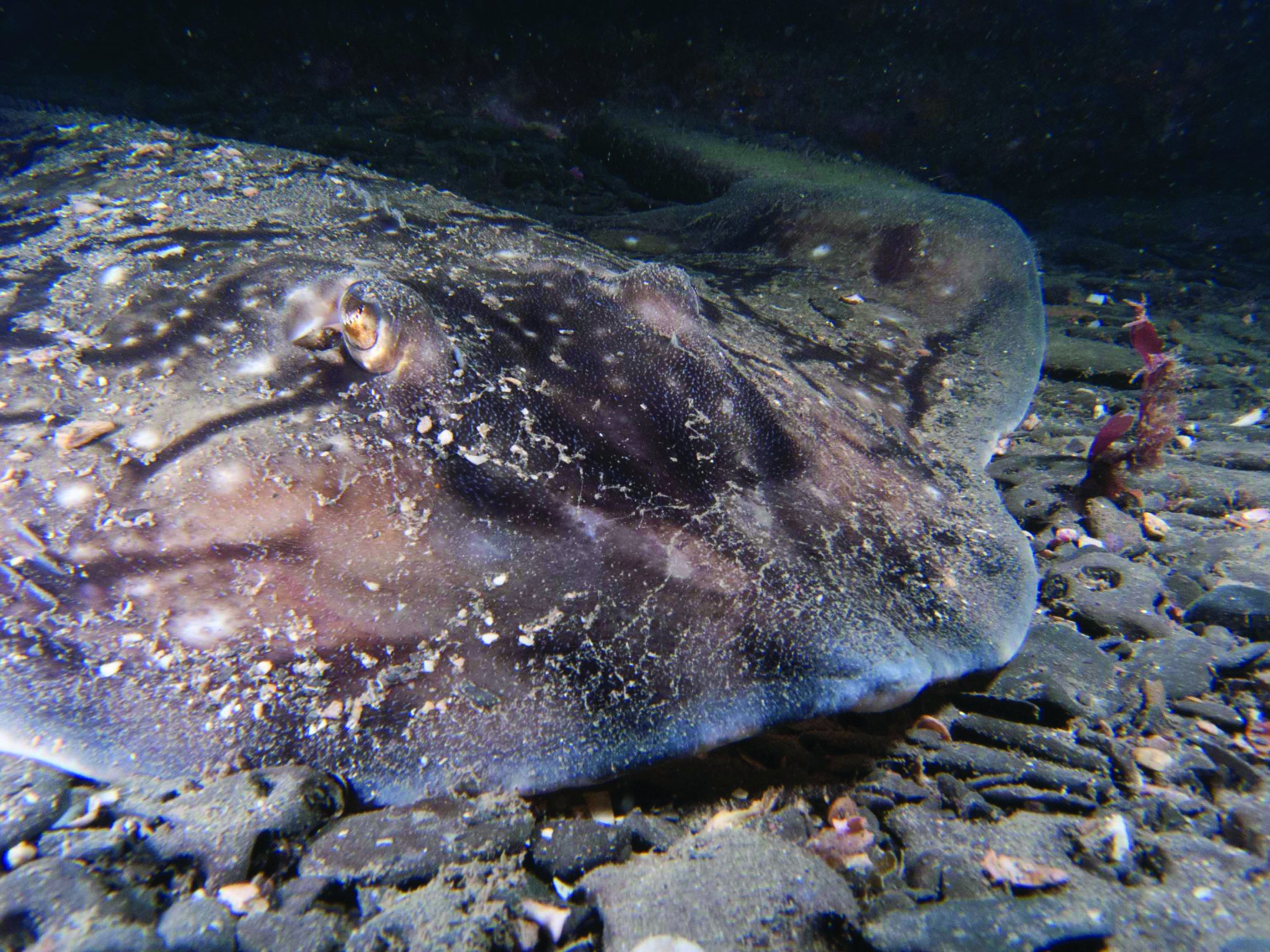
This month we’re looking at the Undulate Ray. Easily identified by its beautiful, ornate pattern, the Undulate Ray gets its name from the undulating patterns of lines and spots on its dorsal side.
This skate is usually found on sandy or muddy sea floors, down to about 200 m deep, although it is more commonly found shallower. They can grow up to 90 cm total length. Depending on the size of the individual, their diet can range from shrimps to crabs.
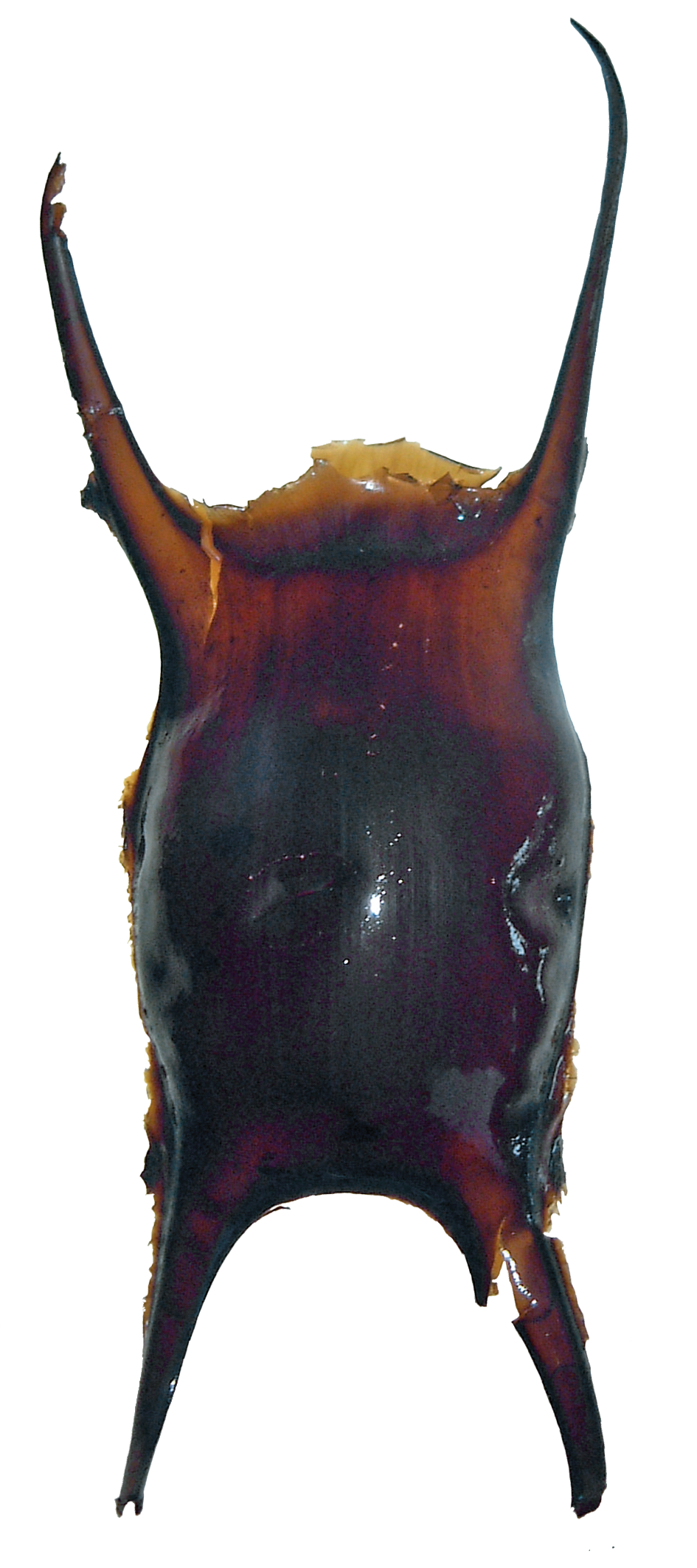
Although sometimes called the Undulate Ray, this is actually a species of skate, meaning that, as all true skates do, they lay eggs. The eggs are contained in keratin eggcases – the same material that our hair and nails are made up of! These eggcases are also commonly called mermaid’s purses and can be found washed up on beaches all around the UK. If you find one, be sure to take a picture and upload your find to the Great Eggcase Hunt – the Shark Trust’s flagship citizen science project.
It is worth noting that on the south coasts, these eggcases can be confused with those of the Spotted Ray, especially as they look very similar and the ranges overlap, so we sometimes informally refer to them as ‘Spundulates’.
Scientific Name: Raja undulata
Family: Rajidae
Maximum Size: 90cm (total length)
Diet: shrimps and crabs
Distribution: found around the eastern Atlantic and in the Mediterranean Sea.
Habitat: shelf waters down to 200m deep.
Conservation Status : As a commercially exploited species, the Undulate Ray is a recovering species in some areas. The good thing is that they have some of the most comprehensive management measures of almost any elasmobranch species, with both minimum and maximum landing sizes as well as a closed season. Additionally, targeting is entirely prohibited in some areas. They are also often caught as bycatch in various fisheries – in some areas they can be landed whilst in others they must be discarded.
IUCN Red List Status: Endangered
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Image Credits: Banner – Sheila Openshaw; Illustration – Marc Dando
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoHone your underwater photography skills with Alphamarine Photography at Red Sea Diving Safari in March
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Gear Reviews2 weeks ago
Gear Reviews2 weeks agoGEAR REVIEW – Revolutionising Diving Comfort: The Sharkskin T2 Chillproof Suit
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida
-

 Gear Reviews3 months ago
Gear Reviews3 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone