Marine Life & Conservation
Bluefin Tuna Back in UK Waters
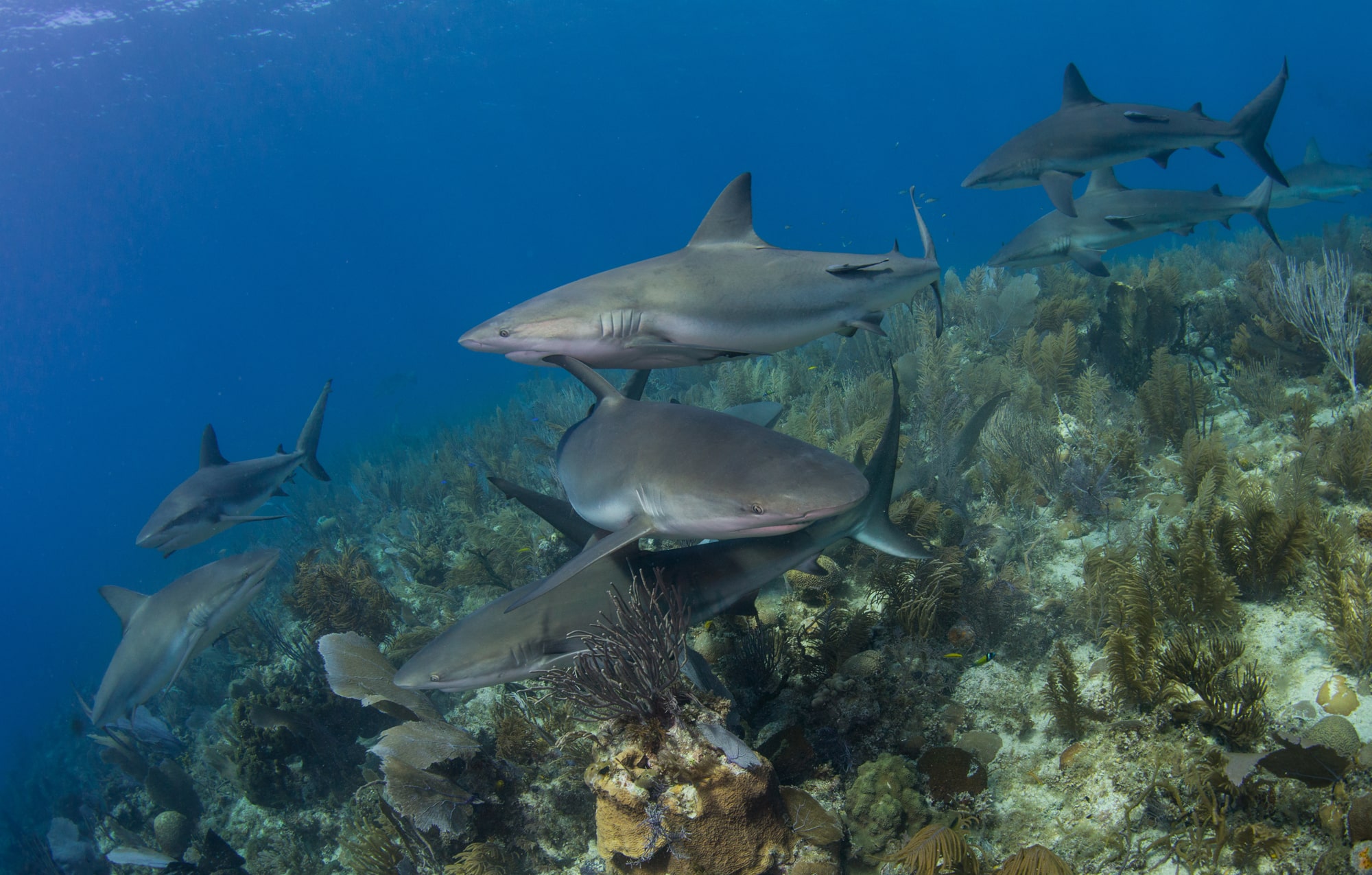
Bluefin Tuna are back in the seas around the UK after decades of decline and absence. It has been proposed this could be due to warming seas rather than species recovery. After generations of overfishing, pollution and lack of food, it is astonishing how resilient these Tuna and other species are in their survival and wondrous that they should be able to return at all. What is not so wondrous is human nature. The Angling Trust are now petitioning for the protection status for these fish to be changed to establish a catch and release licensed fishery in what seems to me to be a case of self gratification and financial profit over sensible environmental concern.
New research by Dr Robin Faillettaz from the University of Lille (France), his French co-workers Drs Gregory Beaugrand and Eric Goberville, and Dr Richard Kirby from the UK – as part of the scientific programme CLIMIBIO (www.climibio.univ-lille.fr/) – has revealed that warmer seas can explain the reappearance of tuna around the UK.
Dr Richard Kirby says “Bluefin tuna have been extensively overfished during the 20th century and the stock was close to its lowest in 1990, a fact that further indicates the recent changes in distribution are most likely environmentally driven rather than due to fisheries management and stock recovery. Before we further exploit bluefin tuna either commercially or recreationally for sport fishing, we should consider whether it would be better to protect them by making the UK’s seas a safe space for one of the ocean’s most endangered top fish.”
I asked him for more information and he sent me the following report:
“Bluefin tuna are back in the sea around the UK after decades of absence and a new study says that warming seas can explain why. Bluefin tuna are one of the biggest, most valuable, most sought after, and most endangered fish in the oceans. Sport fishermen excited at the prospect of catching a fish that can grow to over 900kg have already launched a UK campaign to allow recreational fishing for one of game fishing’s top targets. But should we catch and exploit this endangered species or should we make UK waters a safe space for this incredible fish? Important questions to answer are why has this endangered fish suddenly returned to the UK after an absence of nearly 40 years and are bluefin tuna now more abundant or have they just changed in their distribution?
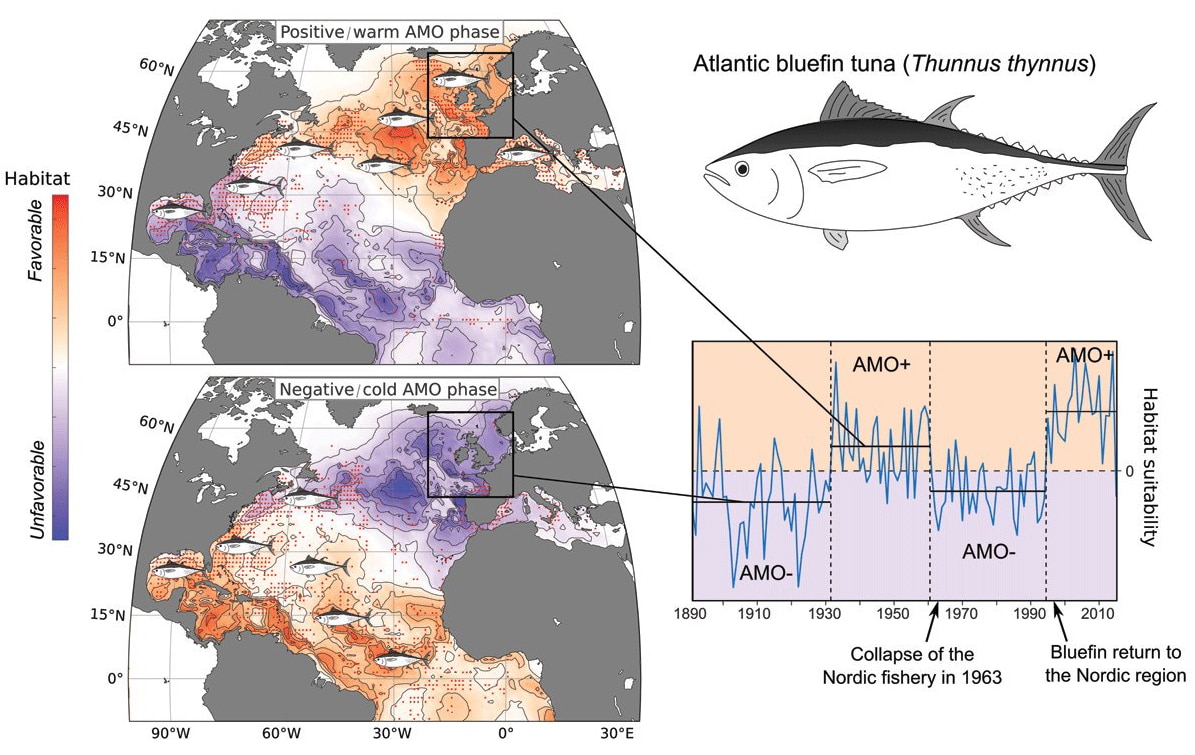
CLIMIBIO’s research shows that the disappearance and reappearance of bluefin tuna in European waters can be explained by hydroclimatic variability due to the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), a northern hemisphere climatic oscillation that increases the sea temperature when in its positive phase like it is now.
To come to their conclusion, the scientists examined the changing abundance and distribution of bluefin tuna in the Atlantic Ocean over the last 200 years. They combined two modelling approaches, focusing on the intensity of the catches over time and on the distribution of the fish’s occurrence, i.e. when it was observed or caught. Their results are unequivocal: the AMO is the major driver influencing both the abundance and the distribution of the bluefin tuna.
The Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation affects complex atmospheric and oceanographic processes in the northern hemisphere including the strength and direction of ocean currents, drought on land, and even the frequency and intensity of Atlantic hurricanes. Approximately every 60 to 120 years the AMO switches between positive and negative phases to create a basin-scale shift in the distribution of Atlantic bluefin tuna. During a warm AMO phase, such as since the mid-1990s, bluefin tuna forage as far north as Greenland, Iceland and Norway and almost disappear from the central and south Atlantic. During its previous warm phase – at the middle of the 20th century – the North Sea had a bluefin tuna fishery that rivalled the Mediterranean and the Bluefin Tunny sportfishing club – known worldwide – was founded in Scarborough. However, during a cold AMO phase, such as that between 1963-1995, bluefin tuna move south and are more frequently found in the western, central, and even southern Atlantic, with few fish caught above 45°N. Dr Faillettaz says that “The ecological effects of the AMO have long been overlooked and our results represent a breakthrough in understanding the history of bluefin tuna in the North Atlantic.”
In fact, the most striking example of the effect of the AMO on bluefin tuna is the sudden collapse of the large Nordic bluefin tuna fishery in 1963. The collapse coincides perfectly with the most rapid known switch in the AMO from its highest to its lowest recorded value in only two years. After that switch tuna also vacated the North Sea, and the conditions remained unfavourable for bluefin tuna in the northern Atlantic until the late 1990s when it started to reappear around the UK.
The scientists expect that bluefin tuna will continue to migrate to the UK and North Sea waters every year until the AMO reverses to a cold phase. However, they also highlight that the additional effect of global warming on sea temperatures will make the future response of bluefin tuna to changes in the AMO uncertain. Further to the effect of the AMO on where and when bluefin tuna occur in the Atlantic, the study also found that this climatic oscillation influences their recruitment, i.e., how many juvenile bluefin tuna grow to become adults.
Dr Faillettaz said that “when water temperature increases during a positive AMO, bluefin tuna move further north. However, the most positive phases of the AMO also have a detrimental effect upon recruitment in the Mediterranean Sea, which is currently the most important spawning ground, and that will affect adult abundance a few years later. If the AMO stays in a highly positive phase for several years, we may encounter more bluefin tuna in our waters, but the overall population could actually be decreasing.”
Consequently, Dr Beaugrand warns that “global warming superimposed upon the AMO is likely to alter the now familiar patterns we have seen in bluefin tuna over the last four centuries. Increasing global temperatures may cause Atlantic bluefin tuna to persist in the Nordic region and shrink the species distribution in the Atlantic Ocean, and it may even cause the fish to disappear from the Mediterranean Sea, which is currently the most important fishery.”
Dr Goberville also raises another important observation saying that “because bluefin tuna are so noticeable, they are also an indicator of current temperature driven changes in our seas that are occurring throughout the marine food chain, from the plankton to fish and seabirds”.
The Atlantic bluefin tuna fishery indeed encompasses most of the problems seen in fisheries around the world, including fleet overcapacity and political mismanagement; the species’ distribution crosses exclusive economic zones and spans international, open-access waters (i.e. the entire North Atlantic, from the Mediterranean Sea to the Gulf of Mexico). Added to that, the long-term fluctuation in Atlantic bluefin tuna abundance was hitherto understood poorly, which represents a fundamental gap in this fish’s sustainable management.
Dr Kirby says that “we have shown why bluefin tuna occur when and where in the North Atlantic and what may influence their recruitment and abundance, and this is fundamental to understanding the management of a fish that is endangered due to overfishing. Bluefin tuna have been extensively overfished during the 20th century and the stock was close to its lowest in 1990, a fact that further indicates the recent changes in distribution are most likely environmentally driven rather than due to fisheries management and stock recovery.”
Before we further exploit bluefin tuna either commercially or recreationally for sport fishing, we should consider whether it would be better to protect them by making the UK’s seas a safe space for one of the ocean’s most endangered top fish.”
The lead author Dr Faillettaz concludes: “Our results demonstrate that local changes in Atlantic bluefin tuna abundance can reflect large-scale shifts in a species’ distribution that are unrelated to improvements or worsening of a stock’s abundance. In this context we hope that our study will highlight the need to consider the environment when planning the sustainable management of all migratory fish species.”
For further information
Dr Richard Kirby
E-mail: Richard.Kirby@planktonpundit.org
Dr Robin Faillettaz
E-mail: Robin.Faillettaz@univ-lille1.fr
For further reading
Could big-game fishing return to the UK?
Warming Seas linked to bluefin tuna surge in UK waters
Marine Life & Conservation
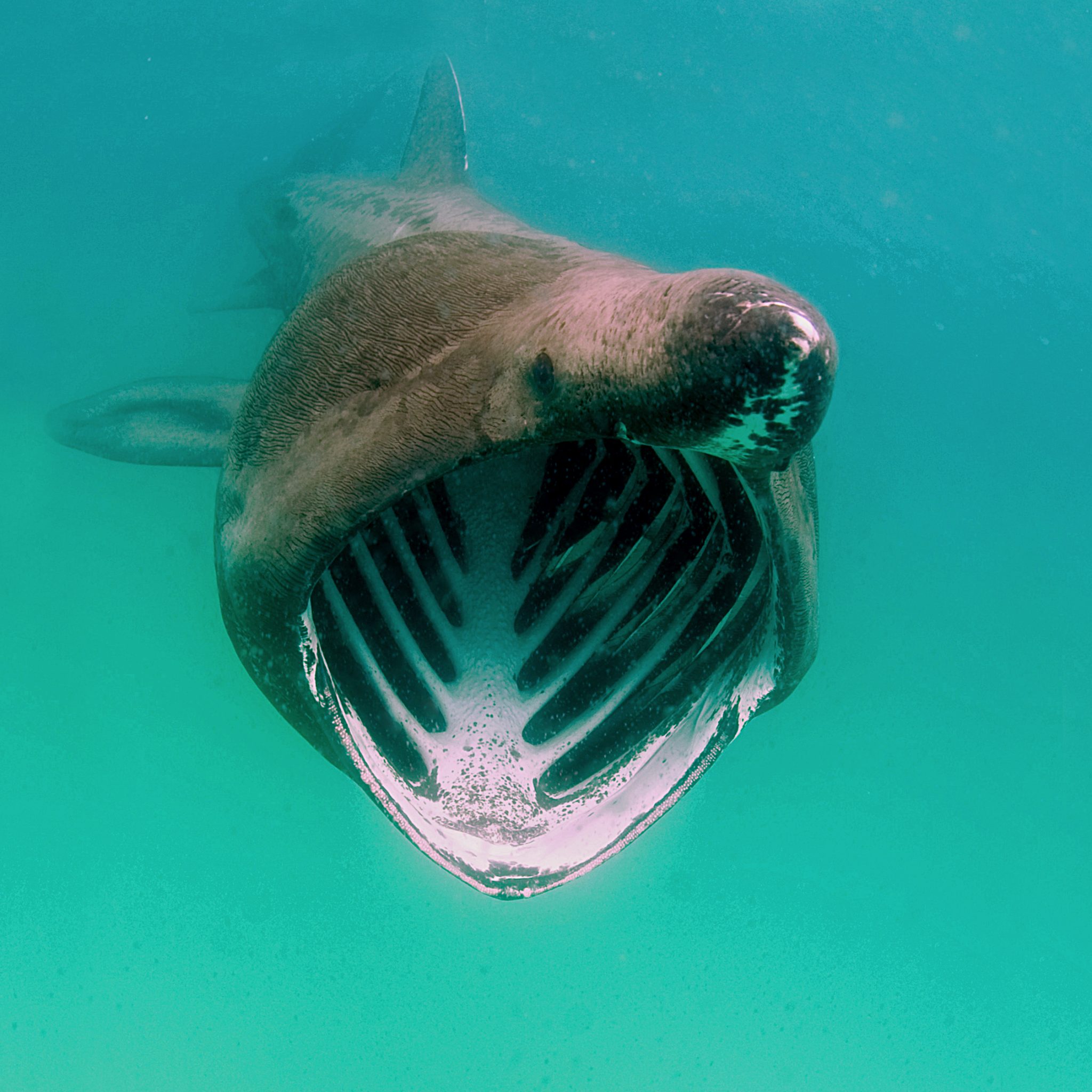
Double Bubble for Basking Sharks

 The Shark Trust is excited to announce that, for two more days only, all donations, large or small, will be doubled in the Big Give Green Match Fund!
The Shark Trust is excited to announce that, for two more days only, all donations, large or small, will be doubled in the Big Give Green Match Fund!
Donate to Basking in Nature: Sighting Giants
The Shark Trust is hoping to raise £10k which will be doubled to £20k. This will go towards Basking in Nature: Sighting Giants. And they need YOUR help to reach they’re goal.
The Shark Trust’s citizen science project is to monitor and assess basking sharks through sightings; encouraging data collection, community engagement, and promoting nature accessibility. This initiative aims to enhance health and wellbeing by fostering a deeper connection with British Sharks.
Campaign Aims
- Increase citizen science reporting of Basking Sharks and other shark sightings to help inform shark and ray conservation.
- Provide educational talks about the diverse range of sharks and rays in British waters and accessible identification guides!
- Create engaging and fun information panels on how to ID the amazing sharks and rays we have on our doorstep! These can be used on coastal paths around the Southwest. With activities and information on how you can make a difference for sharks and rays!
- Promote mental wellbeing through increasing time in nature and discovering the wonders beneath the waves!
Donate, and double your impact. Click Here
Marine Life & Conservation
Leading UK-based shark conservation charity, the Shark Trust, is delighted to announce tour operator Diverse Travel as a Corporate Patron

 Corporate Patrons provide a valuable boost to the work of The Shark Trust. The Trust team works globally to safeguard the future of sharks, and their close cousins, the skates and rays, engaging with a global network of scientists, policymakers, conservation professionals, businesses and supporters to further shark conservation.
Corporate Patrons provide a valuable boost to the work of The Shark Trust. The Trust team works globally to safeguard the future of sharks, and their close cousins, the skates and rays, engaging with a global network of scientists, policymakers, conservation professionals, businesses and supporters to further shark conservation.
Specialist tour operator Diverse Travel has operated since 2014 and is committed to offering its guests high quality, sustainable scuba diving holidays worldwide. Working together with the Shark Trust will enable both organisations to widen engagement and encourage divers and snorkellers to actively get involved in shark conservation.
“Sharks are truly at the heart of every diver and at Diverse Travel, we absolutely share that passion. There is nothing like seeing a shark in the wild – it’s a moment that stays with you forever!” says Holly Bredin, Sales & Marketing Manager, Diverse Travel.
“We’re delighted to celebrate our 10th year of business by becoming a Corporate Patron of the Shark Trust. This is an exciting partnership for Diverse and our guests. We will be donating on behalf of every person who books a holiday with us to contribute towards their vital shark conservation initiatives around the world. We will also be working together with the Trust to inspire divers, snorkellers and other travellers to take an active role – at home and abroad – in citizen science projects and other activities.”
Paul Cox, CEO of The Shark Trust, said:
“It’s an exciting partnership and we’re thrilled to be working with Diverse Travel to enable more divers and travellers to get involved with sharks and shark conservation. Sharks face considerable conservation challenges but, through collaboration and collective action, we can secure a brighter future for sharks and their ocean home. This new partnership takes us one more valuable step towards that goal.”
For more information about the Shark Trust visit their website here.
For more about Diverse Travel click here.
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoHone your underwater photography skills with Alphamarine Photography at Red Sea Diving Safari in March
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Gear Reviews3 weeks ago
Gear Reviews3 weeks agoGEAR REVIEW – Revolutionising Diving Comfort: The Sharkskin T2 Chillproof Suit
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida
-

 Gear Reviews3 months ago
Gear Reviews3 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone


















