Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Serendipity

Serendipity means a “fortunate happenstance” or “pleasant surprise”. The New Oxford Dictionary of English defines serendipity as the occurrence and development of events by chance in a satisfactory or beneficial way, understanding the chance as any event that takes place in the absence of any obvious project.
This was exactly how I came to connect with Ocean Crest Alliance who the Marine Foundation are forming a new partnership with. I was asked by the TerraMar project to be a guest host for the Daily Catch on Global Ocean TV. As with any request I receive, I researched the organisation and saw the great work they are doing. I would recommend you help this cause and that of our seas and get yourself an ocean passport.
I wanted to better understand what they would expect from me as a guest presenter, so I watched a number of previous episodes and was fortunate enough to discover one featuring Joseph Ierna, the founder of Ocean Crest Alliance. OCA is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organisation, registered in the United States and the Bahamas and was established to create awareness, to inspire, and to educate others about our Earth and Oceans and to illustrate the real issues we all face today. Joseph like myself has fallen in love with our Oceans and Seas and as I watched their Global TV episode I had that tingling feeling I get when I know something serendipitous is brewing.
I rode the wave, as they say, and looked up their website to learn their goal is ‘to Honor, Protect, and Restore the Health of the Worlds Oceans and the life of the Earth’s Systems through Conservation, Research, Education, Science and Technology programs’. These objectives share much in common with those of the Marine Foundation’s work and are very much in alignment with my own dreams. They were just lacking the key word that is the essence of our unique approach, creativity, and I knew I wanted to connect with them.
As I read on, I was very happy to learn they have worked closely with the community and government in establishing the 215,000 acre Marine Protected Area called Long Island Marine Management Area, or LIMMA for short. LIMMA from the onset has engaged the locals and are looking at some very innovative ways to establish long term economic based solutions. This innovative approach immediately struck me.
By unfortunate chance it has been discovered that the traditional approach to funding and implementing an MPA is fraught with problems, often implemented through a top down approach. There is insufficient socialisation and people resent the laws and restrictions that they feel are implemented by outsiders, taking away their livelihoods. “ A careful consideration of the receptivity of the fishing communities to MPAs is fundamental for their long term success.” (Agardy et al. 2003).
Even a seemingly windfall success of large amounts of funding has its downfalls, with initial investments going into complex infrastructures that cannot be sustained longterm, either economically or by an untrained local community. In the long term, leaving these MPA areas underfunded with no way to implement the laws and a local community who are not invested. I saw this first hand at Bunaken where we installed ‘the love mermaids” last November. This MPA was once considered such a success but I saw first hand evidence that dynamite fishing was still occurring; the reefs were suffering a decline in health and even though large funding had paid for boats and staff to enforce fishing restrictions, they were too scared to go out and defend their seas.
In a conversation I later had with Joseph (once I had asked Robert Foos of the Terra Project to connect us), we discussed that with people so desperate and so much money able to be made in illegal fishing, It is very complicated to enforce fishing restrictions… and dangerous.
An MPA’s best asset is a vested local community; if they feel empowered and positioned to benefit from its success, there is an inherent and genuine love for their heritage that is hard to buy! I hate being told what to do so I can only imagine what it must feel like for a fisherman who’s family has fished for generations that now they must now stop.
The Economist William Russell Easterly who specialises in economic development wrote an interesting book called The White Man’s Burden (the title refers to Rudyard Kipling’s famous poem of the same name). Controversially, Easterly suggests that ’messianic do-good missions are ultimately modern reincarnations of the infamous colonial conceit.’ I have seen many so called experts imposing theories thought out in institutions far away from the sea!
I am not suggesting that grants should be extinguished. We certainly rely on them, but valuing the local community and their wisdom and love for their sea is essential. A fisherman understands when their livelihood is under threat and like any father wishing to feed his family, I think learning how to take control and feel like a decider in the fortune of their own destiny is something that when not permitted brings tears to my eyes.
I love the OCA’s Lionfish Fisheries Program which has been developed to bring direct and immediate economic opportunity for large numbers of the local community. The program shows that removal of lionfish is an effective management tool to protect and preserve the biodiversity of the Bahamas’ native fish life, and a much welcome and needed addition to the local economy! These are an invasive species that have come into the Caribbean from The Indo Pacific in the hull of ships in their Ballast water. Ballast water is water carried in ships’ ballast tanks to improve stability and balance. The water is taken into the hull or discharged when cargo is unloaded or loaded to maintain weight or when a ship needs extra stability in foul weather. When ships take on the ballast water, plants and animals that live in the ocean are also picked up. The cargo travels around the Globe and the same animals are then released into foreign seas. The Lionfish look stunning but are predators, and destroy the eco-system’s delicate balance in their new marine home. They are challenging to catch as they have toxic spines but they are actually incredibly good to eat. On my recent trip to Belize I came across a jewellery artist who was cleverly making stunning earrings and other items from the tails and fins.
OCA is also establishing a Coral Nursery Restoration Program, and this is where The Marine Foundation comes in. We bring a uniquely creative approach; Our Living sculpture in the Sea program has proven highly effective as an aspect to a successful marine management strategy. I feel it was by a seemingly unfortunate events that I was even able to conceive the Living Sculpture in the sea Program. During my research it was divers love of wreck diving that seeded the concept. Ships that have come to an untimely end and sunk to the bottom of our seas only to become thriving marine eco-systems.
‘The notion of serendipity is a common occurrence throughout the history of scientific innovation such as Alexander Fleming’s accidental discovery of penicillin in 1928. Innovations presented as examples of serendipity have an important characteristic: they were made by individuals able to “see bridges where others saw holes” and connect events creatively, based on the perception of a significant link.’
Our times are calling to each and every one of us to be creative and innovative. We desperately need to realise we have some major challenges to face in our beautiful world both above and below and I am thrilled to announce The Marine Foundation’s new partnership with Ocean Crest Alliance.
“I have noticed that even those who assert that everything is predestined and that we can change nothing about it still look both ways before they cross the street.” – Stephen Hawking
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Creature Feature: Dusky Shark

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
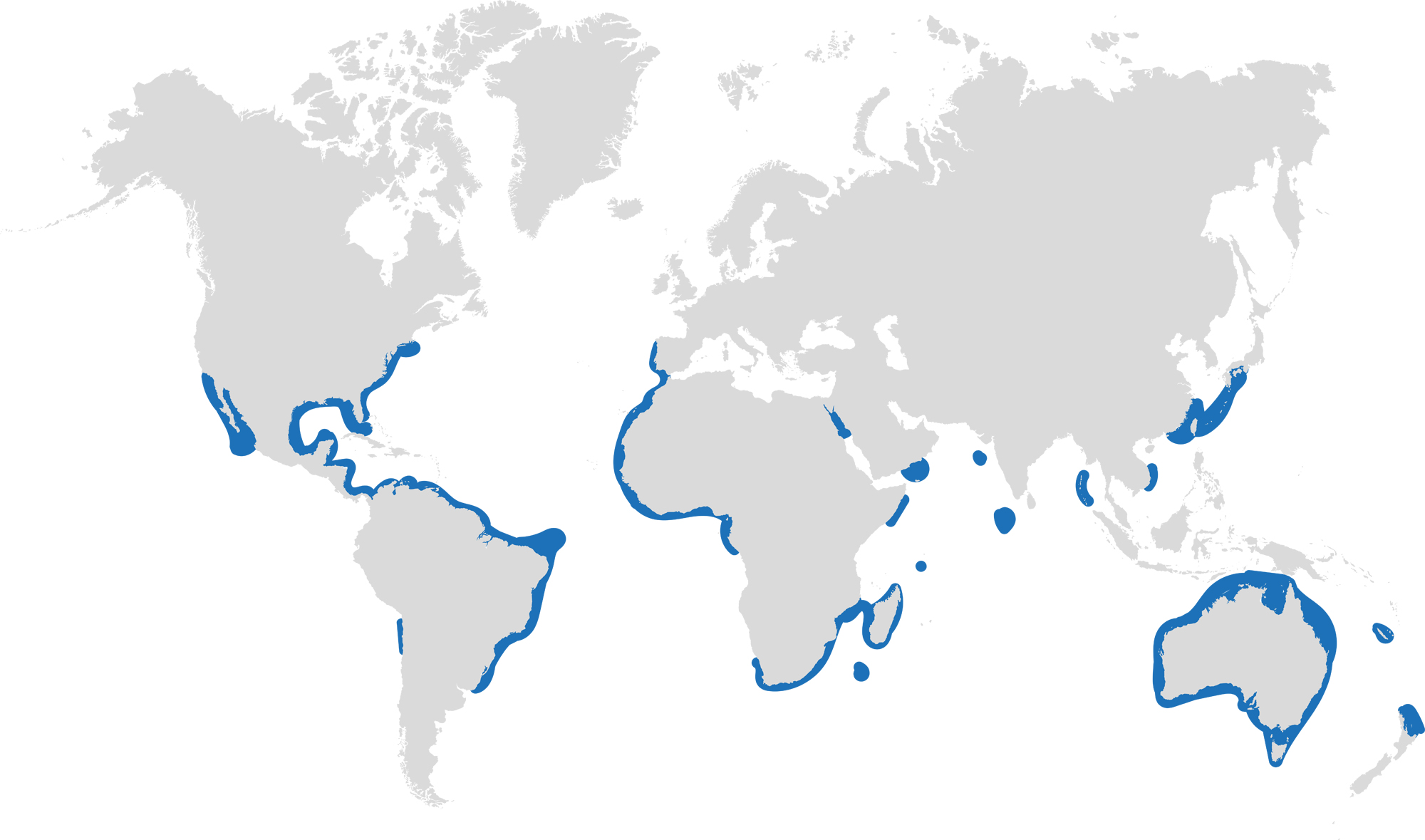
This month we’re taking a look at the Dusky Shark, a highly migratory species with a particularly slow growth rate and late age at maturity.
Dusky sharks are one of the largest species within the Carcharhinus genus, generally measuring 3 metres total length but able to reach up to 4.2 metres. They are grey to grey-brown on their dorsal side and their fins usually have dusky margins, with the darkest tips on the caudal fin.
Dusky Sharks can often be confused with other species of the Carcharhinus genus, particularly the Galapagos Shark (Carcharhinus galapagensis). They have very similar external morphology, so it can be easier to ID to species level by taking location into account as the two species occupy very different ecological niches – Galapagos Sharks prefer offshore seamounts and islets, whilst duskies prefer continental margins.
Hybridisation:
A 2019 study found that Dusky Sharks are hybridising with Galapagos Sharks on the Eastern Tropical Pacific (Pazmiño et al., 2019). Hybridisation is when an animal breeds with an individual of another species to produce offspring (a hybrid). Hybrids are often infertile, but this study found that the hybrids were able to produce second generation hybrids!
Long distance swimmers:
Dusky sharks are highly mobile species, undertaking long migrations to stay in warm waters throughout the winter. In the Northern Hemisphere, they head towards the poles in the summer and return southwards towards the equator in winter. The longest distance recorded was 2000 nautical miles!
Very slow to mature and reproduce:
The Dusky Shark are both targeted and caught as bycatch globally. We already know that elasmobranchs are inherently slow reproducers which means that they are heavily impacted by overfishing; it takes them so long to recover that they cannot keep up with the rate at which they are being fished. Dusky Sharks are particularly slow to reproduce – females are only ready to start breeding at roughly 20 years old, their gestation periods can last up to 22 months, and they only give birth every two to three years. This makes duskies one of the most vulnerable of all shark species.
The Dusky Shark is now listed on Appendix II of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS), but further action is required to protect this important species.
Scientific Name: Carcharhinus obscurus
Family: Carcharhinidae
Maximum Size: 420cm (Total Length)
Diet: Bony fishes, cephalopods, can also eat crustaceans, and small sharks, skates and rays
Distribution: Patchy distribution in tropical and warm temperate seas; Atlantic, Indo-Pacific and Mediterranean.
Habitat: Ranges from inshore waters out to the edge of the continental shelf.
Conservation status: Endangered.
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Images: Andy Murch
Diana A. Pazmiño, Lynne van Herderden, Colin A. Simpfendorfer, Claudia Junge, Stephen C. Donnellan, E. Mauricio Hoyos-Padilla, Clinton A.J. Duffy, Charlie Huveneers, Bronwyn M. Gillanders, Paul A. Butcher, Gregory E. Maes. (2019). Introgressive hybridisation between two widespread sharks in the east Pacific region, Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 136(119-127), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.04.013.
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
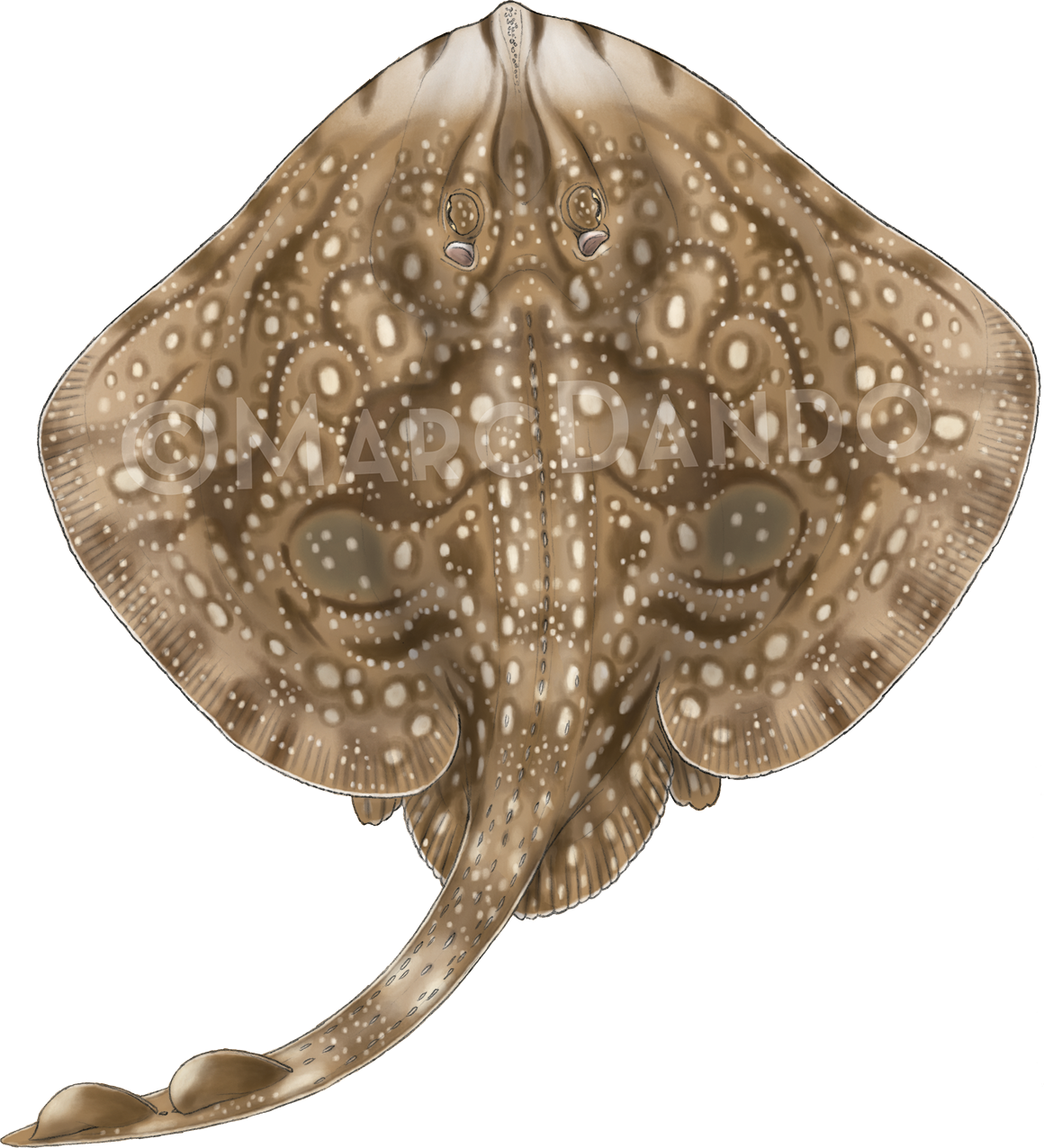
Creature Feature: Undulate Ray

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
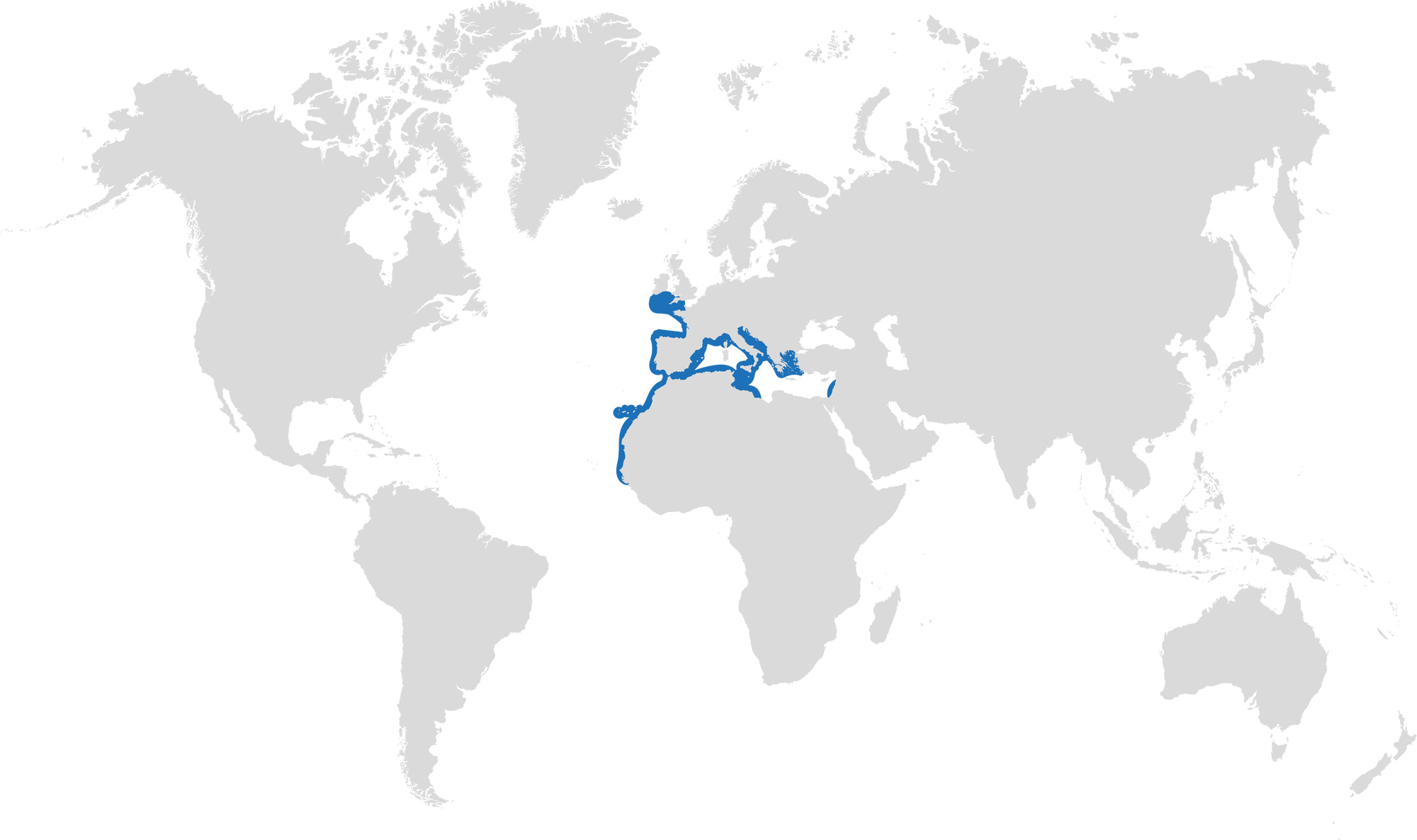
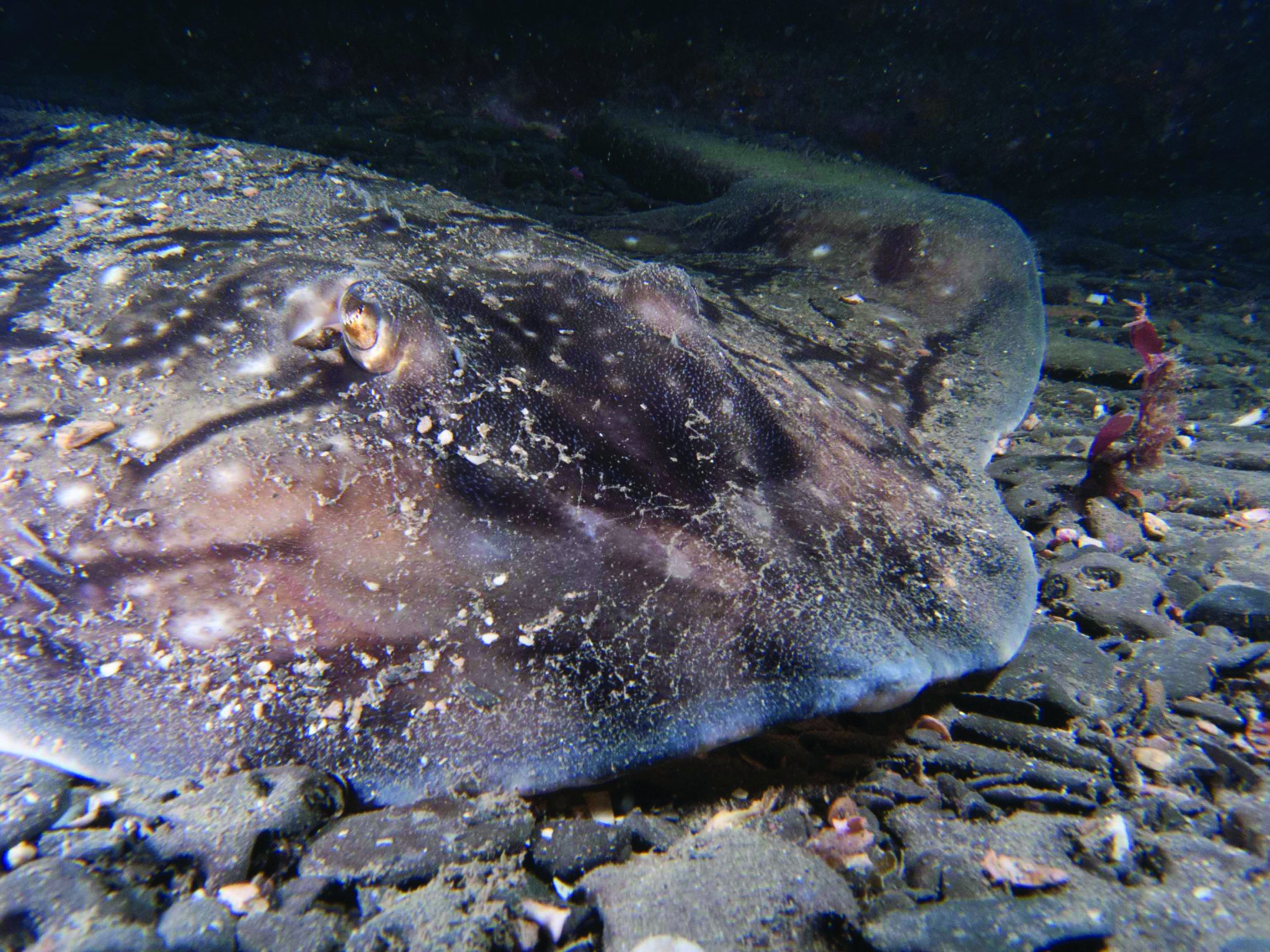
This month we’re looking at the Undulate Ray. Easily identified by its beautiful, ornate pattern, the Undulate Ray gets its name from the undulating patterns of lines and spots on its dorsal side.
This skate is usually found on sandy or muddy sea floors, down to about 200 m deep, although it is more commonly found shallower. They can grow up to 90 cm total length. Depending on the size of the individual, their diet can range from shrimps to crabs.
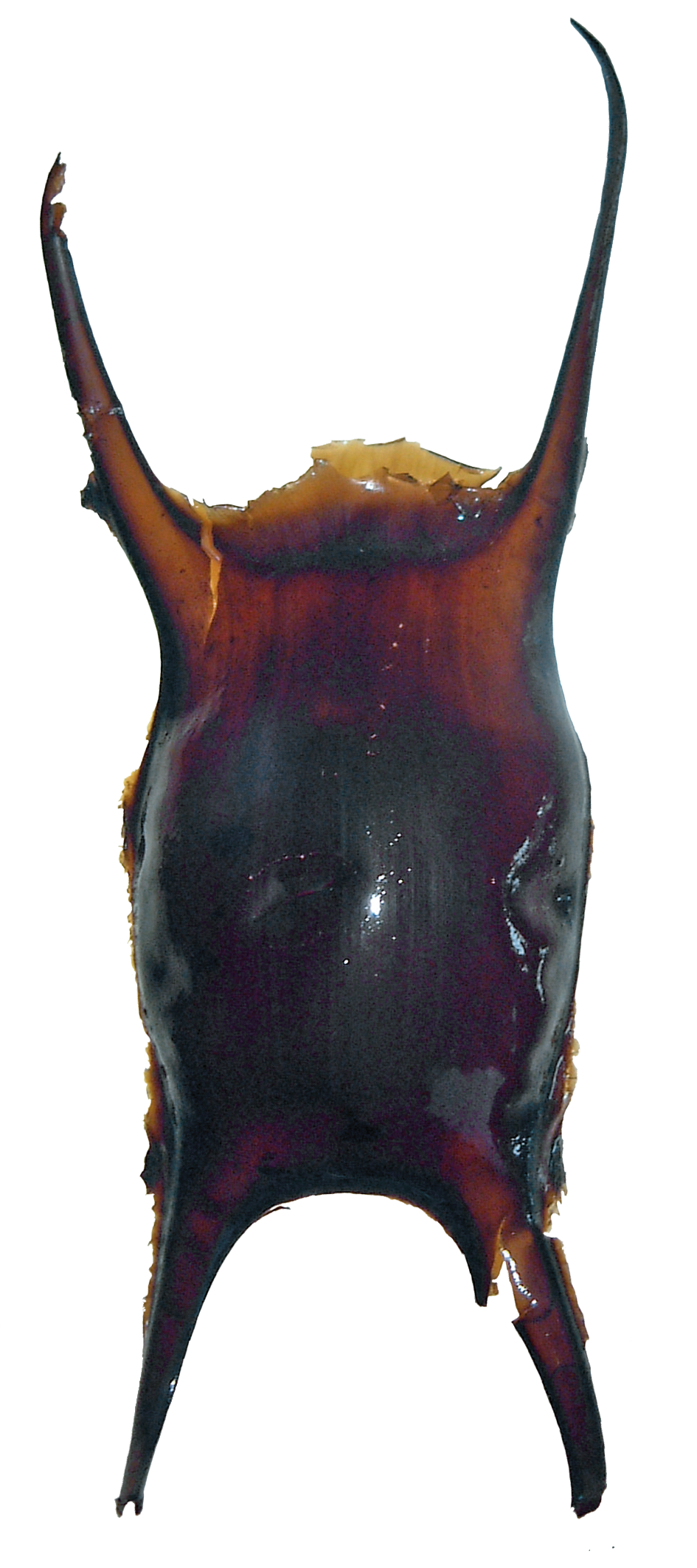
Although sometimes called the Undulate Ray, this is actually a species of skate, meaning that, as all true skates do, they lay eggs. The eggs are contained in keratin eggcases – the same material that our hair and nails are made up of! These eggcases are also commonly called mermaid’s purses and can be found washed up on beaches all around the UK. If you find one, be sure to take a picture and upload your find to the Great Eggcase Hunt – the Shark Trust’s flagship citizen science project.
It is worth noting that on the south coasts, these eggcases can be confused with those of the Spotted Ray, especially as they look very similar and the ranges overlap, so we sometimes informally refer to them as ‘Spundulates’.
Scientific Name: Raja undulata
Family: Rajidae
Maximum Size: 90cm (total length)
Diet: shrimps and crabs
Distribution: found around the eastern Atlantic and in the Mediterranean Sea.
Habitat: shelf waters down to 200m deep.
Conservation Status : As a commercially exploited species, the Undulate Ray is a recovering species in some areas. The good thing is that they have some of the most comprehensive management measures of almost any elasmobranch species, with both minimum and maximum landing sizes as well as a closed season. Additionally, targeting is entirely prohibited in some areas. They are also often caught as bycatch in various fisheries – in some areas they can be landed whilst in others they must be discarded.
IUCN Red List Status: Endangered
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Image Credits: Banner – Sheila Openshaw; Illustration – Marc Dando
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoHone your underwater photography skills with Alphamarine Photography at Red Sea Diving Safari in March
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Gear Reviews2 weeks ago
Gear Reviews2 weeks agoGEAR REVIEW – Revolutionising Diving Comfort: The Sharkskin T2 Chillproof Suit
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida
-

 Gear Reviews3 months ago
Gear Reviews3 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone