Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
Citizen Science with Marine Megafauna Foundation
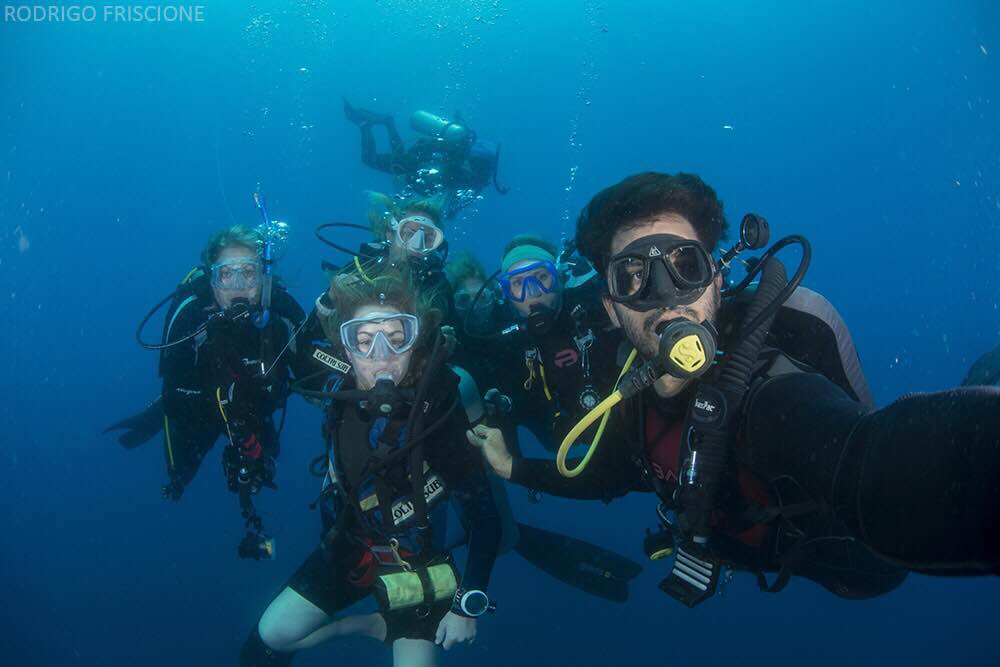

The Marine Megafauna Foundation Ray of Hope Expedition 2015 included a marine biologist (USA), a geneticist (Japan, living and working in the US), a biologist from the Maldives (a Scot by birth), a scuba instructor from the Maldives (a Kiwi), a Penn biology major (from Mexico), a videographer (South Africa), and those of us, scuba divers and/or photographers, who care deeply about our watery world, both Canadian and US. Our mission was to photograph animals (Whale Sharks and Manta Rays) for Identification, upload to Whaleshark.org and MantaMatcher.org, and to take genetic samples from the Manta Rays of the Yucatan. We were not entirely successful with the Mantas…the elusive creatures… well, they eluded us! We did manage to get 7 or so, but we fell far short of the desired 30 samples.
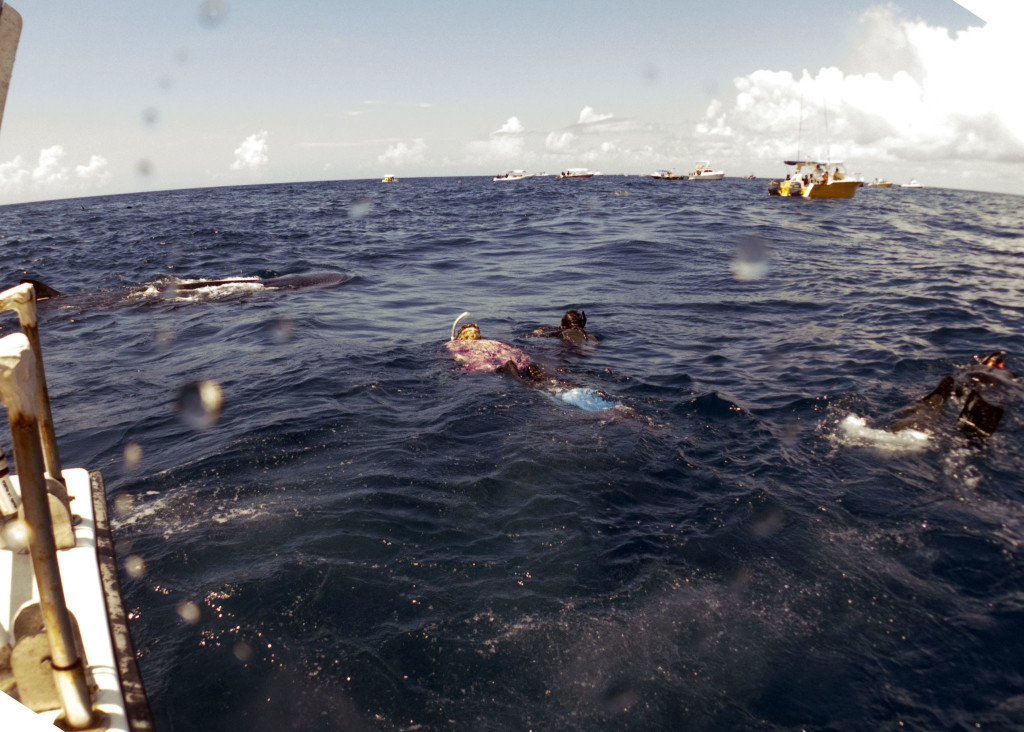
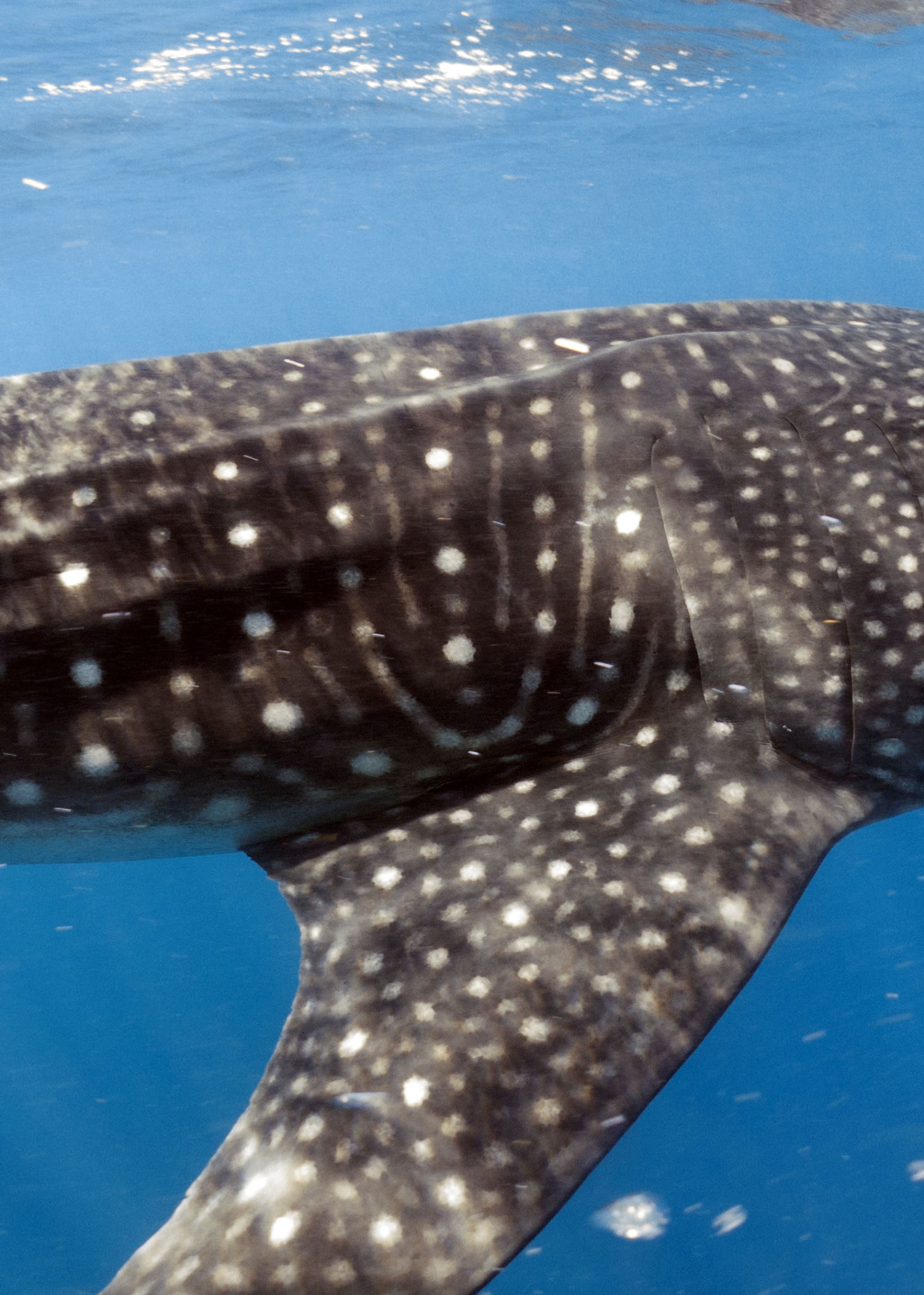
Whale Sharks, on the other hand, were in abundance. The Yucatan is one of the world’s largest aggregations of whale sharks, if not the largest. We headed out in the mornings for a 90 minute boat ride to the shark area, typically just before sunrise, and seeing the dawn out on the calm Caribbean Sea was a serenely beautiful experience. Once out to the shark area (wherever the whale sharks are gathering and feeding that particular day) it became disheartening to see all the tourist boats. There must have been 50 boats on some days.
Please do not get me wrong. We are trying to conserve and preserve these animals by showing how valuable they are to tourism, and valuable they certainly are. Tourists are out in droves to see and to swim with them. 40 or 50 boats at a time can seem pretty excessive, though. The first day we hung out on the edges, swimming with the sharks who were on the periphery of the tourists. We were on a scientific vessel and had a permit to be in the water with them for study. The first day was very shark rich, and I was able to get several ID shots, as did other members of the group. The best day was ahead, however.
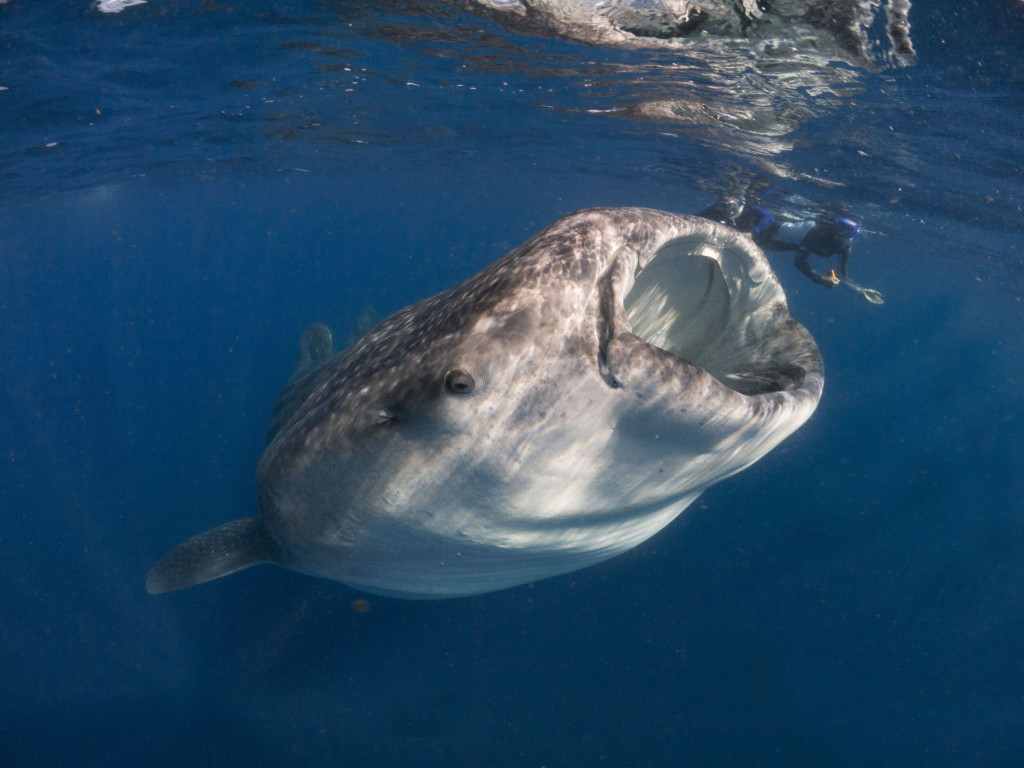
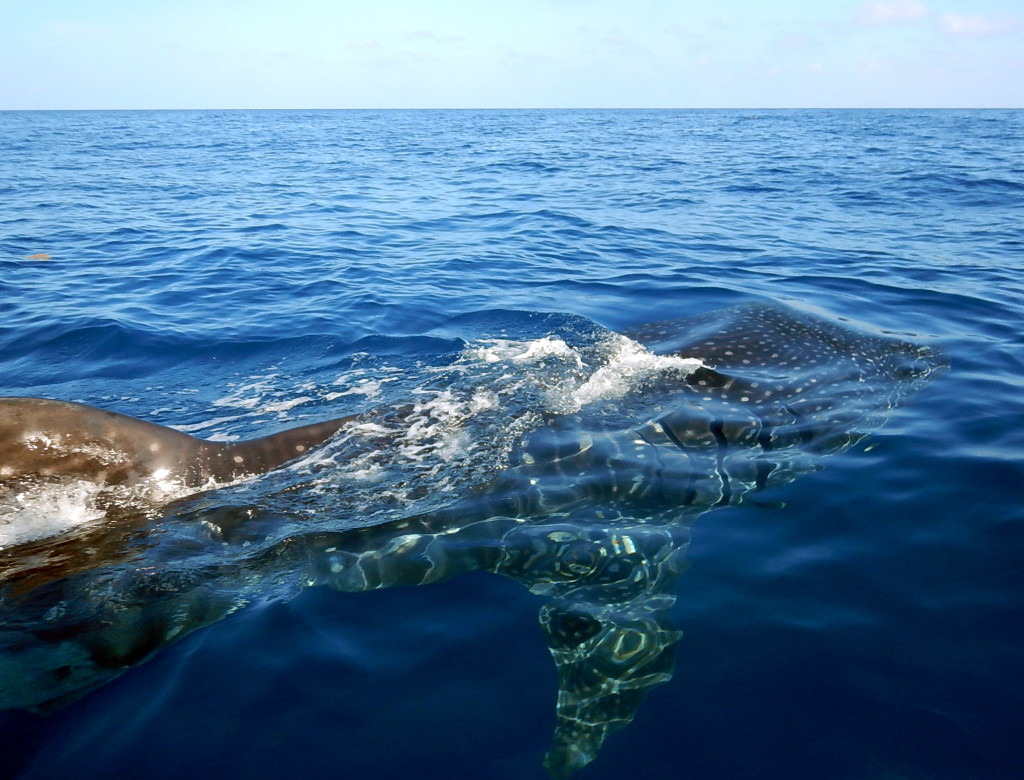
On the third day of the expedition we headed out looking for mantas, and skipped the whale sharks until around noon. By that time, the boats were gone. We had 30 or so whale sharks to ourselves, and one other boat. It had to have been one of the best animal encounters I have ever had. Without the hoard of boats, one could be patient, waiting for feeding whale sharks to swim by. We didn’t have to chase them, or even swim that hard to stay up with them (they may look as though they are moving slow, but they are really going much faster than you think) because they were lazily filtering the surface of the water, knowing they were pretty much alone and in no hurry. With several boats, it gets confusing, and the sharks often have to change course to avoid snorkelers, but on this day, they were content and feeding happily on tuna spawn. Every time we got out of the water we had to brush off tuna eggs from our wetsuits and hair.
I have not been happy with the whale shot photographs I have taken over the years. On this glorious day, alone with whale sharks, I took the best photographs I have ever taken of these spotted, gentle giants. Just incredible!
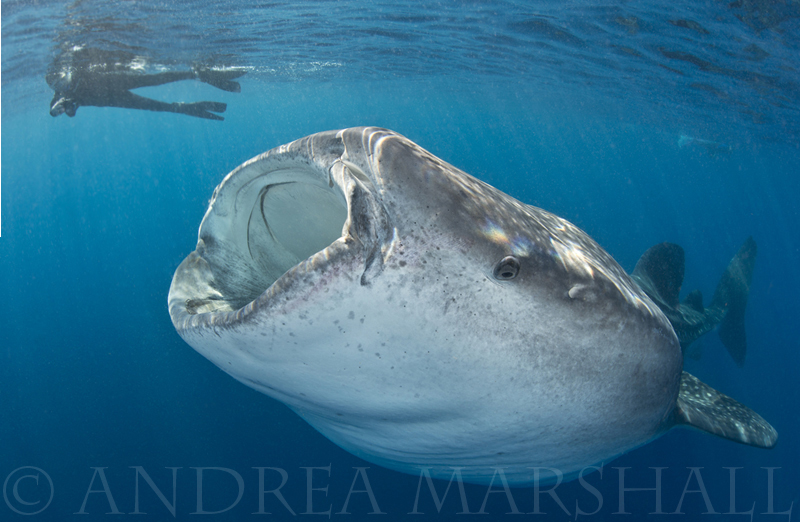
My dream has always been to watch a whale shark vertically feeding in the water, and to capture photos of it. My dream came true with a huge, pregnant Whale Shark who had to be 40 feet long. She was immense, and it was amazing to watch her, vertical and still, while she filtered tuna spawn. Ah, she was such a beauty! And lucky for me, Dr Andrea Marshall (the Director of Marine Megafauna Foundation and Ray of Hope) was in the water and captured an incredible, once in a lifetime photo of me with the whale shark. Yes, I will be framing it! I can’t tell you how thrilling it is to have a photo of this quality! Thank you, Andrea!
I took several ID photos and uploaded them to www.whaleshark.org. It was exciting to receive a few matches, telling me that I had photographed a shark who had been photographed several times over the past 5 years. It’s also exciting NOT to receive matches, meaning I uploaded photos of sharks who were new to the system. I am thrilled to be able to assist conservation science by being a Citizen Scientist.
“In today’s world, it’s clear that our natural environment cannot be preserved and protected by the few people officially designated with this task. It will take all of us, in all parts of the world. We all need to find ways to help in this monumental task.
Citizen Science offers each of us a path to find special ways in which we can each help protect our part of the world. It’s an elegant, efficient, and engaging solution to the huge environmental problems we face in the 21st century.” www.citizenscientists.com
I cannot begin to express the wonder and the thrill of being near to these ocean pelagics. It is truly awe-inspiring… and I am so grateful I can help in their conservation. Check out http://www.citizenscientists.com/ and check out how many ways there are to help!
For more from Tam, visit www.travelswithtam.com.
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
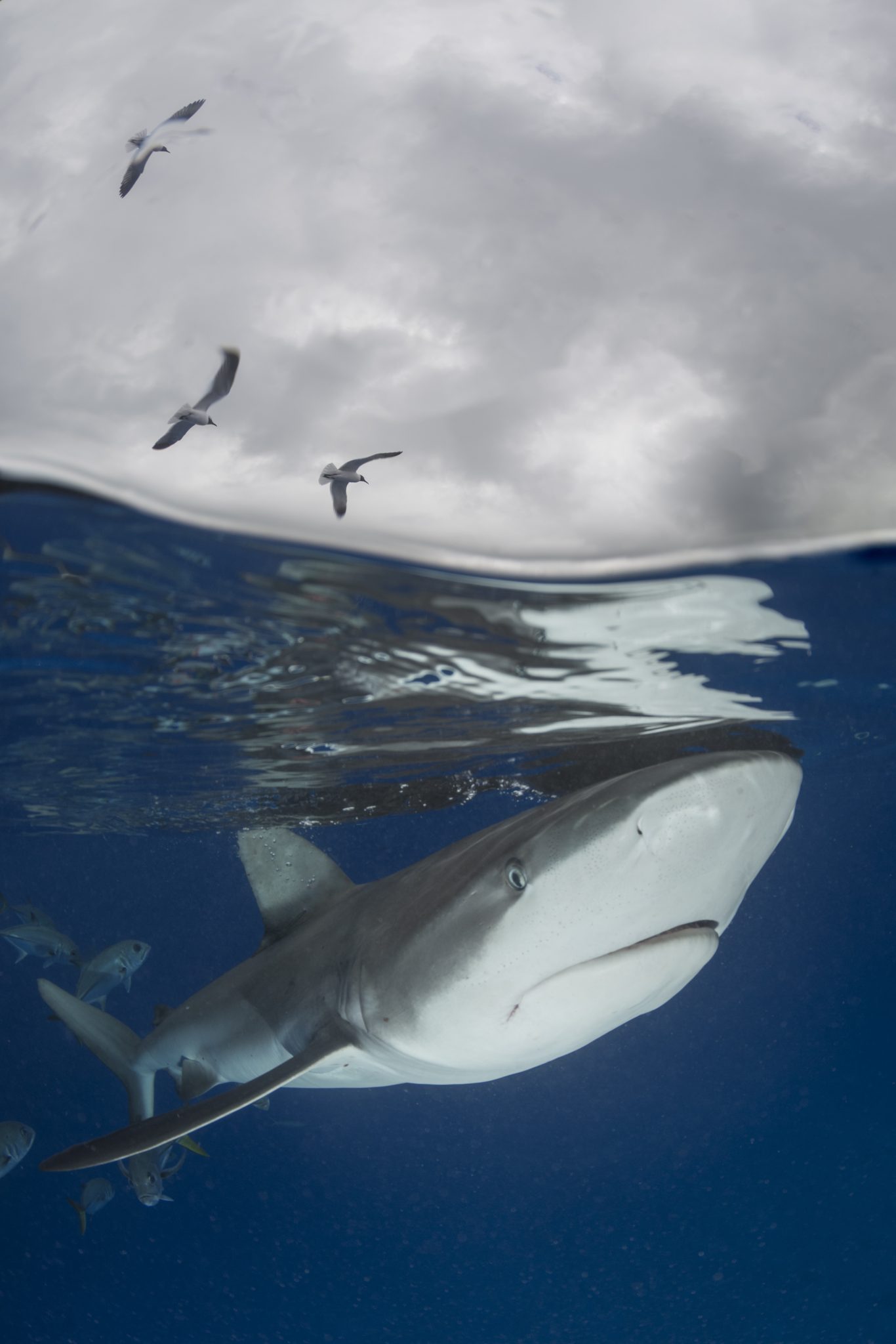
Creature Feature: Dusky Shark

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
This month we’re taking a look at the Dusky Shark, a highly migratory species with a particularly slow growth rate and late age at maturity.
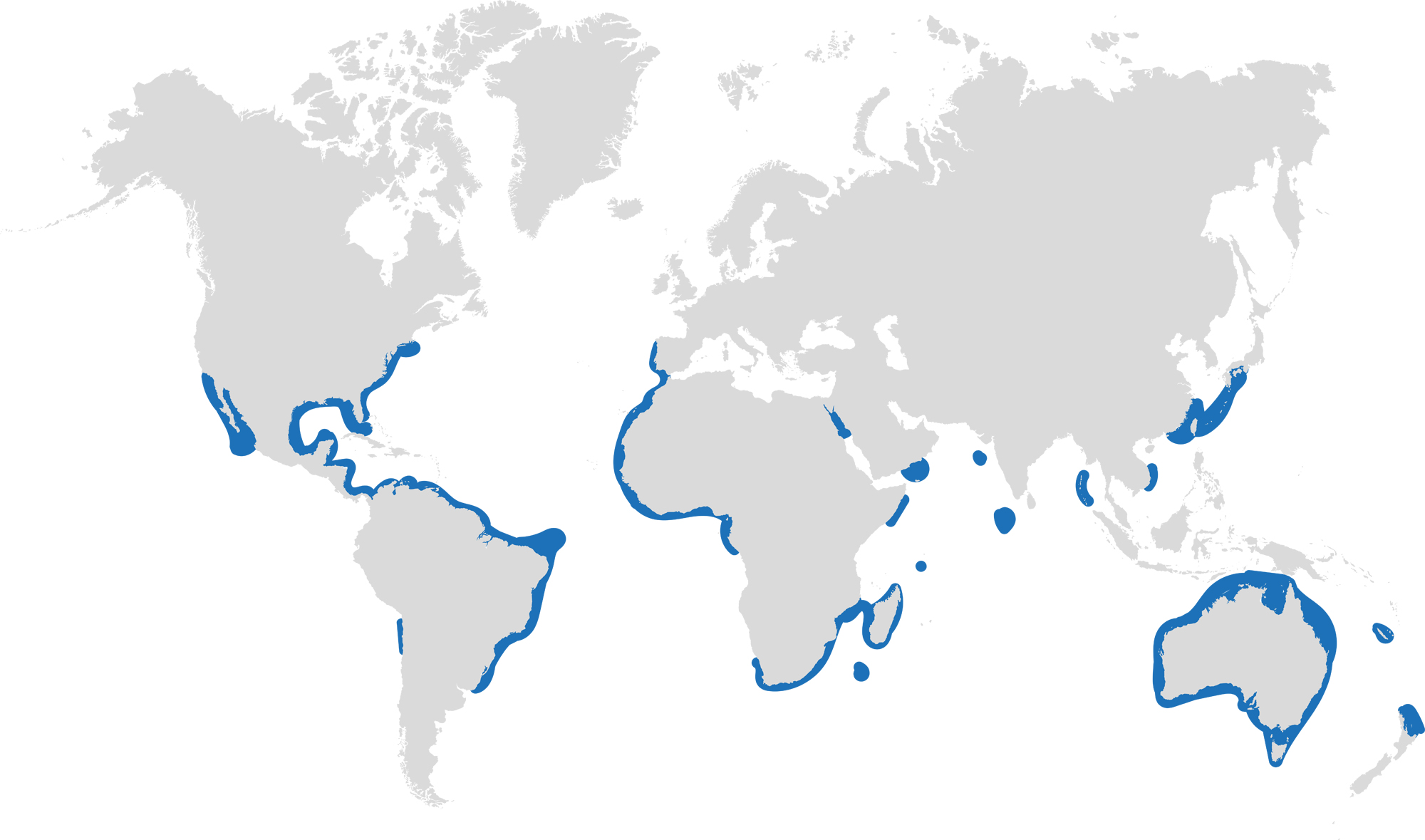
Dusky sharks are one of the largest species within the Carcharhinus genus, generally measuring 3 metres total length but able to reach up to 4.2 metres. They are grey to grey-brown on their dorsal side and their fins usually have dusky margins, with the darkest tips on the caudal fin.
Dusky Sharks can often be confused with other species of the Carcharhinus genus, particularly the Galapagos Shark (Carcharhinus galapagensis). They have very similar external morphology, so it can be easier to ID to species level by taking location into account as the two species occupy very different ecological niches – Galapagos Sharks prefer offshore seamounts and islets, whilst duskies prefer continental margins.
Hybridisation:
A 2019 study found that Dusky Sharks are hybridising with Galapagos Sharks on the Eastern Tropical Pacific (Pazmiño et al., 2019). Hybridisation is when an animal breeds with an individual of another species to produce offspring (a hybrid). Hybrids are often infertile, but this study found that the hybrids were able to produce second generation hybrids!
Long distance swimmers:
Dusky sharks are highly mobile species, undertaking long migrations to stay in warm waters throughout the winter. In the Northern Hemisphere, they head towards the poles in the summer and return southwards towards the equator in winter. The longest distance recorded was 2000 nautical miles!
Very slow to mature and reproduce:
The Dusky Shark are both targeted and caught as bycatch globally. We already know that elasmobranchs are inherently slow reproducers which means that they are heavily impacted by overfishing; it takes them so long to recover that they cannot keep up with the rate at which they are being fished. Dusky Sharks are particularly slow to reproduce – females are only ready to start breeding at roughly 20 years old, their gestation periods can last up to 22 months, and they only give birth every two to three years. This makes duskies one of the most vulnerable of all shark species.
The Dusky Shark is now listed on Appendix II of the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS), but further action is required to protect this important species.
Scientific Name: Carcharhinus obscurus
Family: Carcharhinidae
Maximum Size: 420cm (Total Length)
Diet: Bony fishes, cephalopods, can also eat crustaceans, and small sharks, skates and rays
Distribution: Patchy distribution in tropical and warm temperate seas; Atlantic, Indo-Pacific and Mediterranean.
Habitat: Ranges from inshore waters out to the edge of the continental shelf.
Conservation status: Endangered.
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Images: Andy Murch
Diana A. Pazmiño, Lynne van Herderden, Colin A. Simpfendorfer, Claudia Junge, Stephen C. Donnellan, E. Mauricio Hoyos-Padilla, Clinton A.J. Duffy, Charlie Huveneers, Bronwyn M. Gillanders, Paul A. Butcher, Gregory E. Maes. (2019). Introgressive hybridisation between two widespread sharks in the east Pacific region, Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 136(119-127), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.04.013.
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs
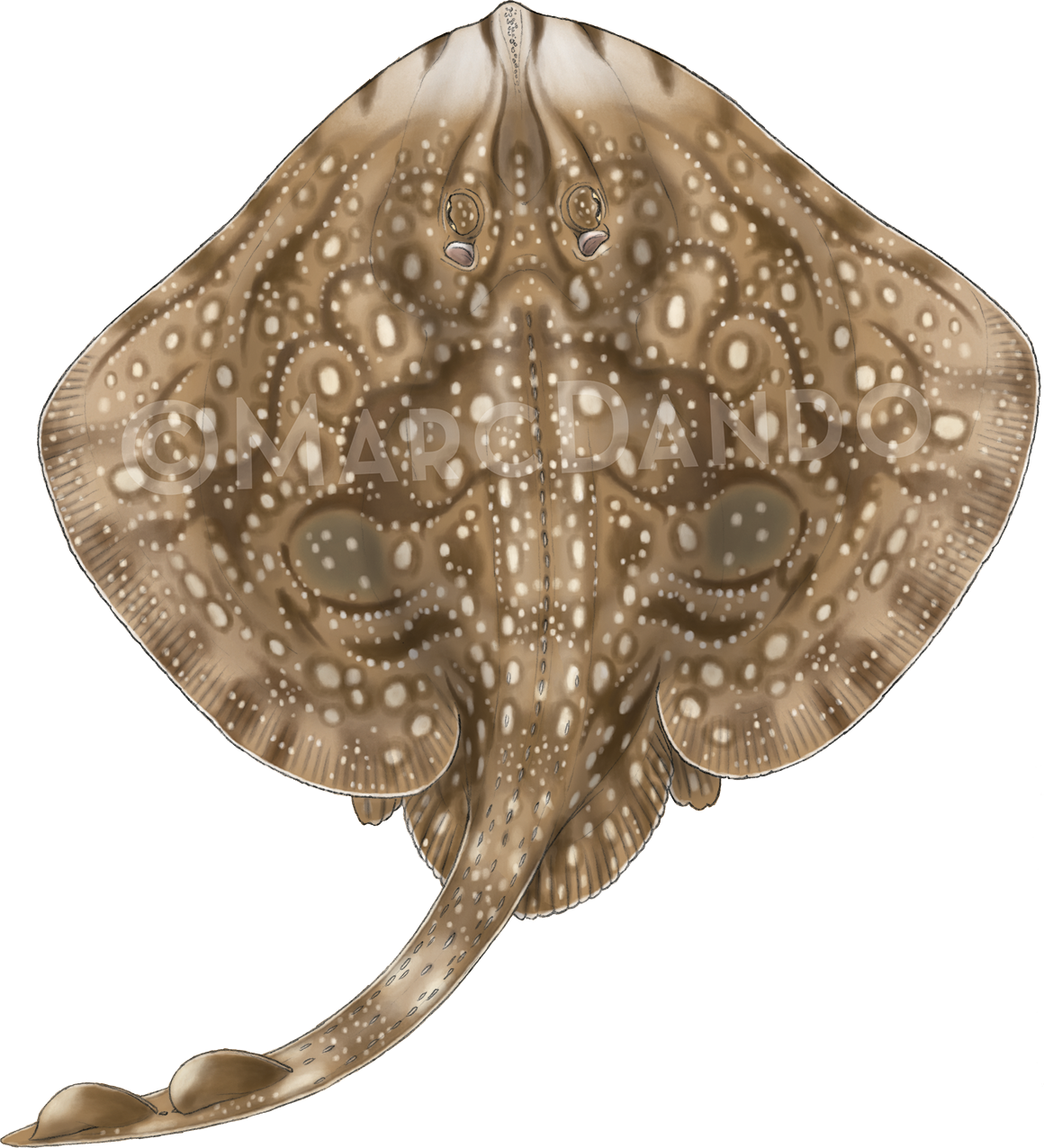
Creature Feature: Undulate Ray

 In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
In this series, the Shark Trust will be sharing amazing facts about different species of sharks and what you can do to help protect them.
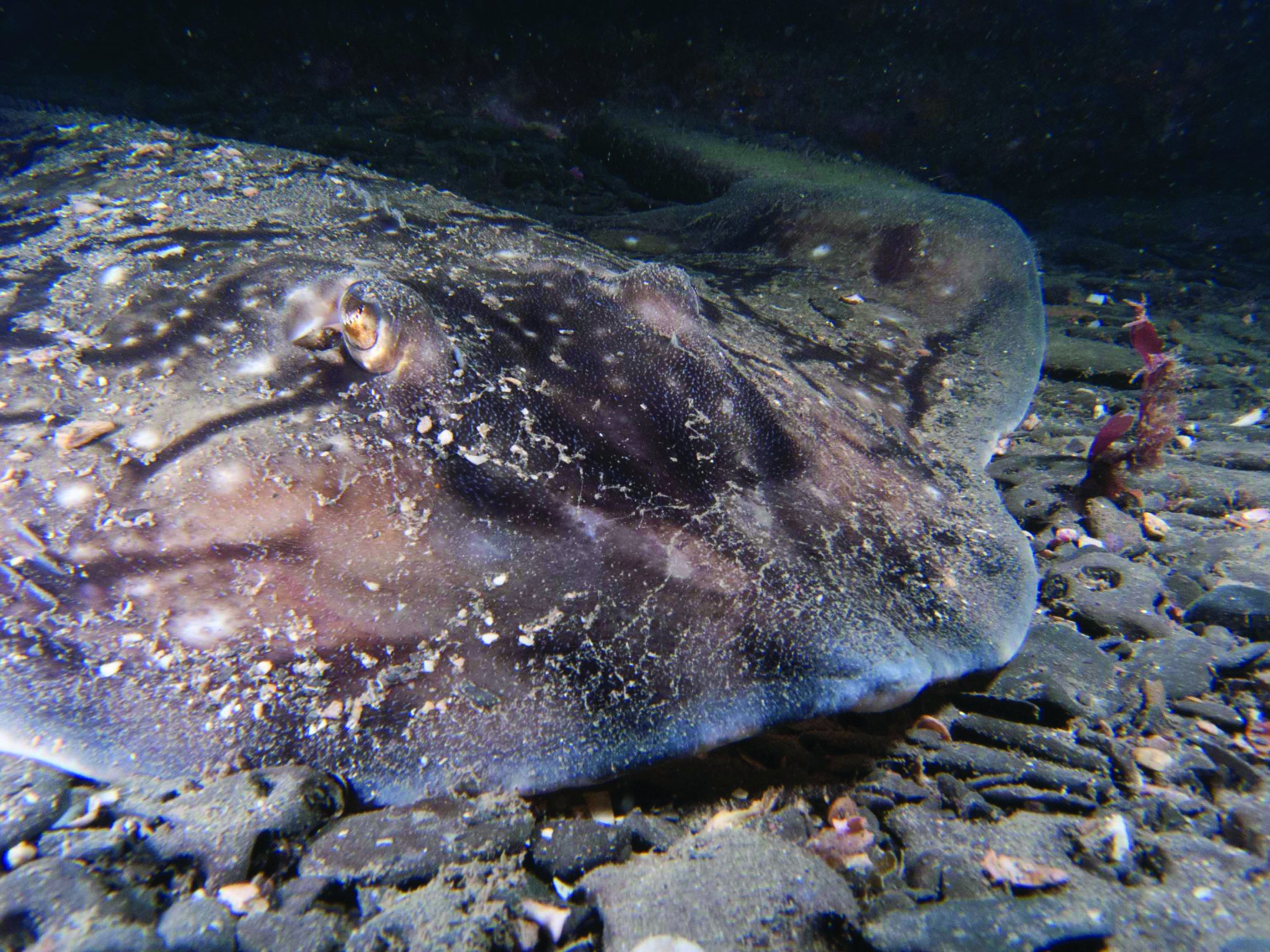
This month we’re looking at the Undulate Ray. Easily identified by its beautiful, ornate pattern, the Undulate Ray gets its name from the undulating patterns of lines and spots on its dorsal side.
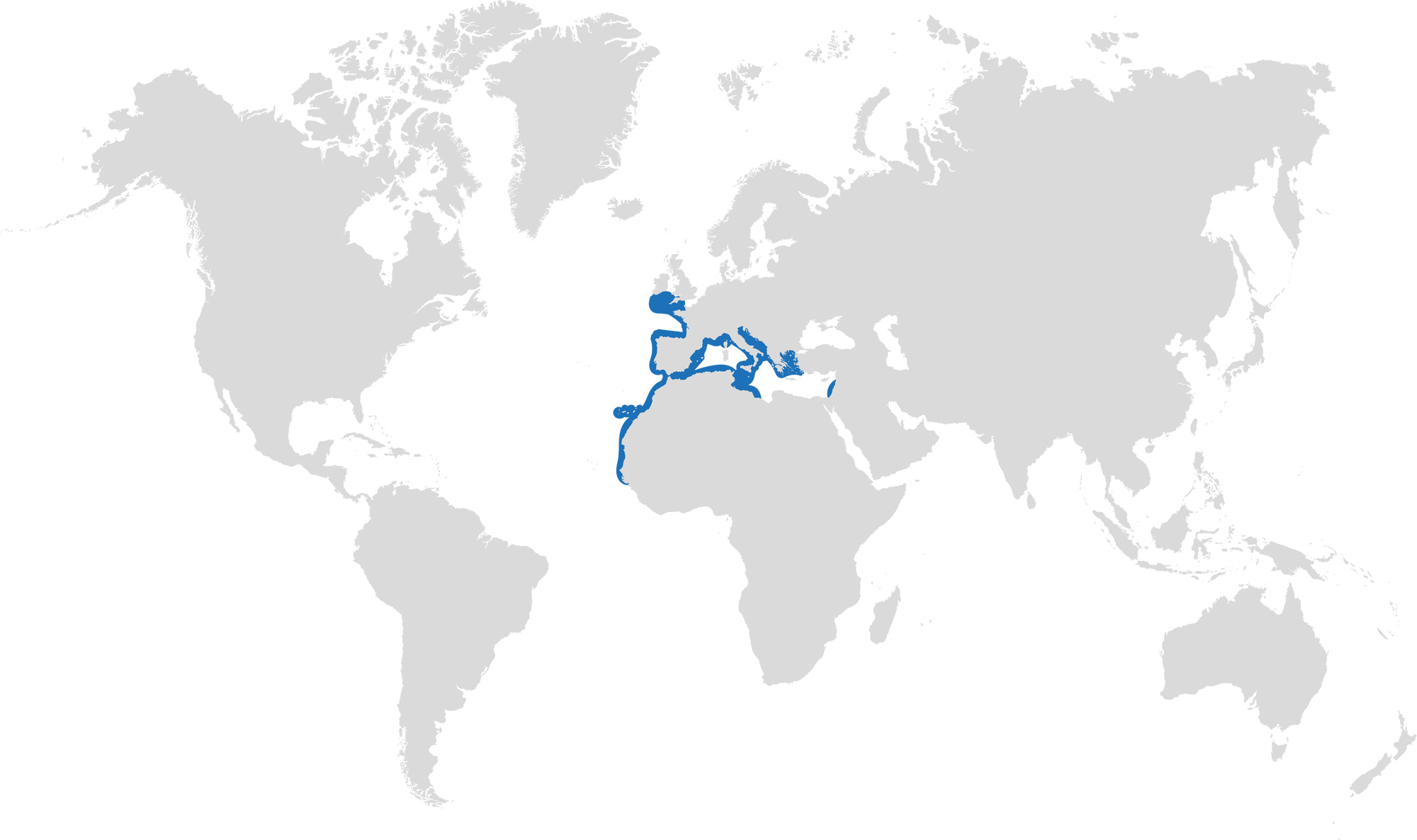
This skate is usually found on sandy or muddy sea floors, down to about 200 m deep, although it is more commonly found shallower. They can grow up to 90 cm total length. Depending on the size of the individual, their diet can range from shrimps to crabs.
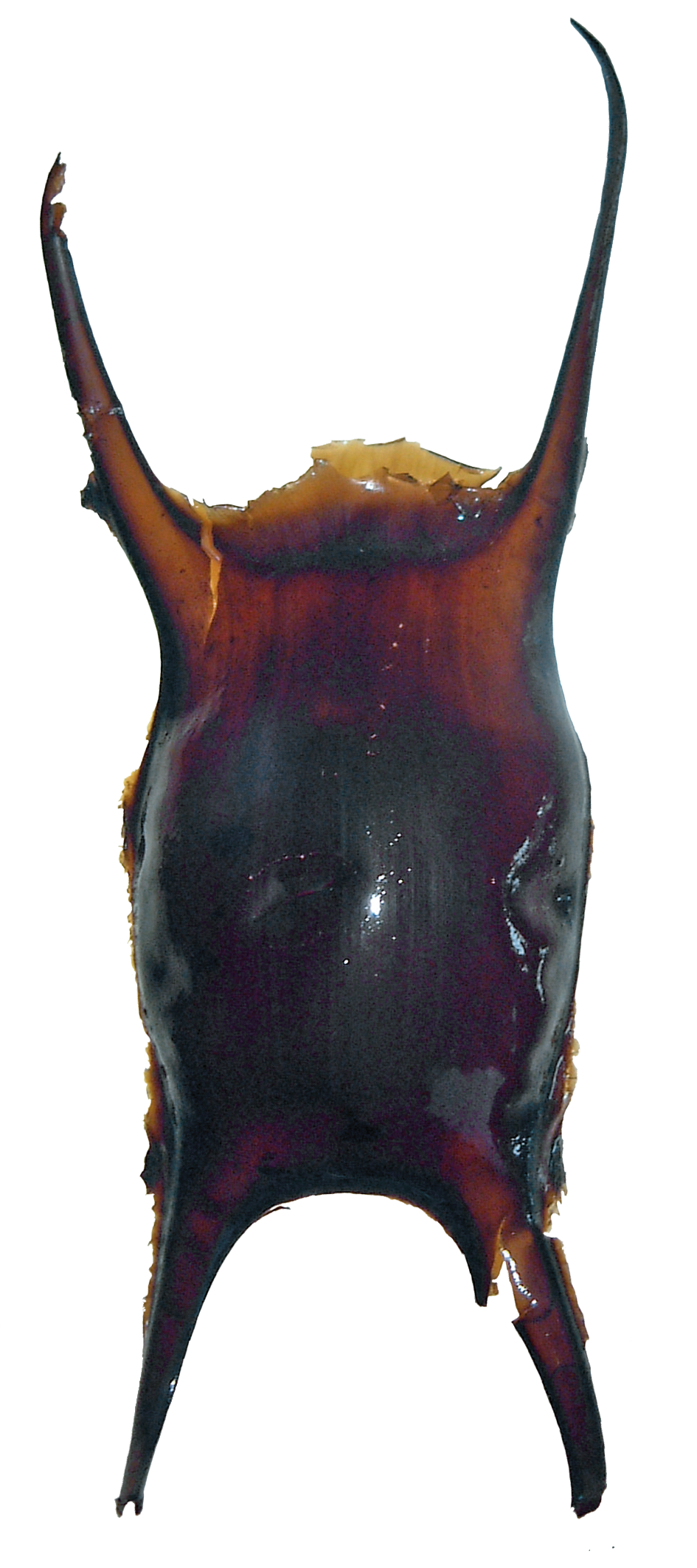
Although sometimes called the Undulate Ray, this is actually a species of skate, meaning that, as all true skates do, they lay eggs. The eggs are contained in keratin eggcases – the same material that our hair and nails are made up of! These eggcases are also commonly called mermaid’s purses and can be found washed up on beaches all around the UK. If you find one, be sure to take a picture and upload your find to the Great Eggcase Hunt – the Shark Trust’s flagship citizen science project.
It is worth noting that on the south coasts, these eggcases can be confused with those of the Spotted Ray, especially as they look very similar and the ranges overlap, so we sometimes informally refer to them as ‘Spundulates’.
Scientific Name: Raja undulata
Family: Rajidae
Maximum Size: 90cm (total length)
Diet: shrimps and crabs
Distribution: found around the eastern Atlantic and in the Mediterranean Sea.
Habitat: shelf waters down to 200m deep.
Conservation Status : As a commercially exploited species, the Undulate Ray is a recovering species in some areas. The good thing is that they have some of the most comprehensive management measures of almost any elasmobranch species, with both minimum and maximum landing sizes as well as a closed season. Additionally, targeting is entirely prohibited in some areas. They are also often caught as bycatch in various fisheries – in some areas they can be landed whilst in others they must be discarded.
IUCN Red List Status: Endangered
For more great shark information and conservation visit the Shark Trust Website
Image Credits: Banner – Sheila Openshaw; Illustration – Marc Dando
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoHone your underwater photography skills with Alphamarine Photography at Red Sea Diving Safari in March
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoCapturing Critters in Lembeh Underwater Photography Workshop 2024: Event Roundup
-

 Marine Life & Conservation Blogs2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation Blogs2 months agoCreature Feature: Swell Sharks
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoMurex Resorts: Passport to Paradise!
-

 Blogs2 months ago
Blogs2 months agoDiver Discovering Whale Skeletons Beneath Ice Judged World’s Best Underwater Photograph
-

 Gear Reviews3 months ago
Gear Reviews3 months agoGear Review: Oceanic+ Dive Housing for iPhone
-

 Marine Life & Conservation2 months ago
Marine Life & Conservation2 months agoSave the Manatee Club launches brand new webcams at Silver Springs State Park, Florida
-

 News3 months ago
News3 months agoWorld’s Best Underwater Photographers Unveil Breathtaking Images at World Shootout 2023