Marine Life & Conservation
New research shows 98% decrease in bottom-towed fishing in Marine Protected Area since ban
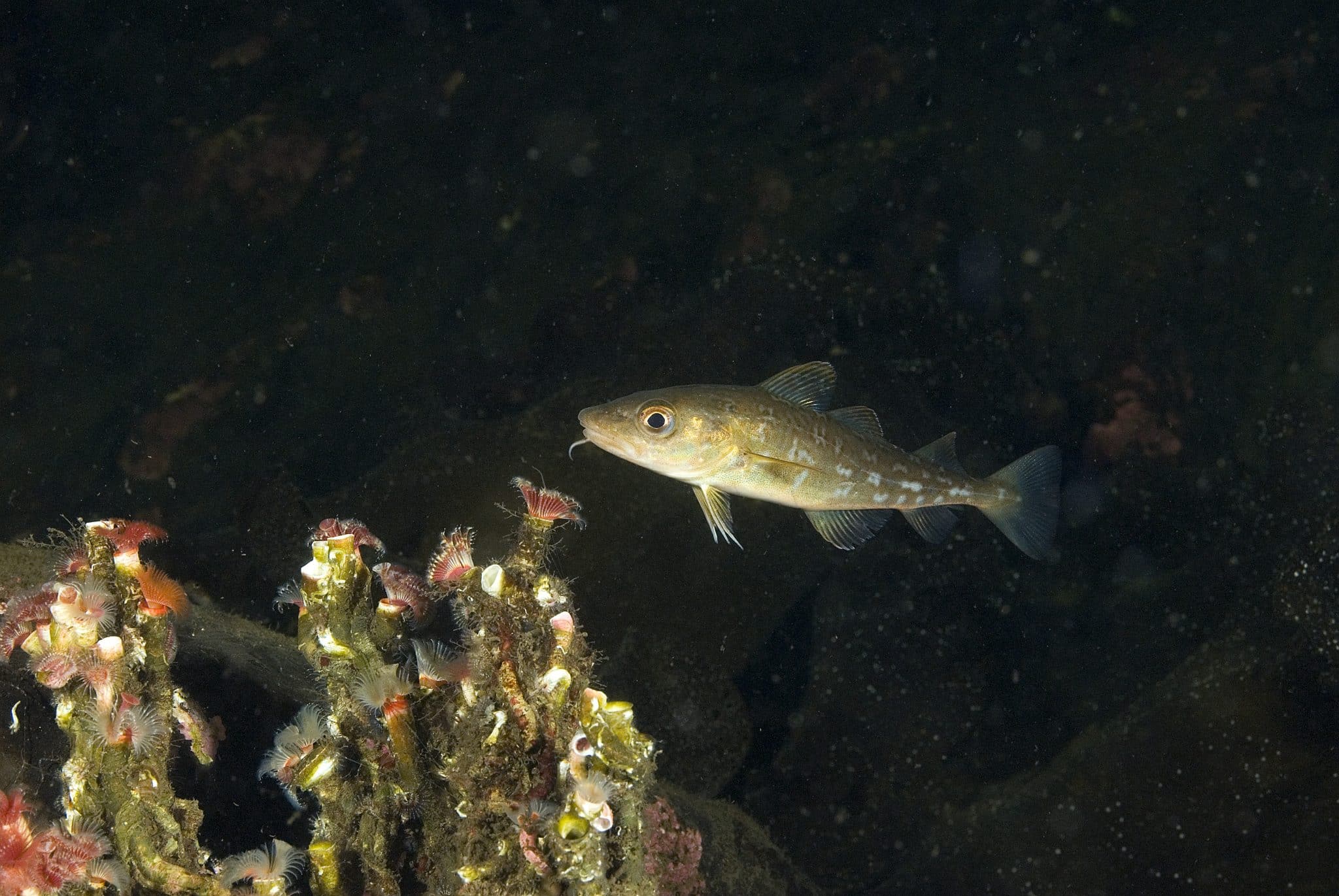

 New analysis from the Marine Conservation Society of fishing in Marine Protected Areas (MPA) has shown how effective byelaws banning bottom-towed fishing in MPAs can be.
New analysis from the Marine Conservation Society of fishing in Marine Protected Areas (MPA) has shown how effective byelaws banning bottom-towed fishing in MPAs can be.
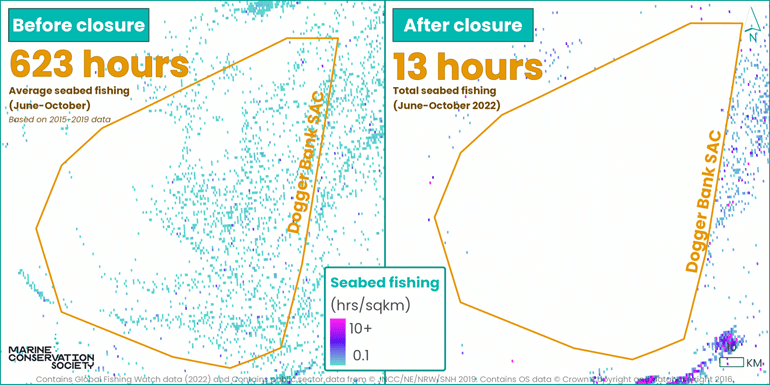
Between June and October, from 2015-2019, an average of 623 hours of bottom-towed fishing took place within the English Dogger Bank MPA. Located about 120 kilometres east of Hull, Dogger Bank has been heavily fished for decades.
However, between June and October 2022, since the ban has been in place, fishing activity dropped to just 13 hours; a 98% decrease in seabed fishing. This steep decline in fishing highlights how effective proper protections in these vulnerable and vital areas can be.
Jean-Luc Solandt, Principal MPA Specialist at the Marine Conservation Society said, “The huge reduction in seabed fishing we’ve identified shows how effective governments can be in protecting our ocean. This needs to be replicated across all offshore MPA’s to help recover fish stocks, provide sanctuary for marine life, and protect sensitive habitats from destruction.
“Our ocean has an incredible ability to recover when it’s given a chance. The Government must meet its target to fully protect all English offshore MPAs before 2024. The sooner this happens, the sooner our seas can restore themselves.”
To more accurately monitor fishing activity, the Marine Conservation Society is working with WWF and RSPB, as the Future Fisheries Alliance, to campaign for the Government to implement the use of Remote Electronic Monitoring with cameras on boats. Not only would this technology allow scientists to see where boats fish, but it would also help reduce bycatch and prevent overfishing. You can read the charity’s report here.
Protection of England’s offshore MPAs is critical for both climate and nature recovery. However, the UK Government has a long way to go to reach its promise of properly protecting all 40 of England’s offshore MPA sites by 2024.
Sandy Luk, Marine Conservation Society CEO, said: “With the UN Conference on Biodiversity (COP15) currently taking place, world leaders must turn their attentions to urgently protecting our planet from nature loss. If we’re to achieve 30% of land and sea protected by 2030, our ocean cannot be forgotten. When our ocean is protected, habitats can recover and support the incredible diversity of life in our seas.”
At five times the size of the Lake District National Park, Dogger Bank was once abundant in species such as halibut, cod and angelshark, whose populations are currently struggling in UK waters. There is hope that, with these new protections in place, these species and many more will be able to recover and thrive.
However, the charity’s evidence shows that fishing efforts continue to be high in adjacent Dutch and German sections of the Dogger Bank MPA. Whilst the ban in English waters of the MPA will encourage local wildlife stocks to recover, the charity’s data does show intense fishing elsewhere.
To address this, the Marine Conservation Society continues to work with a coalition of European NGOs, Seas at Risk, fighting to protect all of Europe’s MPAs from the damage done by bottom trawling. In particular, the charity is working with Dutch and German colleagues to ensure that protection of their part of the Dogger Bank follows the UK protection.
For more information visit the Marine Conservation Society website
Header Image: Paul Naylor
Marine Life & Conservation
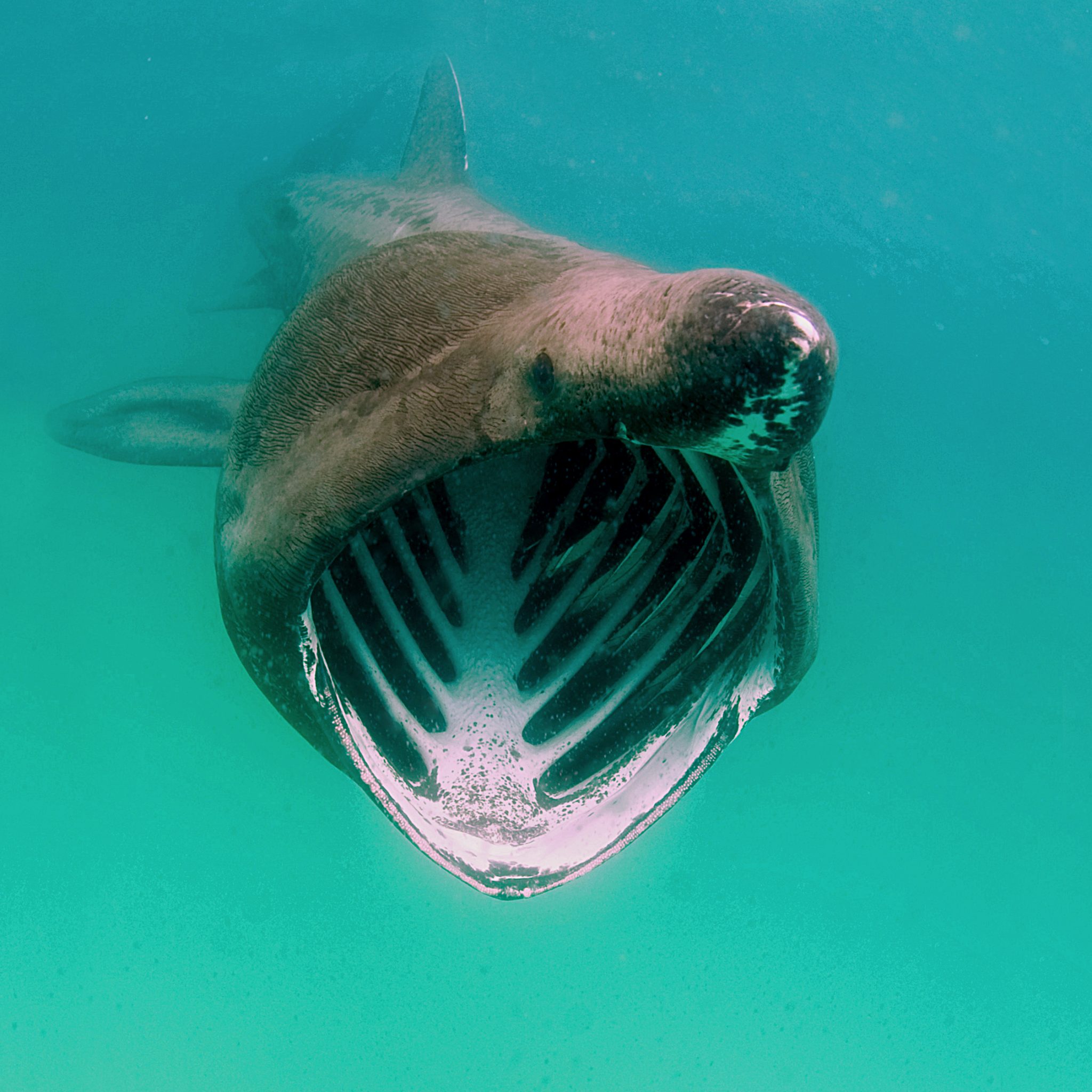
Double Bubble for Basking Sharks

 The Shark Trust is excited to announce that, for two more days only, all donations, large or small, will be doubled in the Big Give Green Match Fund!
The Shark Trust is excited to announce that, for two more days only, all donations, large or small, will be doubled in the Big Give Green Match Fund!
Donate to Basking in Nature: Sighting Giants
The Shark Trust is hoping to raise £10k which will be doubled to £20k. This will go towards Basking in Nature: Sighting Giants. And they need YOUR help to reach they’re goal.
The Shark Trust’s citizen science project is to monitor and assess basking sharks through sightings; encouraging data collection, community engagement, and promoting nature accessibility. This initiative aims to enhance health and wellbeing by fostering a deeper connection with British Sharks.
Campaign Aims
- Increase citizen science reporting of Basking Sharks and other shark sightings to help inform shark and ray conservation.
- Provide educational talks about the diverse range of sharks and rays in British waters and accessible identification guides!
- Create engaging and fun information panels on how to ID the amazing sharks and rays we have on our doorstep! These can be used on coastal paths around the Southwest. With activities and information on how you can make a difference for sharks and rays!
- Promote mental wellbeing through increasing time in nature and discovering the wonders beneath the waves!
Donate, and double your impact. Click Here
Marine Life & Conservation
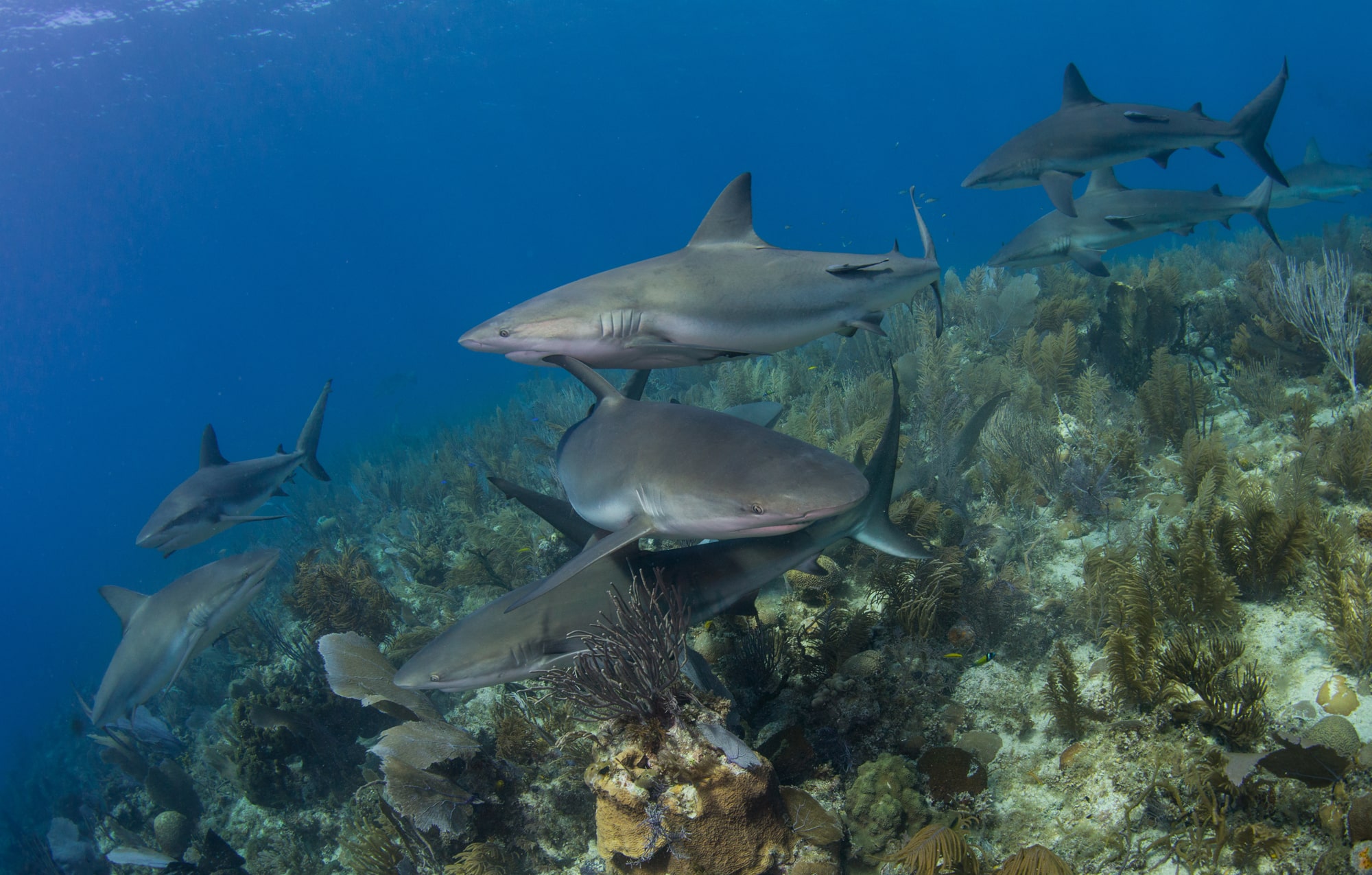
Leading UK-based shark conservation charity, the Shark Trust, is delighted to announce tour operator Diverse Travel as a Corporate Patron

 Corporate Patrons provide a valuable boost to the work of The Shark Trust. The Trust team works globally to safeguard the future of sharks, and their close cousins, the skates and rays, engaging with a global network of scientists, policymakers, conservation professionals, businesses and supporters to further shark conservation.
Corporate Patrons provide a valuable boost to the work of The Shark Trust. The Trust team works globally to safeguard the future of sharks, and their close cousins, the skates and rays, engaging with a global network of scientists, policymakers, conservation professionals, businesses and supporters to further shark conservation.
Specialist tour operator Diverse Travel has operated since 2014 and is committed to offering its guests high quality, sustainable scuba diving holidays worldwide. Working together with the Shark Trust will enable both organisations to widen engagement and encourage divers and snorkellers to actively get involved in shark conservation.
“Sharks are truly at the heart of every diver and at Diverse Travel, we absolutely share that passion. There is nothing like seeing a shark in the wild – it’s a moment that stays with you forever!” says Holly Bredin, Sales & Marketing Manager, Diverse Travel.
“We’re delighted to celebrate our 10th year of business by becoming a Corporate Patron of the Shark Trust. This is an exciting partnership for Diverse and our guests. We will be donating on behalf of every person who books a holiday with us to contribute towards their vital shark conservation initiatives around the world. We will also be working together with the Trust to inspire divers, snorkellers and other travellers to take an active role – at home and abroad – in citizen science projects and other activities.”
Paul Cox, CEO of The Shark Trust, said:
“It’s an exciting partnership and we’re thrilled to be working with Diverse Travel to enable more divers and travellers to get involved with sharks and shark conservation. Sharks face considerable conservation challenges but, through collaboration and collective action, we can secure a brighter future for sharks and their ocean home. This new partnership takes us one more valuable step towards that goal.”
For more information about the Shark Trust visit their website here.
For more about Diverse Travel click here.
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoHone your underwater photography skills with Alphamarine Photography at Red Sea Diving Safari in March
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Gear Reviews2 weeks ago
Gear Reviews2 weeks agoGEAR REVIEW – Revolutionising Diving Comfort: The Sharkskin T2 Chillproof Suit
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida
-

 Gear Reviews3 months ago
Gear Reviews3 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone