Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Licensed to Cull

Over the past few years lionfish have been dominating the news headlines. In fact they are probably the most talked about marine species in the Caribbean. There are even ‘wanted’ posters on display in many dive centres. But these posters are not advertising underwater photography or promoting marine life; they are basically ‘kill on sight’ orders.
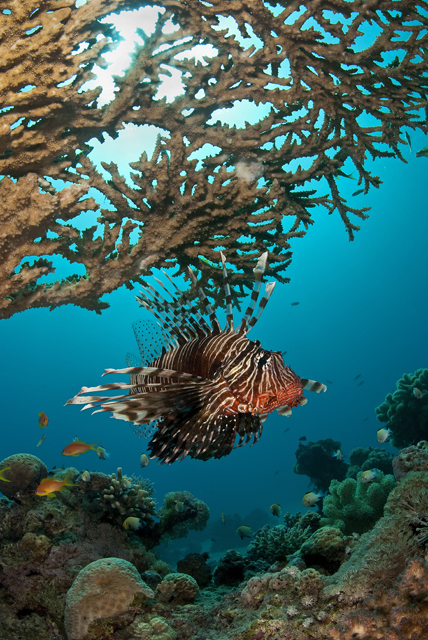
 In the Red Sea lionfish (Pterois volitans) are extremely popular with divers. Their bold stripy colours and large venomous spines look great in photographs and they are fascinating to watch, especially when hunting in packs. But the Atlantic Ocean is not their home territory and what’s deemed as an attraction on one continent is seriously threatening the very existence of another.
In the Red Sea lionfish (Pterois volitans) are extremely popular with divers. Their bold stripy colours and large venomous spines look great in photographs and they are fascinating to watch, especially when hunting in packs. But the Atlantic Ocean is not their home territory and what’s deemed as an attraction on one continent is seriously threatening the very existence of another.
During a recent trip to the Cayman Islands I spoke with Flower Moye, a researcher for the CCMI (Central Caribbean Marine Institute) based on Little Cayman. She said that the most likely theory is the whole disaster had been caused by a freak accident. Flower said the Caribbean ‘strain’ had probably been released by aquariums somewhere near Miami. They are now sweeping from island to island heading due south. Some have even been reported as far away as Belize. Flower said “we are not sure where they are or where they are going”. She thinks the present crisis could have been caused by as little as 6 original lionfish. She also thought they were dealing with 2 separate species.
Flower said that the Caymans are now on a lionfish high alert. The ‘hardcore scramble’ started in 2007. Two researchers from Oregon State University were taken on to solely study lionfish characteristics. They are checking sizes, weights and DNA strings to see where they originated from. Studies have shown that the Caribbean lionfish are actually growing in size. They have already exceeded their normal length by a massive 15cm and are still getting bigger. This invasive species has no natural enemies so are just decimating one reef after another. Flower said “no one was prepared or expected such an aggressive full on attack”.
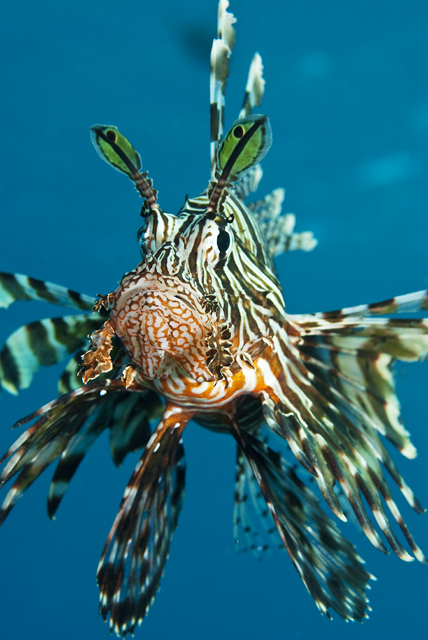
 The alien invasion has now reached critical levels and is threatening the whole eco-system. Lionfish are just eating their way through entire cleaning stations. Flower said a dissected specimen had more than 32 fish in its stomach. The local fish population just don’t know how to react. The voracious predator is herding up the unsuspecting fish using their spines and then it’s a full on feeding frenzy. Divers recorded one individual eating 20 juveniles in 30 minutes. Their main targets are damsels and cardinals but every species is under threat. Flower said that the survival rate for reef inhabitants has reduced by a staggering 80 percent. This has a huge knock on effect. The loss of grazers like parrotfish means seaweeds and algae can thrive. This will eventually overwhelm the coral reefs.
The alien invasion has now reached critical levels and is threatening the whole eco-system. Lionfish are just eating their way through entire cleaning stations. Flower said a dissected specimen had more than 32 fish in its stomach. The local fish population just don’t know how to react. The voracious predator is herding up the unsuspecting fish using their spines and then it’s a full on feeding frenzy. Divers recorded one individual eating 20 juveniles in 30 minutes. Their main targets are damsels and cardinals but every species is under threat. Flower said that the survival rate for reef inhabitants has reduced by a staggering 80 percent. This has a huge knock on effect. The loss of grazers like parrotfish means seaweeds and algae can thrive. This will eventually overwhelm the coral reefs.
Grand Cayman Authorities have realised the seriousness of the problem and are responding rapidly. It’s basically a case of exterminate or be exterminated. They have given divers the authorisation to actively seek out and destroy as many lionfish as possible. But before being issued with a license to cull they have to first sit through an hour long Powerpoint presentation. This explains the reasons behind the drastic measures, how to catch them (without getting stung) and what to do with them afterwards. Flower said the most humane way of killing them is to put them in the freezer so that they ‘go to sleep’ and then bury them on land or eat them.
Some divers are even grilling lionfish steaks on the barbecue but obviously the poisonous spines have to be cut off with scissors before the fleshy parts can be sliced up into pieces. Gladys, the owner of Pirates Point on Little Cayman, had prepared some lionfish Sushi for me. I tried a few pieces and although it had a strange twangy taste, it wasn’t at all offensive or inedible. Adding some Wasabi was all it took to spice up the flavour and make it palatable. At Cobalt Coast resort they invited me to a lionfish cook out where I tried all sorts of dishes from deep fried goujons to an extremely tasty bouillabaisse. At least lionfish was proving good to eat!
Dive guides are even trying to ‘train’ the local Nassau grouper population to eat the lionfish. Laura, an Instructor working at the Little Cayman Beach resort, dropped a freshly caught lionfish in front of a grouper and after a few seconds of deliberation it decided to take a bite. But unless the lionfish are actually placed in front of them they don’t seem to be interested. It’s just not seen as a natural food source.
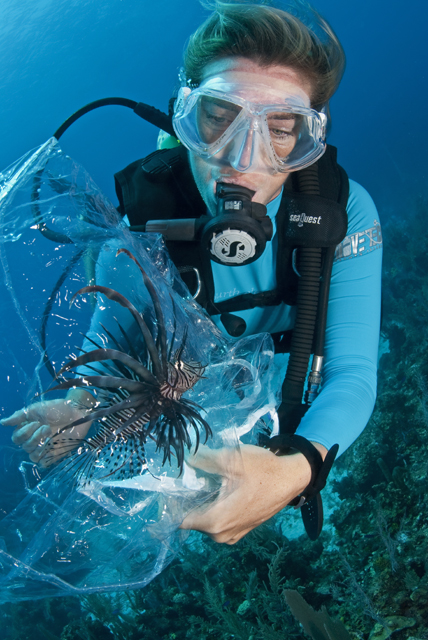 I went for a quick dive with Laura hunting for lionfish and within 10 minutes we managed to find one under a coral mount. Laura scooped the lionfish into a plastic bag and then put it into an ice box back on board the boat. All sightings are reported to the D.O.E. so they can get a good idea where they are and in what numbers. But lionfish are proving a tough species to eradicate. They adapt very quickly. At one dive site I searched below 40 metres and found a number of big 20 – 30cm lionfish lurking underneath ledges all along the wall. I’m sure they had cottoned on that recreational divers don’t usually go this deep so there was less likelihood of being caught.
I went for a quick dive with Laura hunting for lionfish and within 10 minutes we managed to find one under a coral mount. Laura scooped the lionfish into a plastic bag and then put it into an ice box back on board the boat. All sightings are reported to the D.O.E. so they can get a good idea where they are and in what numbers. But lionfish are proving a tough species to eradicate. They adapt very quickly. At one dive site I searched below 40 metres and found a number of big 20 – 30cm lionfish lurking underneath ledges all along the wall. I’m sure they had cottoned on that recreational divers don’t usually go this deep so there was less likelihood of being caught.
The licenses are proper looking ID cards complete with a head and shoulders photograph of the holder. The culling is being promoted as a form of ‘pest control’. But numbers are still growing at an incredible rate. Lionfish can release up to 30,000 eggs a month which equates to more than 2,000,000 eggs every year. Flower said that when they grow to a size of 10cm they are ready to spawn and from then on will keep spawning every 4 days for the rest of their lives! At present there seems to be very little information available on mating habits etc. The only way of finding out the sex of each individual fish is to dissect it. Flower estimates that numbers around Little Cayman are in the high hundreds but this is considered to be a very conservative estimation. In 2008 a researcher caught a total of 197 Lionfish in a small defined area.
At present there is no long term solution to the Lionfish catastrophe. These underwater terminators are not afraid of anything and literally can’t be stopped. In other parts of the world reef fish have learnt to avoid them and there are more natural predators like groupers or stonefish keeping population levels in check. Unfortunately Caribbean grouper numbers have fallen dramatically due to overfishing. This situation requires a more drastic approach but introducing another ‘alien’ species specifically to kill the lionfish is not seen as a good idea. Flower said “Having 2 invasives will not solve the problem and could in fact just make the situation a whole lot worse”. And so the war continues….
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Creature Feature: Undulate Ray

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
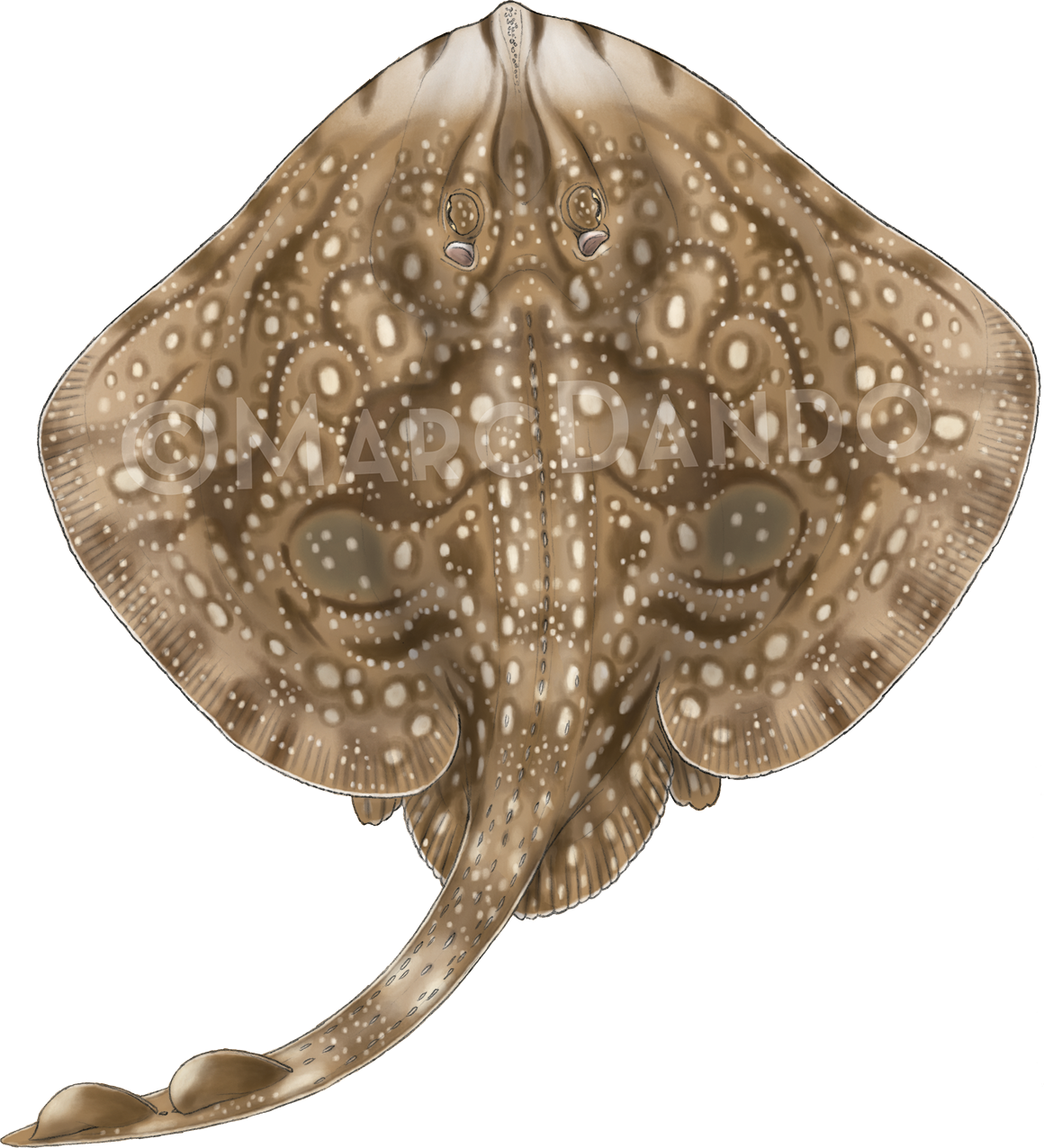
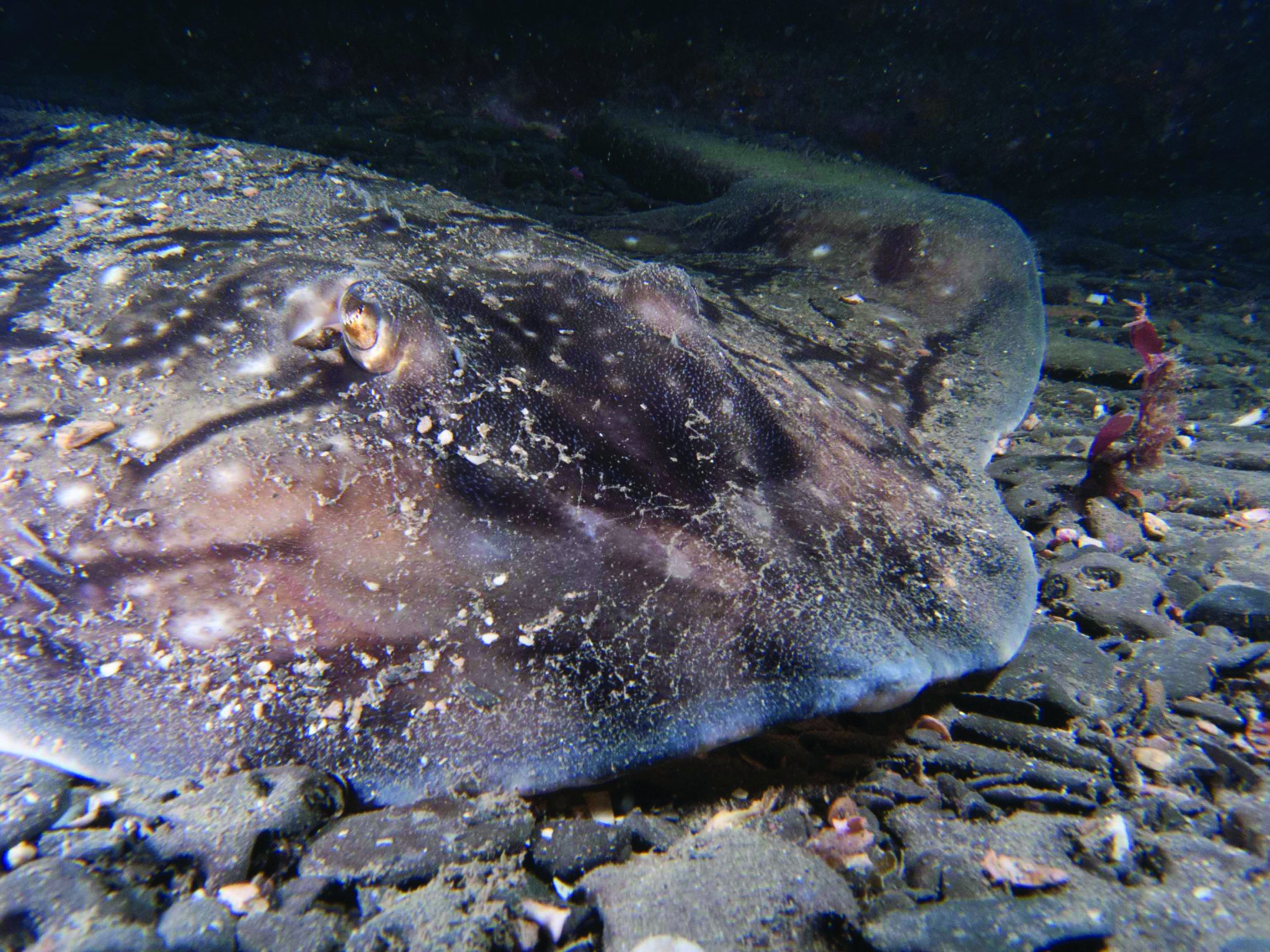
This month we’re looking at the Undulate Ray. Easily identified by its beautiful, ornate pattern, the Undulate Ray gets its name from the undulating patterns of lines and spots on its dorsal side.
This skate is usually found on sandy or muddy sea floors, down to about 200 m deep, although it is more commonly found shallower. They can grow up to 90 cm total length. Depending on the size of the individual, their diet can range from shrimps to crabs.
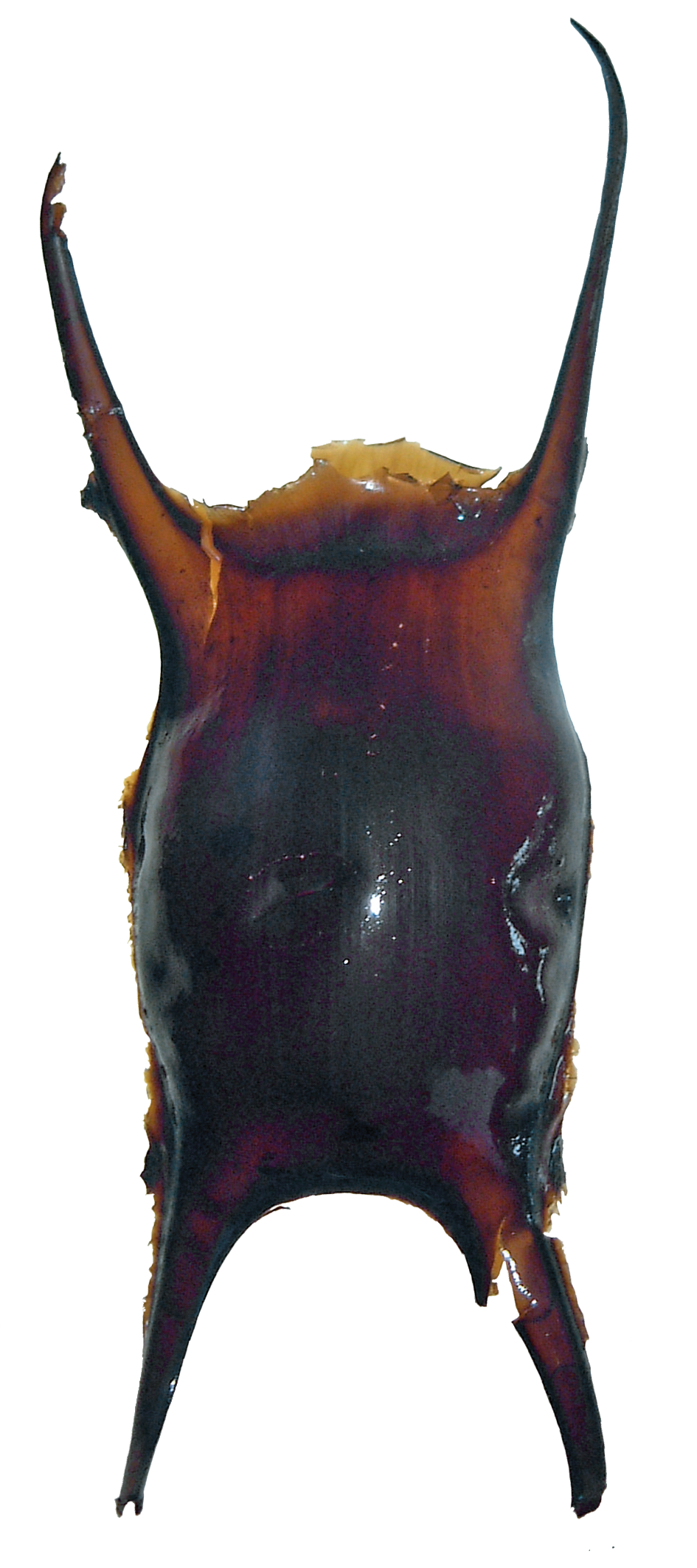
Although sometimes called the Undulate Ray, this is actually a species of skate, meaning that, as all true skates do, they lay eggs. The eggs are contained in keratin eggcases – the same material that our hair and nails are made up of! These eggcases are also commonly called mermaid’s purses and can be found washed up on beaches all around the UK. If you find one, be sure to take a picture and upload your find to the Great Eggcase Hunt – the Shark Trust’s flagship citizen science project.
It is worth noting that on the south coasts, these eggcases can be confused with those of the Spotted Ray, especially as they look very similar and the ranges overlap, so we sometimes informally refer to them as ‘Spundulates’.
Scientific Name: Raja undulata
Family: Rajidae
Maximum Size: 90cm (total length)
Diet: shrimps and crabs
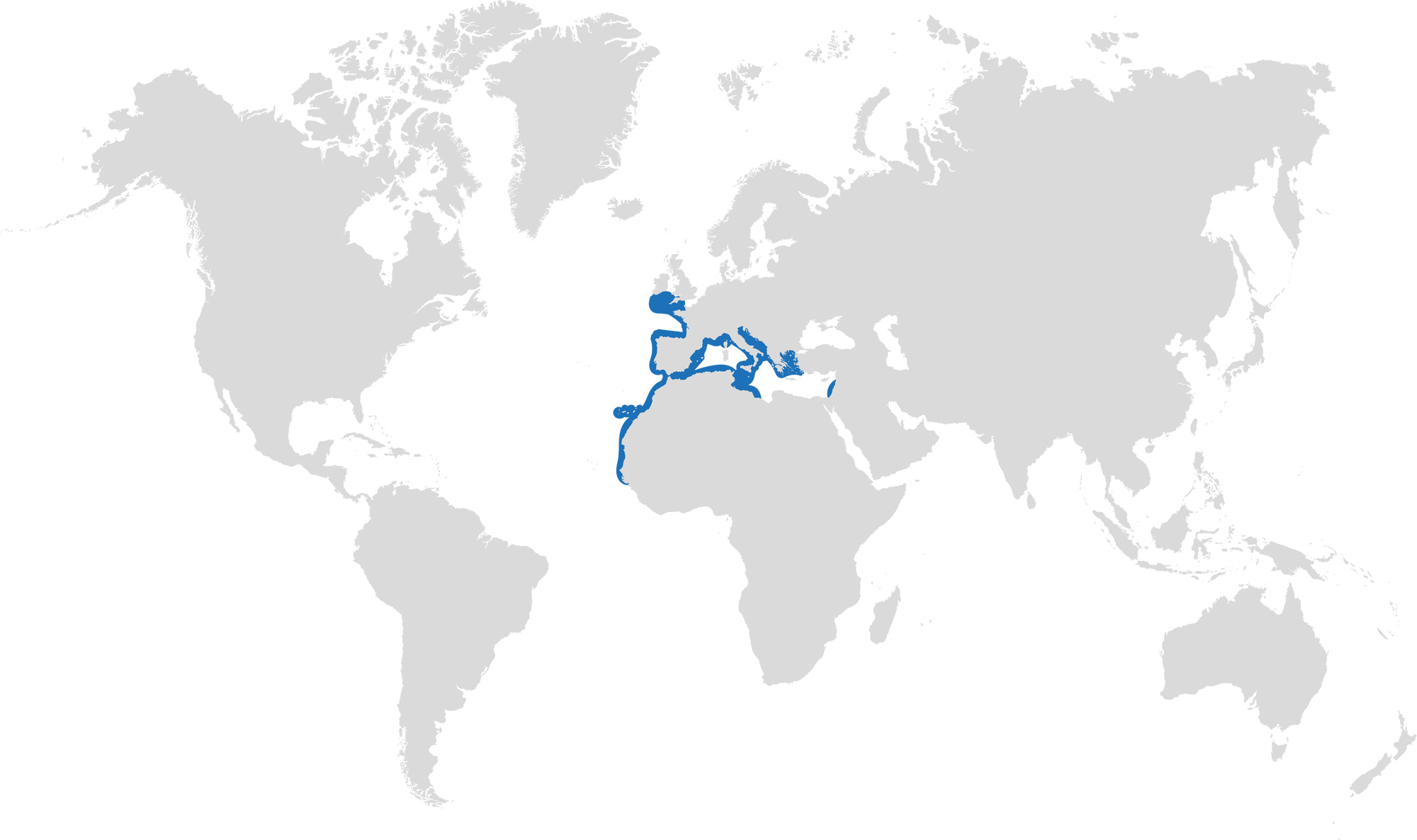
Distribution: found around the eastern Atlantic and in the Mediterranean Sea.
Habitat: shelf waters down to 200m deep.
Conservation Status : As a commercially exploited species, the Undulate Ray is a recovering species in some areas. The good thing is that they have some of the most comprehensive management measures of almost any elasmobranch species, with both minimum and maximum landing sizes as well as a closed season. Additionally, targeting is entirely prohibited in some areas. They are also often caught as bycatch in various fisheries – in some areas they can be landed whilst in others they must be discarded.
IUCN Red List Status: Endangered
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Image Credits: Banner – Sheila Openshaw; Illustration – Marc Dando
Blogs
Guarding Against Coral Invaders

Protecting (Dutch) Caribbean Reefs from Unomia stolonifera
Recent reports highlight the concerning spread of the invasive soft coral, Unomia stolonifera, currently devastating Venezuela’s marine ecosystems and detected in Cuba. With the potential threat of its expansion to the (Dutch) Caribbean islands, urgent action and awareness are essential to safeguard marine biodiversity and local economies from possible catastrophic consequences.
Invasive species are animals or plants from another region of the world that don’t belong in their new environment. These species can have major ecological effects by decimating native flora or fauna. They can also cause large economic losses and impact human health. Invasive species also pose a significant threat to marine ecosystems worldwide, including the Dutch Caribbean. Among these invaders is the octocoral species Unomia stolonifera or “Pulsing Xenia”, originally from the Indo-Pacific. With its rapid growth and lack of natural predators, this species can outcompete native species and disrupt fragile marine habitats such as seagrass beds and coral reefs.
Background
The invasive soft coral U. stolonifera was first identified in 2014, off the coast of Venezuela. It is believed to have been introduced via the illegal aquarium trade. Since this species can reproduce sexually and asexually (or fragment), even small pieces can regenerate to spread. Once introduced it quickly took over shallow reefs and hard substrate at depths of 0-50 meters, outcompeting local corals and seagrass for space. Follow on surveys found that this coral species exhibited average percentage cover as high as 80%, vastly outcompeting native corals. In highly colonized areas, fish are disappearing due to loss of habitats.
In 2022, during a survey conducted in Cuba by the University of Havana, an unknown octocoral was discovered which was later identified as the invasive Unomia stolonifera. It is suspected that the coral larvae arrived in ballast water from fossil fuel ships originating from Venezuela, as nearby sites adjacent to Venezuelan ports have been heavily affected by the invasion.
How to help
Prevention through continuous monitoring, particularly in high-risk areas such as marine harbors and oil facilities, is paramount. Early detection plays a pivotal role in mitigating the threat posed by Unomia stolonifera.
The public’s involvement and awareness are also vital. Local communities, recreational divers, tourists, and all stakeholders are urged to participate in early detection efforts by reporting sightings (photo, location and date) of this invasive coral to their respective Protected Area Management Organization (PMO’s)- the Fundacion Parke Nacional Aruba (FPNA), STINAPA Bonaire, CARMABI Curaçao , Saba Conservation Foundation (SCF), Nature Foundation St. Maarten (NFSXM) and St. Eustatius National Parks (STENAPA). If an invaded area is confirmed, follow the recommendations by the local PMO’s.
Keys to Success
Despite the challenges, early detection is key to mitigating the threat posed by Unomia stolonifera. With continued vigilance, research, and community engagement, there is hope for containing this potential issue before it becomes a major threat.
About the DCNA
The Dutch Caribbean Nature Alliance (DCNA) supports (science) communication and outreach in the Dutch Caribbean region by making nature related (scientific) information more widely available through amongst others the Dutch Caribbean Biodiversity Database, DCNA’s news platform BioNews and through the press. This article contains the results from several scientific studies but the studies themselves are not DCNA studies. No rights can be derived from the content. DCNA is not liable for the content and the in(direct) impacts resulting from publishing this article.
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoHone your underwater photography skills with Alphamarine Photography at Red Sea Diving Safari in March
-

 News2 months ago
News2 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs2 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Gear News3 months ago
Gear News3 months agoBare X-Mission Drysuit: Ideal for Both Technical and Recreational Divers
-

 Gear Reviews2 months ago
Gear Reviews2 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida