Marine Life & Conservation
Narwhal’s tusk is super sensitive

Narwhals’ distinctive long tusks are super sensitive, research has found.
The whales are known for their tusks which can reach 2.6m (9ft) in length, earning them comparisons with mythological unicorns.
The tusk is an exaggerated front tooth and scientists have discovered that it helps the animals sense changes in their environment.
Experts suggest males could use the tusks to seek out mates or food.
The results are published in the journal The Anatomical Record.
Dr Martin Nweeia from the Harvard School of Dental Medicine, US, undertook the study alongside an international team of colleagues.
Through the years, many theories have tried to explain the function of the narwhal’s impressive tusk.
“People have said it’s everything from an ice pick to an acoustic probe, but this is the first time that someone has discovered sensory function and has the science to show it,” said Dr Nweeia.
More recently, experts have agreed that the tusk is a sexual characteristic because it is more often exhibited by males and they appear to use them during fights to assert their social hierarchy.
But because the animals are rarely seen, the exact function of the tusk has remained a mystery.
Previous studies have revealed that the animals have no enamel on their tusk – the external layer of the tooth that provides a barrier in most mammal teeth.
Dr Nweeia and the team’s analysis revealed that the outer cementum layer of the tusk is porous and the inner dentin layer has microscopic tubes that channel in towards the centre.
In the middle of the tusk lies the pulp, where nerve endings which connect to the narwhal’s brain are found.
“Although it’s a rigid tooth, it has a very permeable membrane,” said Dr Nweeia.
He explained that because of this structure, the tusk is sensitive to temperature and chemical differences in the external environment.
The researchers proved the link when the tusk was exposed to different salt levels in the water and there was a corresponding change in the narwhal’s heart rate.
He described the tusk as “unique” in the animal kingdom because its porous outer layer is usually only found below the gum line in mammals, where it is only exposed by damage or disease.
“The narwhal is the only example documented where teeth are shown to have the ability to constantly sense environmental stimuli that would not necessarily be considered a threat,” he said.
“If you were looking for an ideal and fascinating tooth to study there’s no question this would be it.”
The tusk grows in a counter-clockwise spiral so it does not curve in the same way as an elephant’s tusk but protrudes straight out.
Dr Nweeia is fascinated by the fact that narwhals put all their tooth-growing energy into a single tusk rather than having a set of teeth to help them eat their diet of large fish, such as halibut.
His previous studies of narwhal skulls and tusks held in museums revealed that the distinctive tusk is the left canine tooth that erupts through the upper lip of males.
Their right canine tooth remains embedded in their skull and in females neither of these teeth usually erupt; though in some rare cases they have a pair of tusks reaching up to 30cm long.
It remains unclear whether the animals have evolved the tusk’s sense functions or whether it is an evolutionary throw back.
“We’re just looking at one time frame in evolutionary history,” said Dr Nweeia.
“We don’t know if this is a sensory organ that is gaining more function, or is this a sensory function that is losing some of its ability?”
He added: “It’s an incomplete puzzle and basically we’ve added a few important pieces.”
The dentist suggests the sensory ability of the tusk might have advantages for males as they could use it to detect where females are, whether they are ready to mate, or how to find food for newborn calves.
His research is now focusing on traditional knowledge, asking hunters in the high Arctic for their observations in the hope that more information on the secretive animals’ behaviour can unravel the mystery of the narwhal’s tusk.
Source: www.bbc.co.uk/nature
Blogs
The Ocean Cleanup Breaks 10,000,000 KG Barrier
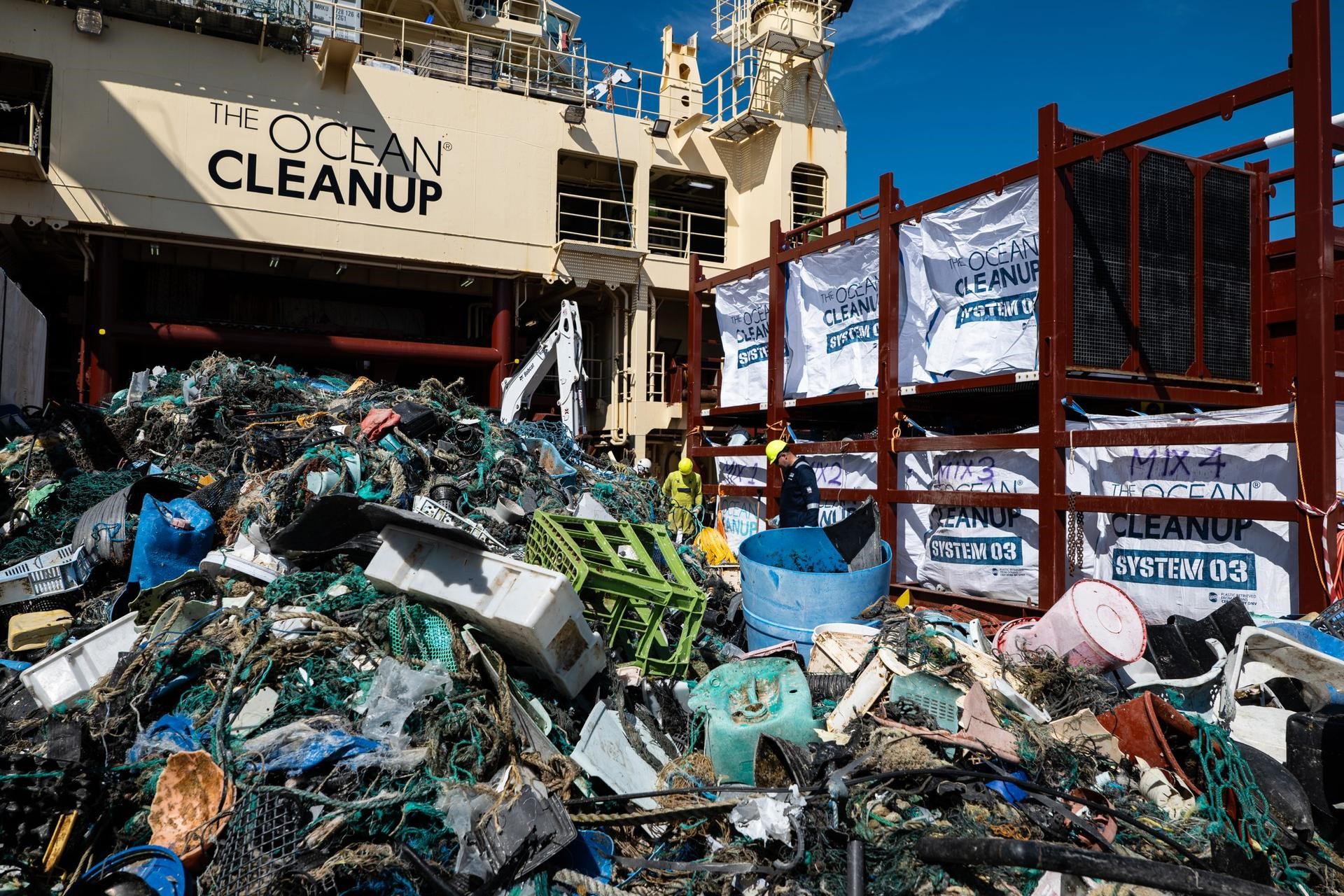

The Ocean Cleanup, the global non-profit project, has removed a verified all-time total of ten million kilograms (22 million lbs.) of trash from oceans and rivers around the world – approximately the same weight as the Eiffel Tower.
To complete its mission of ridding the oceans of plastic, The Ocean Cleanup uses a dual strategy: cleaning up the Great Pacific Garbage Patch (GPGP) to remove the plastic already afloat in the oceans, while stopping the flow of plastic from the world’s most polluting rivers.
Through cleaning operations in the GPGP and in rivers in eight countries, the cumulative total of trash removed has now surpassed ten million kilograms. This milestone demonstrates the acceleration of The Ocean Cleanup’s impact, while underlining the astonishing scale of the plastic pollution problem and the need for continued support and action.
While encouraging for the mission, this milestone is only a staging point: millions more tons of plastic still pollute our oceans and The Ocean Cleanup intends to continue learning, improving and innovating to solve this global catastrophe.
This announcement comes as governments from around the world meet to continue negotiations to develop a new legally binding instrument to end plastic pollution at INC4 in Ottawa, Canada. Representatives of The Ocean Cleanup will be in attendance and the organization will be urging decision-makers to collaborate towards a comprehensive and ambitious global treaty which addresses plastic at all stages of its life cycle and in all marine environments worldwide, including in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
It is encouraging to see that the need for remediation is reflected in the various options for potential treaty provisions. It is essential that the final treaty contains clear targets for the remediation of legacy plastic pollution, and reduction of riverine plastic emissions.
Tackling plastic pollution requires innovative and impactful solutions. The treaty should therefore incentivize the innovation ecosystem by fostering innovations that make maximal use of data, technology and scientific knowledge – such as those designed and deployed by The Ocean Cleanup.
‘After many tough years of trial and error, it’s amazing to see our work is starting to pay off – and I am proud of the team who has brought us to this point.’ said Boyan Slat, Founder and CEO of The Ocean Cleanup. ‘While we still have a long way to go, our recent successes fill us with renewed confidence that the oceans can be cleaned.’
The Ocean Cleanup was founded in 2013 and captured its first plastic in 2019, with the first confirmed catch in the GPGP coming soon after the deployment of Interceptor 001 in Jakarta, Indonesia. After surpassing one million kilograms of trash removed in early 2022, the non-profit project has since progressed to the third iteration of its GPGP cleaning solution, known as System 03, and a network of Interceptors currently covering rivers in eight countries, with more deployments set for 2024.
About The Ocean Cleanup
The Ocean Cleanup is an international non-profit organization that develops and scales technologies to rid the world’s oceans of plastic. They aim to achieve this goal through a dual strategy: stemming the inflow via rivers and cleaning up the legacy plastic that has already accumulated in the ocean. For the latter, The Ocean Cleanup develops large-scale systems to efficiently concentrate the plastic for periodic removal. This plastic is tracked and traced through DNV’s chain of custody model to certify claims of origin when recycling it into new products. To curb the tide via rivers, The Ocean Cleanup has developed Interceptor™ solutions to halt and extract riverine plastic before it reaches the ocean. Founded in 2013 by Boyan Slat, The Ocean Cleanup now employs a broadly multi-disciplined team of approximately 140. The foundation is headquartered in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit: theoceancleanup.com and follow @theoceancleanup on social media.
Marine Life & Conservation
Steve Backshall to headline Shark Trust’s flagship event: For the Love of Sharks

Join a host of amazing, shark loving, speakers including Steve Backshall and the Shark Trust team for an evening celebrating shark conservation at the Royal Geographical Society in London this November.
Date: 29th November 2024
Time: 6-10pm
Location: Royal Geographical Society, London
Tickets: https://www.sharktrust.org/Event/flos24
The event will be a celebration of all things shark. Those lucky enough to get hold of tickets will hear from engaging guest speakers with a passion for sharks.
The line-up includes (*subject to change if unforeseen circumstances arise)
Steve Backshall: One of television’s busiest presenters, BAFTA award-winning wildlife expert Steve has been passionate about the wild world ever since he was young.
Steve’s impressive TV career has taken him all around the world, investigating a wide array of species and environments. Steve has filmed over 100 hours of children’s wildlife programmes with the BAFTA award winning Deadly 60 franchise and recently, with Sky Nature, for his new series ‘Whale with Steve Backshall’. He has been a patron for the Shark Trust for 10 years.
Simon Rogerson: is a photojournalist specialising in natural history, diving and the sea.
He is editor of SCUBA magazine, the official journal of the British Sub-Aqua Club. Simon started his career as a crime reporter but gravitated towards his ‘less depressing’ interest in underwater exploration, joining the staff of DIVE magazine in 1999. In 2005 he was named ‘Editor of the Year’ in the PPA’s Independent Publishing Awards. Simon also works as a freelance writer, contributing frequently to the Sunday Times and Telegraph, in addition to BBC Wildlife, Esquire, and a host of international diving magazines. He is the author of a book, Dive Red Sea, published by Ultimate Sports. Now based in Berkshire, Simon has been a Patron of the Shark Trust for 20 years.
More speakers to be announced soon. Head to the Shark Trust website to learn more.
The evening will also allow guests the final chance to see the Oceanic 31, shark art exhibition. Some of the artwork will be auctioned/raffled at the event, while the rest will be auctioned online to raise money for the Shark Trust Oceanic Programme.
For the Love of Sharks is an evening with something for everyone who is interested and fascinated by sharks. Join the Shark Trust, their Patrons, Trustees and Staff, along with a host of supporters for this celebration of shark conservation.
For more information or to buy a ticket: https://www.sharktrust.org/Event/flos24
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs3 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Gear Reviews3 weeks ago
Gear Reviews3 weeks agoGEAR REVIEW – Revolutionising Diving Comfort: The Sharkskin T2 Chillproof Suit
-

 Blogs3 months ago
Blogs3 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Gear Reviews3 months ago
Gear Reviews3 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone
-

 News2 months ago
News2 months agoPADI Teams Up with Wellness Brand Neuro to Drive Ocean Change and Create a Blue State of Mind
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida