Marine Life & Conservation
Diving with British Marine Life: The Grey Triggerfish
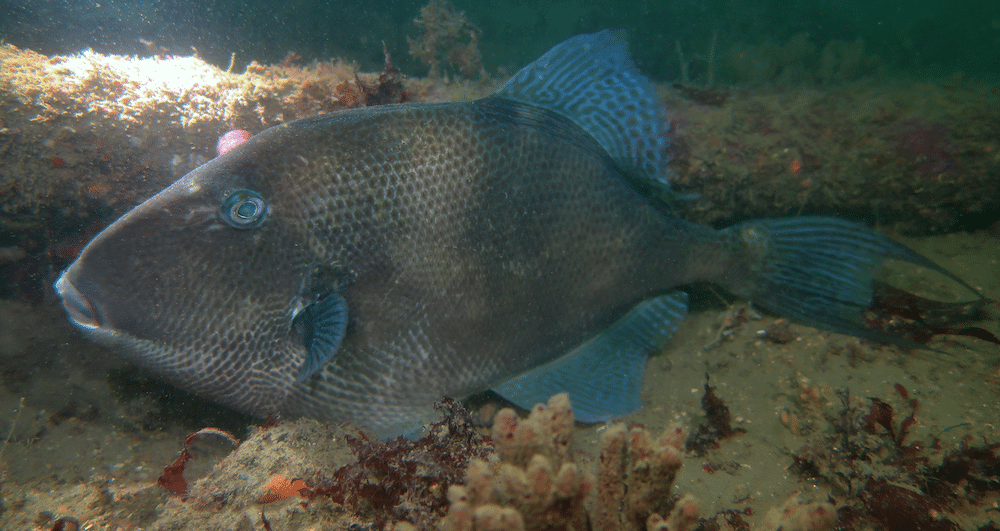
Part 2 of a new series by blogger Georgie Bull…
Before starting University last September, I dove Chesil Cove in the hope that I could get a glimpse of a triggerfish on the Royal Adelaide wreck. Grey triggerfish (Balistes capriscus) are seasonal visitors to our waters and are known to congregate on the wreck at a similar time each year. They are often fished off or battered by storms fairly rapidly, so sightings are temporally confined too.
For anyone unfamiliar with Chesil, large pebble ridges create a wonderful pre and post dive work out for any diver keen enough to get in. Jon Bunker (Instagram: @jon_bunker) my Dorset dive buddy did a fantastic job of locating the wreck, and we had a very pleasant dive overall. Jon has invited me along on lots of his diving antics, and he’s the main reason I have so many photos to share.
On the dive we saw the likes of jewel anemones, congers, and a wonderful variety of wrasse. Without a trigger in sight, a couple of tompot blennies fighting one another became the main highlight. After the dive we spoke to a recreational angler on the beach, who mentioned he’d caught (and returned) a triggerfish while we were in the water. We were so close to a sighting!
Once I’d recovered from the pebble ridges and put my kit away, I accepted that I’d have to wait until next year.
Fast forward to a few weeks time, and the University of Plymouth’s Scuba Society were running their first shore club dive at Firestone Bay. I joined in, hoping to see a few different tunicates or echinoderms that I may not see so often in Lyme Bay. Instead, I was greeted with a large and relatively healthy triggerfish sat on the substrate. It turns out, I didn’t need to scale pebble ridges or use Jon’s impressive navigation skills to have an encounter with this species!
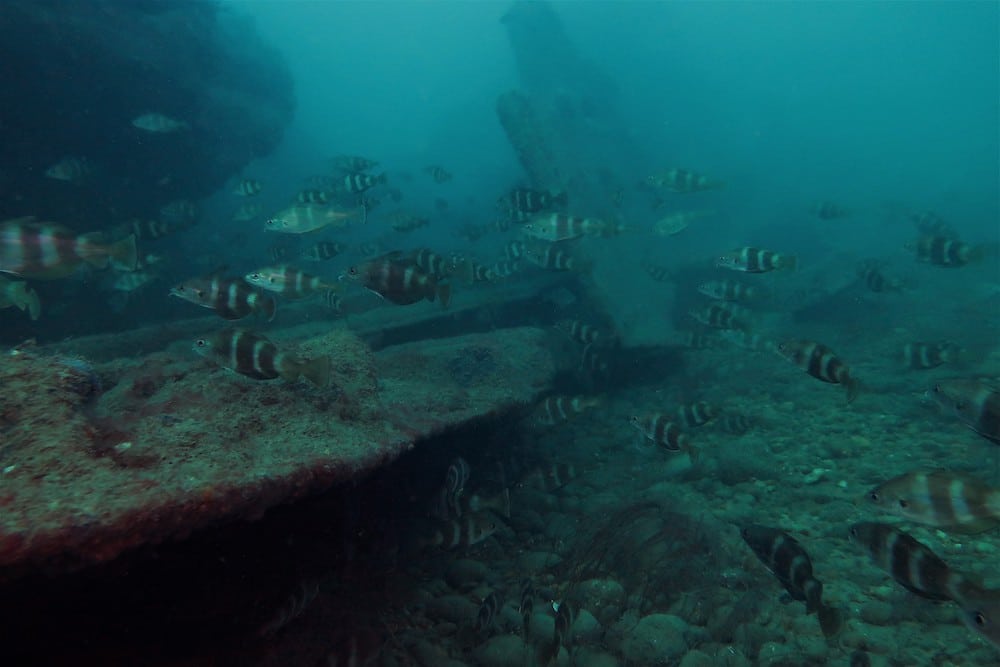

Profile
Triggerfish have defensive spines on their dorsal which are used to avoid predation, but also wedge themselves into crevices outside of harms way. Like their namesake suggests, the erection of their largest spine is triggered by the depression of a smaller spine closer to their head. Triggerfish are also known for aggressive behaviour, as they are particularly territorial over their nests.
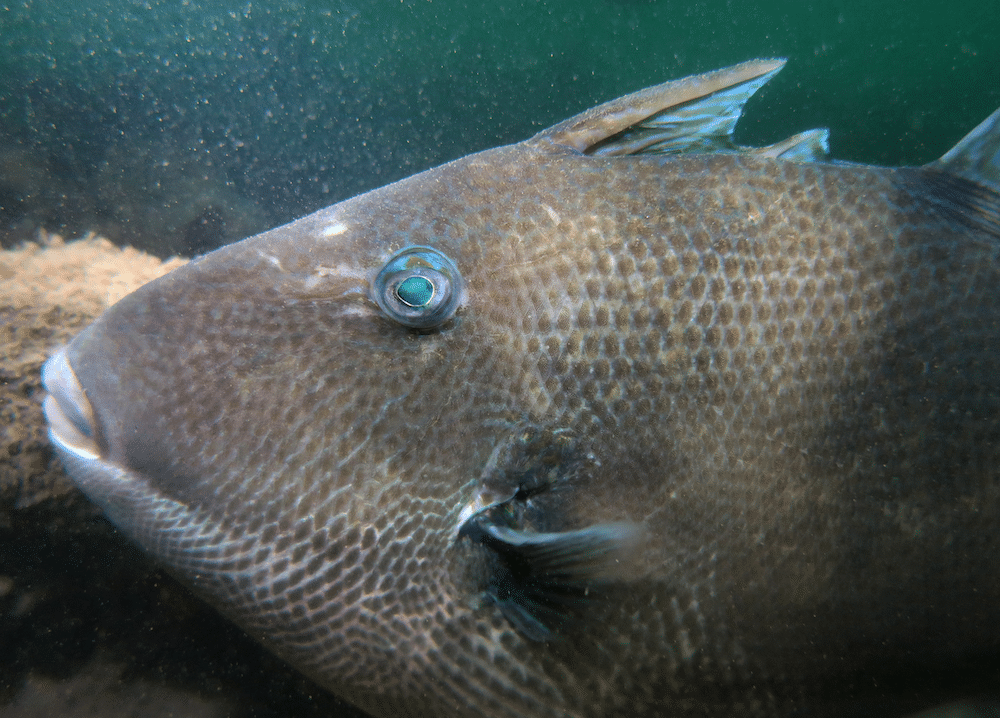

Grey triggerfish are a Southern European species, and are valued by anglers both commercially and recreationally. This value has resulted in them being categorised as ‘vulnerable’ by IUCN. They are also the only triggerfish encountered in UK waters, with the other 39 species of triggerfish found typically in warmer waters.
Literature
In recent years, it’s been reported that grey triggerfish are becoming increasingly common in the UK. We have plenty of evidence to suggest that our oceans are warming, and we know from previous instances that migratory pelagic fish like the grey triggerfish are capable of shifting their distribution in response to environmental change.
In 1930, a grey triggerfish was recorded in St Malo, France; by the 1990s, they were being described as common in Jersey. In southern parts of the UK grey triggerfish sightings were unheard of too, up until the early 2000s. They are now regarded as common in some areas (like Chesil) at certain times of the year. It would be interesting to see this shift quantified more and understand if the increased catch rates may also be influenced by changing fishing methods and intensity.

References:
- https://www.fisheries.noaa.gov/species/gray-triggerfish
- https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/193736/97662794#threats
- https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-jersey-46591920
- https://www.gov.je/SiteCollectionDocuments/Government%20and%20administration/R%20Non-native%20Marine%20Species%20in%20the%20Channel%20Islands%2020171222%20DM.pdf
Hear more from Georgie here: https://georgiebullphotography.home.blog/
Marine Life & Conservation
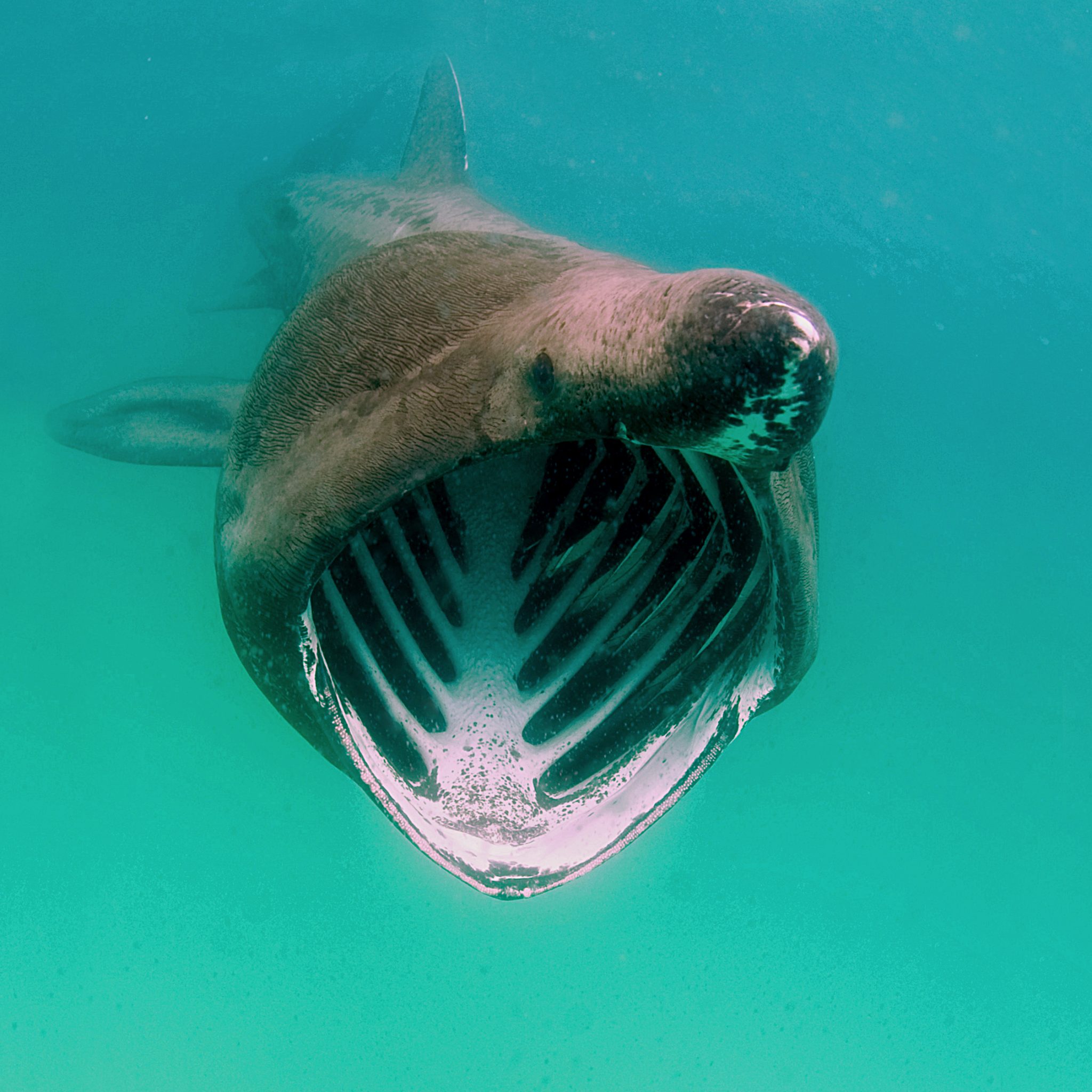
Double Bubble for Basking Sharks

 The Shark Trust is excited to announce that, for two more days only, all donations, large or small, will be doubled in the Big Give Green Match Fund!
The Shark Trust is excited to announce that, for two more days only, all donations, large or small, will be doubled in the Big Give Green Match Fund!
Donate to Basking in Nature: Sighting Giants
The Shark Trust is hoping to raise £10k which will be doubled to £20k. This will go towards Basking in Nature: Sighting Giants. And they need YOUR help to reach they’re goal.
The Shark Trust’s citizen science project is to monitor and assess basking sharks through sightings; encouraging data collection, community engagement, and promoting nature accessibility. This initiative aims to enhance health and wellbeing by fostering a deeper connection with British Sharks.
Campaign Aims
- Increase citizen science reporting of Basking Sharks and other shark sightings to help inform shark and ray conservation.
- Provide educational talks about the diverse range of sharks and rays in British waters and accessible identification guides!
- Create engaging and fun information panels on how to ID the amazing sharks and rays we have on our doorstep! These can be used on coastal paths around the Southwest. With activities and information on how you can make a difference for sharks and rays!
- Promote mental wellbeing through increasing time in nature and discovering the wonders beneath the waves!
Donate, and double your impact. Click Here
Marine Life & Conservation
Leading UK-based shark conservation charity, the Shark Trust, is delighted to announce tour operator Diverse Travel as a Corporate Patron

 Corporate Patrons provide a valuable boost to the work of The Shark Trust. The Trust team works globally to safeguard the future of sharks, and their close cousins, the skates and rays, engaging with a global network of scientists, policymakers, conservation professionals, businesses and supporters to further shark conservation.
Corporate Patrons provide a valuable boost to the work of The Shark Trust. The Trust team works globally to safeguard the future of sharks, and their close cousins, the skates and rays, engaging with a global network of scientists, policymakers, conservation professionals, businesses and supporters to further shark conservation.
Specialist tour operator Diverse Travel has operated since 2014 and is committed to offering its guests high quality, sustainable scuba diving holidays worldwide. Working together with the Shark Trust will enable both organisations to widen engagement and encourage divers and snorkellers to actively get involved in shark conservation.
“Sharks are truly at the heart of every diver and at Diverse Travel, we absolutely share that passion. There is nothing like seeing a shark in the wild – it’s a moment that stays with you forever!” says Holly Bredin, Sales & Marketing Manager, Diverse Travel.
“We’re delighted to celebrate our 10th year of business by becoming a Corporate Patron of the Shark Trust. This is an exciting partnership for Diverse and our guests. We will be donating on behalf of every person who books a holiday with us to contribute towards their vital shark conservation initiatives around the world. We will also be working together with the Trust to inspire divers, snorkellers and other travellers to take an active role – at home and abroad – in citizen science projects and other activities.”
Paul Cox, CEO of The Shark Trust, said:
“It’s an exciting partnership and we’re thrilled to be working with Diverse Travel to enable more divers and travellers to get involved with sharks and shark conservation. Sharks face considerable conservation challenges but, through collaboration and collective action, we can secure a brighter future for sharks and their ocean home. This new partnership takes us one more valuable step towards that goal.”
For more information about the Shark Trust visit their website here.
For more about Diverse Travel click here.
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoHone your underwater photography skills with Alphamarine Photography at Red Sea Diving Safari in March
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs2 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida
-

 Gear Reviews3 months ago
Gear Reviews3 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone
-

 Gear Reviews2 weeks ago
Gear Reviews2 weeks agoGEAR REVIEW – Revolutionising Diving Comfort: The Sharkskin T2 Chillproof Suit



















